Stenosis of the larynx in children
In children's medical practice, there are a number of pathological conditions that require emergency medical care. One of these pathologies is laryngeal stenosis.
What it is?
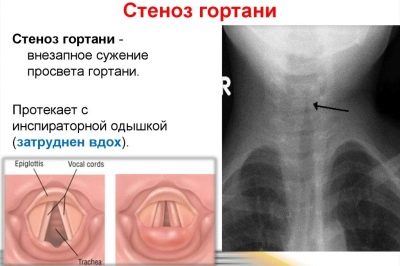
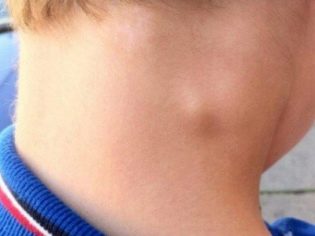
Severe constriction of the larynx is called stenosis. This pathological condition can occur at any age. Usually the development of the disease occurs rapidly. The development of stenosis can lead a variety of reasons. The most dangerous this pathology in newborn babies and infants.
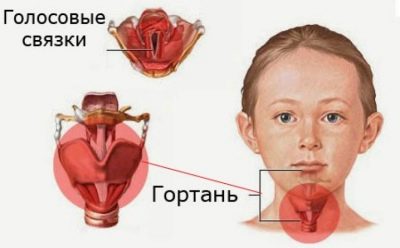
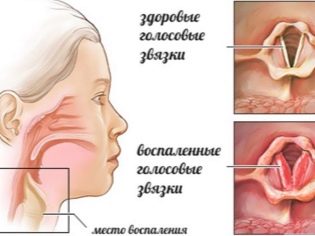
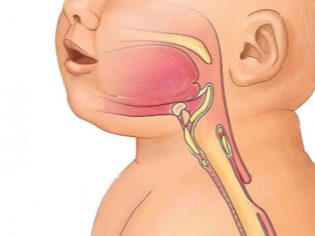
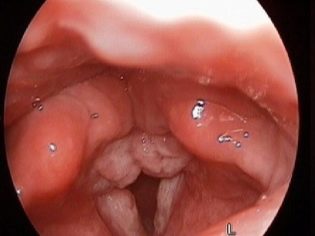
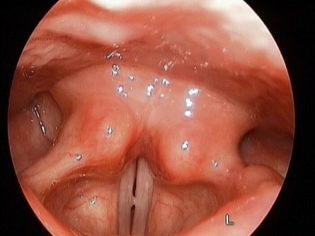
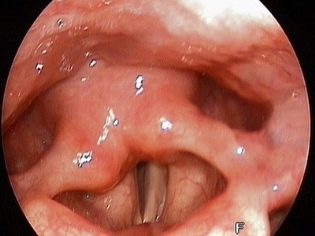
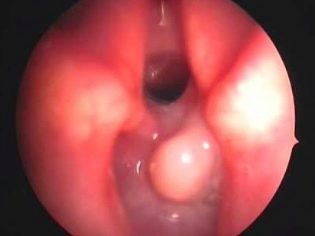
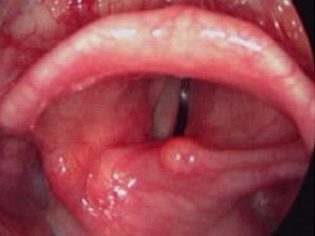
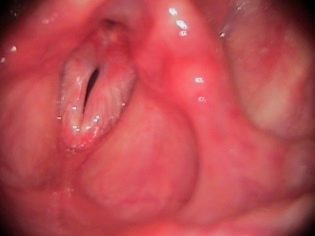
The larynx is the organ responsible for the appearance of the voice. The vocal cords, which are located inside this anatomical element, take an active part in this. Narrowing or stenosis of the glottis, which is normally found in the larynx, and causes the child to develop dangerous respiratory symptoms.
Some doctors also use other terms to indicate this pathological condition in children. They call this narrowing also stenotic laryngotracheitis or acute laryngeal stenosis. These terms largely explain the essence and mechanism of the development of adverse symptoms in the baby.
Kids have several functional and anatomical features of the development of their body. This explains the mechanism of development of the pathological narrowing of the glottis.
The mucous membranes lining the respiratory organs are well supplied with blood and are closely connected with lymphoid formations. This leads to the fact that any infection in the body can lead to the development of a strong narrowing of the glottis.
The abundance of lymphoid tissue in the submucosal space of the vocal apparatus contributes to the development of a severe edema in a sick baby and swelling of damaged tissues.
