Streptococcal infection in children
Bacterial infections in babies are often caused by various microbes of the coccal flora. One of the most common members of this family is streptococcus. What should you know about the problems of streptococcal infection parents will tell this article.
What it is?
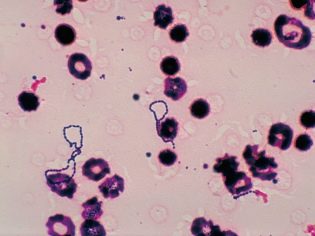
One of the representatives of the cocci families is streptococci. This is a fairly voluminous form, which includes a great many of the most diverse representatives. These microorganisms are capable of causing infectious diseases in both newborns and older children.
The prevalence of streptococcal infections in the pediatric population is quite high. These microorganisms are fairly well preserved in adverse environmental conditions. This feature is due to their cellular structure. While in the external environment, they retain their vitality, even without forming capsular forms.
The effect of insolation, some disinfectants, as well as antibacterial drugs has a detrimental effect on these microbes.
Some types of streptococci are representatives of the healthy microflora of the human body. Such microorganisms are also called opportunistic. The development of the disease in this case leads to their active reproduction with a decrease in immunity as a result of exposure to various factors.
Most often in children, this condition is promoted by severe hypothermia or exacerbation of chronic diseases of internal organs.
The prevalence of streptococcal infections among babies is quite high. In countries with a temperate continental climate, infections caused by different types of streptococci are found in ten out of a hundred babies.
To detect these microorganisms in humans can be in a variety of organs. They live on the skin, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, in the gastrointestinal tract, and also on the epithelial lining of the respiratory tract. Dr. Komarovsky, for example, believes that These microorganisms are an important component of the normal microflora of the child’s body.
Scientific studies that are aimed at studying the morphofunctional properties and the mechanism of active action of microbial data on the human body began to be carried out already from the end of the 19th century. Currently, researchers have found more than twenty different types of streptococcithat exist in the external environment.
Not all of them can cause infectious diseases in babies. Only those species that have pronounced pathogenicity factors (the ability to cause disease) may contribute to the appearance of adverse symptoms of the disease in the baby.
Streptococci come in a variety of groups and types. This division is carried out taking into account the peculiarities of their morphological structure. The most frequent representatives of this class of microbes that contribute to the development of infectious pathologies in babies are Streptococcus group A. Getting into a weakened children's body, these microbes can cause various lesions of the internal organs.
Streptococcus group b also lead to the development of various infectious diseases in babies. Quite often, these microorganisms lead to the development of bacterial sepsis or pneumonia.
According to statistics, these diseases occur more often in newborn babies.Premature babies are in the high-risk group, as well as babies with congenital anomalies and defects in the structure of internal organs.
Pathogenic streptococci have a dangerous property - the ability to exert a damaging effect on red blood cells (red blood cells). According to the severity of this feature, all microorganisms are divided into several main groups:
- Alpha hemolytic. Contribute to the partial death of red blood cells - hemolysis.
- Beta-hemolytic. Lead mainly to complete or massive death of red blood cells in the bloodstream.
- Gamma hemolytic. Have a minimum of damaging effects against red blood cells. Practically do not lead to the development of hemolysis.
Many streptococci are representatives of the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract. One of these microorganisms is streptococcus viridans. These conditionally pathogenic microbes are also quite common in the urinary tract and bronchial tree.
Scientists have found that These microorganisms are found in large numbers in girls in the genital area. The development of the disease can lead to a strong decrease in immunity, contributing to a change in the normal biocenosis.
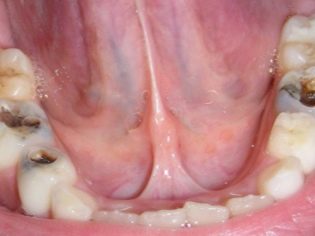
Green streptococci are widely represented in the oral cavity. This class of microorganisms includes many different representatives. Streptococcus mitosis often becomes the culprit of caries and other inflammatory diseases of the teeth.
