Stomatitis in children
Stomatitis is called a lesion of the oral cavity (its mucous membrane), which often manifests itself in the form of spots or ulcers. Why can such a disease develop in a child, what is stomatitis and how should parents react to its occurrence?
Symptoms and signs
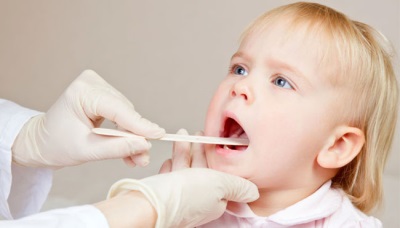
To identify a child with stomatitis can be a characteristic clinical picture.
In infants (children under 1 year)
- Whitish plaque on the oral mucosa is typical of fungal stomatitis.
- On the reddened mucous membrane of the mouth, small bubbles are visible, which are arranged in groups - a sign of herpetic lesions.
- Increased body temperature, weakness, swollen lymph nodes, and other manifestations of intoxication are also characteristic of acute herpes stomatitis.
- The baby cries and refuses to eat.
In children older than a year
At this age, stomatitis symptoms may include:
- Ulcerative painful lesions of the oral cavity (its mucous membrane) in the form of round whitish-gray aft.
- Bubble eruptions on the oral mucosa.
- Slight fever, slight weakness.
- Swollen lymph nodes and their tenderness.
- The appearance of gingivitis.
- Unpleasant smell from the mouth.
The reasons
The disease can be caused by very different reasons - from viruses and dirty hands to severe immunodeficiencies. What thinks about stomatitis known pediatrician E. Komarovskyread in another article.
In infants
The most common cause of stomatitis in nursing babies is fungi. In the period of the appearance of teeth, stomatitis may develop under the action of the bacterial flora, because the child pulls various objects into the mouth and injures the oral mucosa.
An infant older than 6 months may be infected by a mother or other adult herpes virus, as a result of which he develops acute stomatitis with vesicles.
In children older than a year
Violation of oral hygiene rules contributes to the occurrence of stomatitis in older children. The occurrence of stomatitis is associated with injury to the mucous membrane, licking the fingers, allergens entering the child’s body, using toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate, not cured by caries, mouth breathing, sour food and other provoking factors. Also, often the defeat of the oral mucosa in a child is caused by viruses.
Types and forms
Stomatitis in children is of different types, some of which are more common (for example, aphthous and candidal), while others are less.
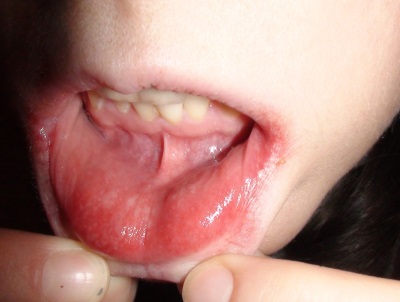
Aphthous
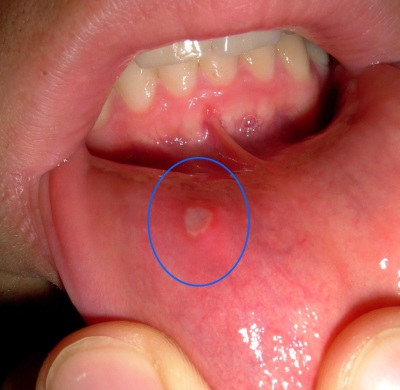
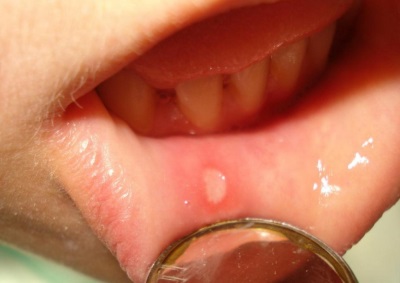
Aphthous form of stomatitis characterized by the appearance in the oral cavity ulcers (aft) white-gray-yellow color. Such ulcers are most often solitary and very painful. For this type of stomatitis inherently relapse.
The disease is both mild, when the sores have a diameter of several millimeters and heal in seven to ten days, and severe, in which large aphthae are formed, which heal within one to one and a half months. This type of stomatitis is usually diagnosed in children over 3 years old.
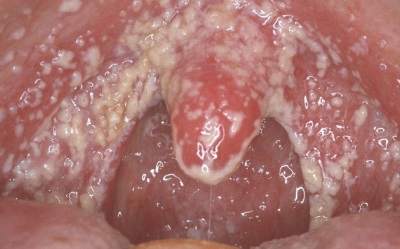
Herpes
This type of oral mucosa is caused by the herpes virus. Herpes Stomatitis most often detected in children 1-3 years.The disease is manifested by the appearance of vesicles in the mouth, from which ulcers are formed. They are quite painful and heal in 1-2 weeks. This form of stomatitis is very contagious, may be accompanied by fever, a skin rash and an increase in lymph nodes.
