Aphthous stomatitis in children and its treatment
Stomatitis is a very unpleasant disease that often occurs in small children as well as in grown-up children. Among all forms of stomatitis The most common is aphthous. What are the features of such stomatitis and how to treat it?
What is it?
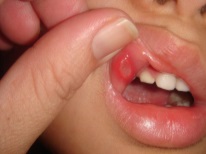
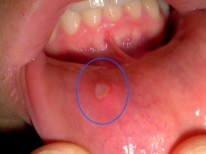
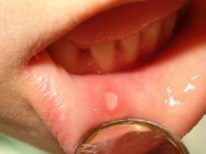
The name of such stomatitis is associated with its main elements, which are called afta. Such aphthae are round or oval sores with reddish edges and yellow-white patina. They are very painful, can have a different size and appear both in a single form and in groups. The apron can be seen on the inside of the lip, on the tongue, under the tongue and on other parts of the oral cavity.
The reasons
The exact reasons why some children have aphthae have not yet been identified, but among the provoking factors are called:
- Infectious pathogens - afta are often affected by staphylococcus, flu, measles, damage by adenoviruses and exposure to other microorganisms.
- The weakening of the immunity of the child.
- The lack of food in the baby vitamin C, selenium, iron, B vitamins, zinc and other compounds.
- Trauma of the mucous membrane.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Burns of the mucous membrane due to the use of very hot dishes or drinks.
- Diseases of the digestive system.
- Allergies to food, dust, drugs and other substances.
- The impact of stress.
- Transferred ARVI.
- Problems with teeth - the presence of stone, plaque, chips, caries, improper bite, poor-quality fillings.

Symptoms
In this form of stomatitis, in addition to the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, these symptoms are noted:
- Loss of appetite.
- Temperature rise.
- Increased salivation.
- The appearance of bad breath.
- Irritability and tearfulness of the child.
In the initial stage of the disease, mucosal changes are characterized by a slight swelling and redness, burning sensation and discomfort.
Forms
Given the nature of the disease, it can be:
- in acute form;
- in chronic form.
In the acute variant of aphthous stomatitis, a great affection of aphtha is noted, an increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees, an increase in lymph nodes, and the appearance of headache.
In chronic form, these symptoms are less pronounced. The child has aphthae several times a year (often in the autumn and spring), which heal within two weeks. However, there is also a severe course of chronic aphthous stomatitis, in which the aphthae are large or appear in large numbers. In this case, the child's condition worsens, and after healing, especially deep lesions leave scars.
Depending on the cause, aphthous stomatitis is viral, allergic, mechanical, candidal and others. Assessing the state of aft, emit such forms of stomatitis, as deforming, necrotic and scarring.
Diagnostics
It is quite simple to detect aphthous stomatitis, since it has a definite clinical picture - one or several aft are detected in a child’s mouth.
It is important to distinguish this disease from herpetic stomatitis. Therefore, noticing aphthy in a child, you should show it to a pediatrician or dentist to make sure that it is aphthous stomatitis, as well as to receive recommendations for treatment.
Treatment
To help a child, parents should:
- Give your baby more drink to ensure normal saliva production.
- Give all food to the child as a liquid or puree, warm and fresh.
- Make sure that the child often rinse his mouth.
- Moisten the air in the room.
Depending on the severity of the disease and the cause of the exacerbation, antiviral drugs may be prescribed to the child, antihistamines drugs, immunomodulators, antibiotics, multivitamins.
In local treatment it is important to conduct antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and relieve pain. To do this, it is recommended to use special gels and sprays with analgesic and antiseptic effects, as well as rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, iodinol, chlorophyllipt. From folk recipes, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with broths and infusions of yarrow, sage, oak bark, chamomile, calendula.
Prevention
To prevent frequent recurrences of aphthous stomatitis, one should:
- Treat chronic diseases of the digestive tract.
- To cure caries and other dental problems.
- Monitor oral hygiene.
- Regularly clean the toys and dishes.
- Provide your child with a balanced diet.
- Prevent contact with people who have stomatitis.
- Avoid the use of allergens in identifying reactions to them.