Thrush in the mouth in newborns and infants
One of frequent forms of stomatitis in infants is candida. In everyday life it is called thrush, it is one of the most common types of stomatitis in early childhood. Especially often this inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs in infants. Why does such stomatitis develop in the baby’s mouth, how does it manifest itself and how is it treated?
Symptoms
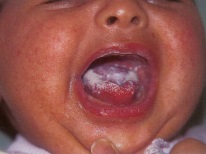
In infants younger than 12 months, stomatitis caused by a fungal infection is manifested by the appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa. They are painful and covered with white bloom, in appearance resembling cottage cheese. The raid can be removed using gauze, and then under it is visible wound that bleeds. Due to the great pain of such sores, the baby with stomatitis behaves restlessly, does not want to eat and cries a lot when they want to feed him.
It is also important for parents to learn that whitish plaque on the tongue does not always indicate stomatitis and can occur in healthy babies who eat both mother's milk and artificial formulas. For thrush, plaque will not only be on the surface of the tongue, but also on other parts of the oral mucosa, and when it is removed, the surface will bleed. If the plaque is milky, then it is easily removed and does not leave wounds. In addition, with stomatitis, symptoms such as itching and soreness will be present, and the baby’s raid will not bother the baby.
The reasons
The causative agent of such a disease in nursing babies is candida. So called yeast fungi, which are in the mouth, intestines and on the skin of many people, without causing disease. So completely protect the baby from candid with hygiene measures will not work.
However, fungi cause inflammation only in cases where the infant’s immunity is reduced (the baby has a cold, dysbacteriosis, teeth are cut, antibiotics had to be taken, the baby was born prematurely) or the mother does not follow the rules of hygiene (often thrush is transmitted from mother). Thrush injuries can also be caused by mucosal injuries, as well as frequent regurgitation.
In addition, fungi reproduce more actively in the presence of sugar, so the risk of thrush increases if the mother gives the baby sweetened water or a very sweet mixture, and also uses sweets in large quantities. when breastfeeding.
Disease progression
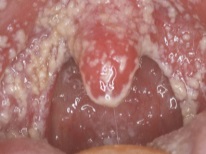
The first signs of the disease are redness on the mucous membrane of the mouth, which may go unnoticed. After two or three days, a white bloom appears on them and the elements of stomatitis become like white specks. They increase in size, can become grayish and yellowish, spread to fairly large areas of the mucous membrane.
The more defeats there are, the more discomfort they will cause in babies. If the disease starts, the plaque covers a large area of the mucous membrane, the child may have a fever, and because of the pain, the baby can neither suck nor swallow.
Forms
Depending on the course of stomatitis caused by Candida, it happens:
- Easy form. The raid is present in a small amount, the general condition of the baby is not disturbed, the child may behave restlessly and often be applied to the breast or nipple. Possible failure to eat.
- Moderate severity. Body temperature may rise to subfebrile, the child is lethargic, refuses to eat. Plaque is very common and is similar to the film covering the mucous membrane.
- Heavy shaped. The child has a fever, he is drowsy, lethargic, refuses to eat. There is also an increase in lymph nodes and odor from the mouth. The bloom thickens, becomes yellowish, and takes up a large surface.

Diagnostics
Since the disease has a rather characteristic clinical picture, only a medical examination is needed for a diagnosis. If the pediatrician has doubts, then a swab from the infant's mouth, which will be used to detect candida, will help confirm the presence of fungal stomatitis.
How to treat?
Before feeding, lesions on the mucous membrane should be treated with agents that give an analgesic effect. These can be special gels with anesthetics, which are used when teething milk teeth.
The treatment of the baby’s mouth with soda solution has a high effectiveness against thrush in the mouth, the main purpose of which is to create an alkaline environment in the mouth:
- A teaspoon of soda dissolves in a glass of warmed boiled water.
- Then the mother wraps a gauze or a bandage around her finger, dips it into the soda solution and gently rubs the baby’s mouth. It does not need to try to remove the white patina, the mother should simply moisten the area of lesions and gently wipe them without seeking the appearance of bleeding wounds.
- The procedure is carried out 4-5 times a day.
If the baby does not have the risk of an allergic reaction, the areas of inflammation can be treated with honey diluted in water. A teaspoon of this sweet delicacy is diluted in two teaspoons of water, and then the child is treated with the mouth up to 5 times a day, just like the treatment with soda.
Antifungal agents, such as fluconazole and nystatin, are used in the treatment of severe fungal stomatitis in newborn babies and infants. An antifungal drug prescribed by a doctor is applied to the oral mucosa after feeding and the baby is not fed for 30 minutes. This treatment is carried out 3-4 times a day.
Treatment Tips
- Many mothers treat the mouth of babies with dye solutions (blue, green paint). Such treatment does not harm the child, but it will not have a strong effect on the flow of thrush.
- It is important for mom to remember that the danger of thrush in newborns and infants is associated primarily with the risk of dehydration. The child, because of painful sores, refuses from food and water, and salivation in this pathology is enhanced. If mom noticed any signs of dehydration, it is important to take action immediately.
- To reduce the risk of recurrence of fungal stomatitis, the nipples and dishes that are used to feed the baby should be treated. The treatment involves boiling in water with the addition of baking soda.
- Mom is also recommended to treat her nipples with a soda or honey solution.
Opinion E. Komarovsky
The famous pediatrician considers the main cause of fungal stomatitis in young children to be the deterioration of the protective properties of saliva due to drying in the mouth. According to Komarovsky, rare walks, prolonged crying, shortness of breath of the little ones, as well as too dry air in the room lead to this.
A popular doctor reminds that the presence of a whitish plaque in the child's language up to one year is a normal variant and should be worried only when such a plaque appears on the inside of the cheeks.
The most effective way to prevent and treat such stomatitis Komarovsky calls the actions aimed at the production of baby saliva and the return of its bactericidal properties. This requires frequent walks and humidification of the air in the room. In addition, after the milk should give the baby a few sips of water. Wiping the elements of fungal stomatitis with a solution of soda Komarovsky also calls effective method.
Do I need a special diet?
Babies who get mother's milk with thrush continue to breastfeed. At the same time, the mother should correct her diet by removing sweets, food with chemical additives, and fast food from her. If the child has already begun to introduce complementary foods, then with stomatitis all food should be soft (the best option would be mashed potatoes), not sweetened, not acidic (acidic fruits are forbidden) and warm (you can not give very hot).
Possible consequences of the disease
In addition to the high risk of dehydration, which is very dangerous for infants, candidal stomatitis can cause more serious infections in the children's body through bleeding wounds in the mouth. In addition, if fungal stomatitis develops in a girl, she increases the risk of Candida and vaginal mucosa, which threatens to form synechiae.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of candidal stomatitis, you should:
- Cure candidiasis in mom during pregnancy.
- Carefully monitor hygiene - wash hands regularly, monitor the frequency of the mammary glands, boil nipples and bottles, wash baby’s toys.
- To feed the baby with the breast, thereby maintaining the immunity of the crumbs.
- After feeding, give the child a few sips of boiled water.
- Limit sweets in the menu of a nursing mother and do not give the child drinks with sugar.