Such manifestations in babies are especially dangerous. at the age of 2-6 months of life. In this case, the course of the disease can be extremely unfavorable. Without the provision of timely medical care, the baby may even die.
The larynx in children has a rather small size and resembles a “funnel” in shape. The location of the vocal cords in children is not at all the same as in adults. They have them slightly higher.
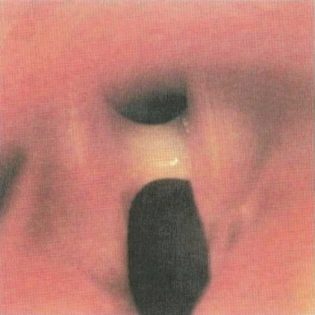
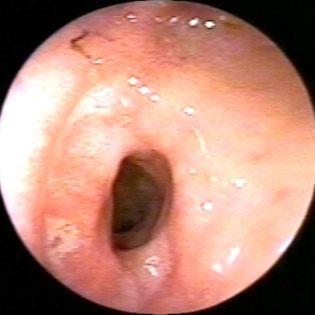
The diameter of the glottis in babies is also somewhat smaller. This contributes to the fact that stenosis of the larynx in them develops much faster and is dangerous by the development of the most dangerous complications.
During its development, the disease can consistently spread to several adjacent anatomical elements. The process begins with the glottis. Then he moves to the under-voice space and the front wall of the larynx. In this case, doctors talk about extended pathological narrowing. Involvement in the pathological process of the posterior wall of the body leads to the development of posterior stenosis.
If the larynx tissues are damaged in a circle, then this clinical variant of the disease is called circular narrowing. In this case, the course of the disease is already getting worse.
Huge process causes the development total stenosis. This condition is extremely dangerous, as it leads to the development of instant acute respiratory failure. Without medical care, such a pathology can even be fatal.
The reasons
A variety of causes can lead to the development of pathological narrowing of the glottis. Their impact may vary in duration, in some cases, only a short and intense impact is sufficient.
The severity of adverse symptoms depends largely on the underlying cause, which led to the development of this pathological condition in the child. The most common causes of stenosis in the baby - infectious pathology. Their development can lead a variety of bacteria and viruses.
Stenosis becomes a fairly frequent complication. acute laryngitis. This pathological condition is usually caused in children by staphylococcal or streptococcal flora. Much less likely to cause adverse symptoms of laryngitis are viral infections.
To the development of pathological narrowing of the glottis in children often lead parainfluenza, scarlet fever, diphtheria, flu, typhus and other infectious pathology. These diseases are also dangerous by the development of pronounced intoxication syndrome, which is manifested by an increase in body temperature in a child and the development of severe general weakness.
Traumatic injury The larynx can also lead to the development of dangerous symptoms of acute respiratory failure in the crumbs. Incorrect childbirth contributes to this pathological condition in newborn babies.
Operations on the thyroid gland can cause dangerous complications in a baby, manifested by the development of a strong pathological narrowing of the glottis.
In the smallest patients, the cause of stenosis of the larynx also quite often becomes foreign bodies in the respiratory tract. Close the lumen of the bronchus in a child can even be a small part of the toy, which the child turns in his hands.
This feature is due to the kids rather narrow bronchial lumen. An object caught in the respiratory tract may cause asphyxia - a pronounced narrowing of the larynx and complete cessation of breathing. In this case, emergency medical care is required in order to save the child's life.
Congenital tracheal diseases may also lead to the development of a child in the strong narrowing of the glottis. In this case, unfavorable clinical signs of stenosis appear in newborn babies already in the first hours after birth.
As a rule, the treatment of pronounced anatomical defects of the structure of the larynx is carried out only with the help of surgical operations. The decision on the need for an operation is taken by an operating pediatric otolaryngologist.
Allergies can also manifest itself in a child by the development of marked stenosis of the larynx. In most cases, this condition results from airborne allergens.
Food and Chemicals become a frequent cause of the development of a pronounced narrowing of the glottis in a child. To improve respiration in this case, it is necessary to completely eliminate the ingress of allergens into the children's body and the prescription of antihistamines or hormones. Allergic pathologies, according to statistics, most often develop in children aged 5-12 years.
Purulent education, which appear in the neck, can also pass to the inner parts of the larynx, thereby causing severe inflammation there. This leads to the fact that the child narrows the lumen of the glottis and breathing is significantly impaired. The course of purulent diseases, as a rule, is rather heavy and proceeds with the development of the most unfavorable symptoms.