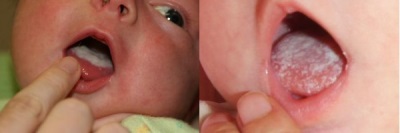
Candida (oral thrush)
This type of stomatitis is caused by candida fungi. It is most often diagnosed in babies of the first year of life. In older children, such damage to the oral mucosa occurs after antibiotic therapy and in immunodeficient states. Thrush in the baby’s mouth manifests painful itchy white-yellow areas. When they are removed, they expose bleeding wounds.
For babies, whitish plaque may be the norm. How to distinguish the state of the norm from the disease, read the article about thrush in the mouth in newborns.
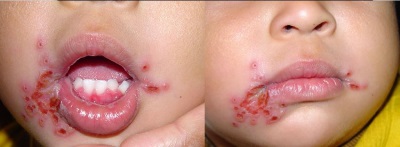
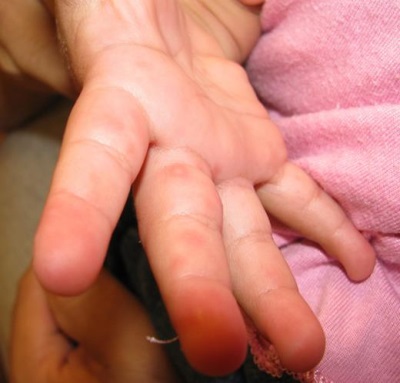
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
This type of stomatitis is manifested not only by the appearance of painful whitish ulcers in the mouth and an increase in temperature, but also by the appearance of a rash on the feet and palms in the form of grayish bubbles that hurt. The same bubbles can appear on the skin of the buttocks and in the genital area.
The disease is contagious and most often diagnosed in children under 10 years of age. It is caused by enteroviruses, which are transmitted by particles of mucus, feces and saliva from a sick person. Infection is possible through a common dish, towel, hand contact, water.
The incubation period lasts about one week. The child becomes contagious a few days before the first manifestations of this syndrome and releases viruses up to 2 months from the onset of the disease.
The child's body temperature suddenly rises (it can reach 39-40 degrees), chills and weakness appear. Further, in the oral cavity (on the lips, cheeks, tongue) ulcerative lesions appear, with uneven edges and a whitish hue. They are very painful and give the child great discomfort. At the same time, parents may notice a rash on their feet and palms, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and sore throat.
Usually such a disease lasts for 7-10 days and ends with a complete recovery. In rare cases, complications affecting the heart and nervous system are possible. Again, this syndrome is sick in very rare cases. In the treatment does not use antiviral means, but only eliminate unpleasant symptoms. When fever a child is given a febrifuge, the sores in the mouth are smeared with anesthetic gel. Bubbles on the skin of the feet and hands do not need to process anything.
It is important that the child during this form of stomatitis is enough to drink. Avoid the use of acidic foods, because of their pain in the mouth may increase. The child can be given cold milk or ice cream.
ABOUT stomatitis in the child's tongue read another article.
Allergic and contact
Such forms of stomatitis are caused by exposure to chemicals and allergens.
The fact that the cause of stomatitis may be allergic, may suggest swelling of the tongue or lips. Also, the allergic nature of the lesion can be judged in all cases of stomatitis, if we analyze the circumstances under which they started. It is necessary to look for contact with food, visiting the dentist, the use of hygiene products.
Most often, such stomatitis is caused by flavoring agents, preservatives and flavoring components of toothpastes, metal prostheses and fillings, sucking tablets and lozenges, sprays for the throat and mouth.
A sign of what diseases can be?
Although rare, stomatitis can be one of the symptoms of such serious pathologies as oral cancer, HIV, leukemia, celiac disease, diabetes mellitus, Crohn's disease, Stevens-Jones syndrome, heavy metal intoxication, Kawasaki disease and other pathologies. To eliminate these diseases, with stomatitis it is important to show the child to the doctor.
When should I see a doctor?
A child with stomatitis must be examined by a doctor if:
- Simultaneously with the defeat of the mouth, the child appeared blisters on the torso, legs or skin of the hands.
- The body temperature of the child has increased and the state of health is deteriorated.
- The child also inflamed other mucous membranes, for example, the genitals and eyes.
- In addition to stomatitis, the child has headaches, a rash appeared, itching is noted, there are problems with breathing and other adverse symptoms.
- An ulcer on the mucous membrane of the mouth is very large - more than one centimeter in diameter.
- In the child's mouth, there are more than 7-10 lesions of the mucous membrane.
- Before the complete healing of old sores, the child appears new.
- Stomatitis bothers the child very often, appearing every month.
- A sore mouth does not heal for more than three weeks.
Treatment of stomatitis in a child should be versatile. Check out stomatitis prevention, to reduce the likelihood of relapse.
What to do if relapses occur frequently?
If stomatitis occurs in a child very often, you should:
- Visit the dentist and cure all teeth.
- Pay attention to oral hygiene - brush your teeth at least twice a day, rinse your mouth after eating, do not rush during brushing and use soft-bristled brushes.
- Stop using antisepticswhich process the oral cavity.
- Eliminate the use of toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Limit food that can injure the mucous membrane or cause irritation on it, for example, citrus fruits, crackers, spicy dishes, chips.
- Exclude all foods that the child is allergic to.
- Regularly take vitamin and mineral supplements.