These microorganisms have the ability to reproduce quickly and enough feel good in bone dental tissue, contributing to the development of acute or chronic inflammation in it.
The most common types of streptococci, which are most common in the pediatric population, are pyogenic microorganisms. They are also called hemolytic group A.
Streptococcus pyogenes is capable of causing a fairly large variety of different bacterial pathologies, which are accompanied by disruption of the work of most internal organs. The prevalence of these microorganisms in the population is very high.
How can you get infected?
Infection with streptococci can be a variety of ways. The most common way of infection is autoinfection.
In this case, excessive growth and reproduction of existing opportunistic colonies occurs. This happens, as a rule, as a result of the influence of various causal factors leading to a weakening of local immunity. The most common cause in children is severe hypothermia.
In severe cases, microorganisms can get into different internal organs, leading to systemic spread of the inflammatory process. Other situations also lead to the development of self-infection:
- Tooth extraction or incorrectly performed pulpitis therapy;
- The consequences of removing tonsils and adenoid growths;
- Carried out bladder catheterization for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes;
- Complications of bacterial pharyngitis and diseases of the paranasal sinuses.
In some cases, the baby can become infected from the outside. This occurs through contact with a sick person or carrier of the infection. This variant of infection is possible mainly in severely weakened babies. As a rule, these are children with severe concomitant pathologies of internal organs, growing neoplasms, pronounced immunodeficiency states, as well as complicated diseases of the endocrine system.
Some types of streptococci are excellent on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract airborne way. These tiny bacteria are contained in the saliva of a sick person or carrier of the infection in large quantities.You can become infected in this case by talking or being near a sneezing and coughing sick child. The rate of infection in this case is quite high.
Violation of the rules of personal hygiene contributes to the so-called "family" outbreaks of infection. The most common method of infection in this case is the use of shared towels, toothbrushes or washcloths. Parents should always remember that the baby should have their own personal belongings, which in no case should not be used by adults.
The towels used by the child in everyday life should be regularly washed in hot water and ironed on both sides with an iron.
Streptococcal flora is perfectly preserved and breeds in various foods. Fermented milk products, poultry meat, various compotes and fruit drinks are the most favorite nutrient medium for microorganisms.
Violation of the rules of storage of such products and the use of their expired shelf life provokes infection in a baby with a huge number of pathogens. In this case, as a rule, various forms of lesions of the gastrointestinal tract organs appear in the child.
Fetal infection with different groups of streptococci is also possible. It should be noted that it occurs quite infrequently. A more frequent source of infection in this case becomes Streptococcus Group B. American scientists claim that with intrauterine infection of a baby with these microorganisms, the risk of developing bacterial pneumonia and a septic condition increases many times.
In the United States, when microbes are detected, even at 36 weeks of pregnancy in pregnant women, they are treated accordingly. In our country, this practice does not apply.
In European countries, all pregnant women during pregnancy must be tested and smeared from the vagina to determine the pathogenic streptococcal flora.
Symptoms
A huge variety of representatives of streptococcal flora contribute to the development of a wide variety of clinical signs in babies. The degree of their severity may be different and depends on many reasons.
Usually severe course of infectious pathologies occurs in newborns and babies during the first months of life. This feature is due to the fact that the immune system of infants is not working as effectively as adults.
The incubation period for streptococcal infections varies greatly. In some cases, the first adverse symptoms appear within a few hours after a large number of pathogens have entered the children's body. In other situations, the disease develops only after 3-4 days.
In children with pronounced signs of immunodeficiency, clinical symptoms appear a little earlier and can be expressed quite strongly.
Very often streptococcal infection in children occurs. multiple respiratory lesions.