In some cases, surgical treatment is required to eliminate ulcers on the neck.
Kinds
In their practice, doctors use a variety of classifications, which include a huge variety of different clinical variants of the disease.
By the time of onset of adverse symptoms, all stenoses can be acute and chronic. For the first time, a narrowing of the glottis in the baby as a result of exposure to various causes is called acute. Usually its course is the most dangerous and quite often complicated by the development of acute respiratory failure.
A subacute process is indicated if unfavorable symptoms persist for 1-3 months. The prognosis of this clinical type of the disease is usually more favorable. When prescribing the correct treatment, all the symptoms usually disappear completely. In some cases, chronic inflammation may occur.
If the kid's pathological narrowing of the glottis persists for more than three months, then the doctors are already talking about a chronic process. Usually this clinical variant of the disease appears in babies who have some congenital anomalies of the structure of the respiratory tract.
Secondary pathology, which contributes to the preservation of the narrowed lumen of the glottis, can also lead to the development in the child of a chronic version of laryngeal stenosis.
Children's otolaryngologists also distinguish several clinical forms of the disease. Each of them has its own characteristics in the development and degree of manifestation of adverse symptoms.
In their practice, doctors use a variety of tables in which the main features of the development of each form of a given pathological condition are included.
Given the reason that led to the narrowing of the glottis, all stenoses can be divided into the following groups:
- Paralytic. They appear in babies more often than in adults. As a rule, they develop in children who have undergone an operation on the thyroid gland or in the area of other formations on the neck. Pathological narrowing in this case arises due to damage to the voice nerve during surgical treatment.
Some babies may develop post-intubation stenosis, which occurs after an incorrectly performed tracheal intubation.
- Scar. May occur after traumatic effects, and after operations on the neck. Traumatic damage to the mucous membranes during surgical incisions leads to the formation of a lot of scar tissue. Such scars tighten the glottis, which contributes to a change in its diameter. Long-term current infectious diseases can also lead to the development of cicatricial changes in a child.
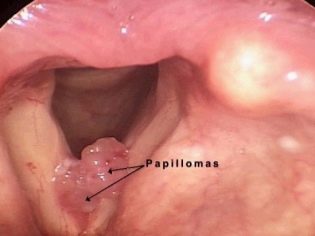
- Tumor. Are extremely unfavorable option for the development of the disease. The narrowing of the glottis in this case develops due to the proliferation of tumor tissue. Severe laryngeal papillomatosis is also a provoking cause of the development of large neoplasms, which during their growth cause a change in the glottis lumen.
- Allergic. They manifest in babies with individual sensitivity to the development of allergies. A variety of allergens can provoke stenosis of the larynx. The most frequent in children are: bites of various insects, inhalation of plant pollen, some chemicals and food.
Symptoms
The severity of the clinical signs of pathological narrowing of the glottis can be very different. It depends on many basic factors:
- child's age;
- the presence of concomitant chronic diseases;
- the cause that led to the constriction of the larynx.
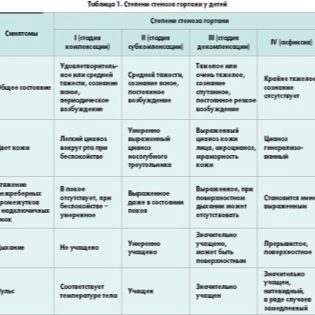
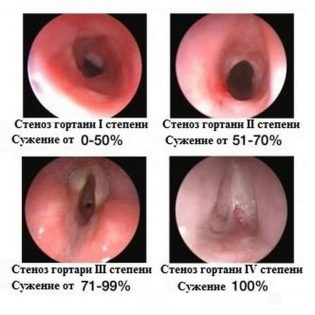
The intensity of the symptoms increases with the narrowing of the lumen of the glottis. So, doctors allocate several stages of development of this pathological condition:
- 1 degree. With a narrowing of 1 degree, the baby's breathing is disturbed. This clinical variant of the disease is also called compensated, as it has a very good prognosis. In this stage of the disease, the baby's voice is disturbed. The child's voice becomes more hoarse.
- 2 degree. The narrowing of the 2nd degree is accompanied by more pronounced adverse symptoms. This variant of the disease is called subcompensated.The baby becomes overly agitated, breathes more often, its skin becomes bright red. Respiratory movements in this case become clearly visible from the side.
The baby "sink" some parts of the chest, which are located between the ribs.
- 3 degree. The most unfavorable option for the development of this pathological condition is narrowing of the 3rd degree. This form of the disease is also called decompensated. In this state, the child can be both extremely excited and completely inhibited. The skin begins to turn very pale, and the region of the nasolabial triangle and lips become blue. In the most severe cases, the child may even completely lose consciousness.
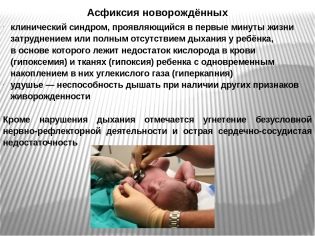
Asphyxia
The most extreme stage of the disease is called asphyxia. This is the most dangerous condition, especially for babies. This pathology is characterized by complete cessation of breathing. In the absence of oxygen, the brain cells begin to die.
If you do not provide emergency care, the baby can die from acute respiratory and heart failure.
Urgent Care
Parents should remember that the appearance of signs of respiratory impairment in a child is an emergency indication in order to to call an ambulance. This must be done before any attempts and actions are taken to quickly remove the attack that has occurred.
After the call to the ambulance, parents should first of all try to calm down and in no case panic! A “cold” mind is a necessary condition for helping your child in such a difficult situation.
While waiting for the doctor, try to calm the baby. To do this, you can take the child in his arms. Constantly monitor the condition of your baby. Open all the vents and doors in the children's room to provide fresh air and oxygen to the room. In the cold season, wear a warm blouse and pants on the child so as not to catch cold.
First aid from parents is only to carry out non-specific actions that will be aimed at some improvement in the child's well-being.
Infants who have laryngeal stenosis due to severe infectious diseases that occur with high fever, can be given antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Such first aid is used only for persistent febrile.
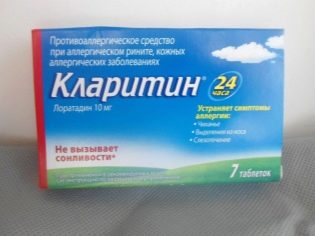
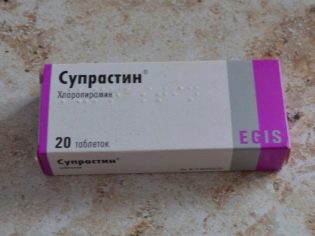
To reduce the swelling of the respiratory tract and improve breathing are used antihistamines. These include: “Claritin"," Suprastin ","Loratadine"," Zyrtec "and many others. They are usually used for 5-7 days. Longer use of drugs is necessarily discussed with your doctor.
Treatment
Therapy of laryngeal stenosis is carried out only by the attending physician. In most cases, this pathological condition is treated in stationary conditions. For this purpose, a whole range of different medicines is used.
In case of more severe illness, the baby is hospitalized. Intensive care and intensive care unit. If the cause of the pathological narrowing of the glottis is a bacterial infection, then antibacterial agents with a broad spectrum of action are necessarily introduced into the treatment regimen.
The frequency of use, the daily dosage, the route of administration and the duration of the course of antibiotic therapy carried out are chosen by the attending physician.
In some chronic forms of stenosis, to improve breathing, sick babies are treated. special inhalations. For this purpose, as a rule, alkaline preparations or isotonic solution of sodium chloride are used. The number of required procedures can be very different. Usually, 12-15 inhalations are performed to achieve a positive effect.
In severe laryngeal stenosis, glucocorticosteroids have a positive effect.The dosage of dexamethasone is selected individually, taking into account the age and weight of the sick child.
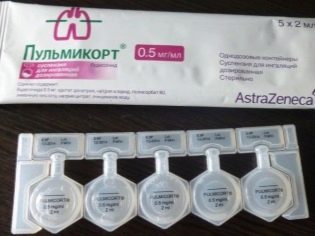
With an easier course can be assigned hormonal drugs in the form of inhalation and aerosols. "Pulmicort" allows you to improve the performance of external respiration and helps to improve the overall well-being of the child.
During the acute period of the disease, all ill children are recommended. follow a special diet. The basis of this therapeutic food - dairy products, as well as vegetables and fruits. All dishes are steamed, baked or boiled. Fatty and hardly digestible products from the children's menu are completely excluded.
After an acute period of illness, a complex of rehabilitation measures is carried out. It is necessary to eliminate the residual symptoms and improve the overall health of the baby.
Trips to the salt cave, various physiotherapeutic procedures and hardening are excellent methods to restore breathing and strengthen the baby’s immunity.
For more information on this issue, you can find out in the next video.