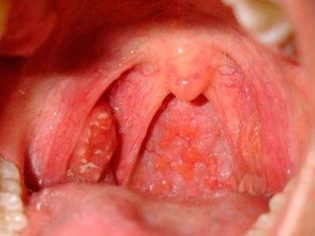
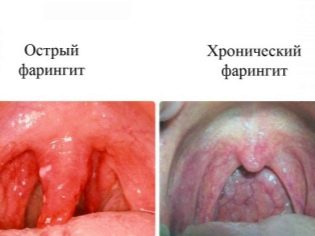
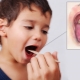
Severe redness in the mouth and bright redness of the palatine arches indicate the presence of bacterial pharyngitis. This condition is also accompanied by the appearance of pain in the throat when swallowing. The general well-being of the child is significantly impaired. The child's appetite decreases, and sleep is disturbed.
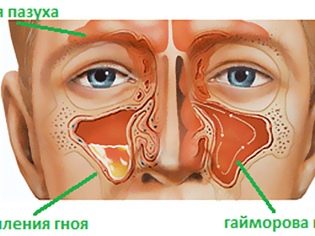
Streptococcal rhinitis - one of the most common childhood pathologies. This pathological condition is characterized by the development in the child of a head cold with copious discharge. Nasal breathing is significantly impaired. The runny nose is usually 7-14 days. Lack of prescribed treatment usually leads to the spread of an infectious process from the nose to nearby organs.
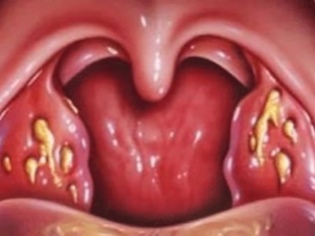
Acute tonsillitis, developed as a result of active reproduction of streptococcal flora, is accompanied by the appearance of a whole complex of adverse symptoms in a child.A sick baby in the throat on a sore tonsil appears greenish or gray. If you try to remove it with a spatula, you may experience increased bleeding.
Acute streptococcal tonsillitis or tonsillitis usually accompanied by high fever in the child and severe symptoms of intoxication.
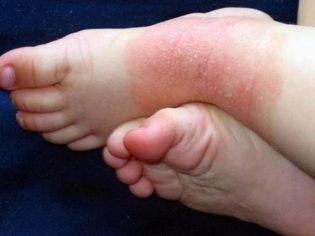
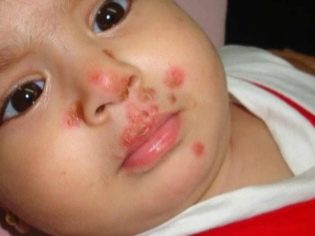
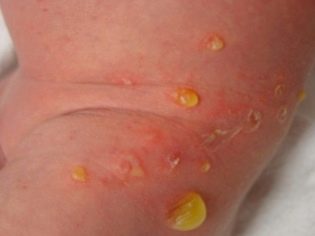
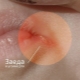
Skin manifestations also occur quite often. when infected with various types of streptococci. Streptococcal dermatitis is manifested by the appearance of various rashes on the skin, which look like bright red spots or blisters on the skin, filled inside with serous or bloody contents. In some cases, skin rashes appear on the face, neck.
Impetigo - This is a fairly common form of the disease, which can be caused by various pathogenic types of streptococcal flora. This pathology is characterized by the appearance on the skin of various purulent rashes.
Often leads to the development of this disease simultaneous infection with streptococci and staphylococci. The culprits of this disease in most cases are representatives of the pyogenic group of streptococcal flora.
Inflammatory pathologies of the middle ear are usually manifested by the appearance of otitis symptoms in a child. This pathology is accompanied by a moderate decrease in hearing, the appearance of “cracking” or “rustling” during a conversation in the ears of a sick baby.
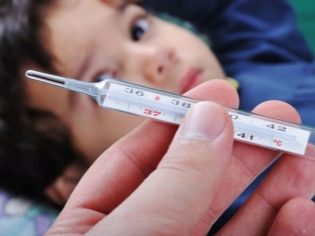
Body temperature in severe streptococcal otitis media usually rises to 38-39 degrees. The child feels bad, he has difficulty falling asleep and the duration of the night's rest.
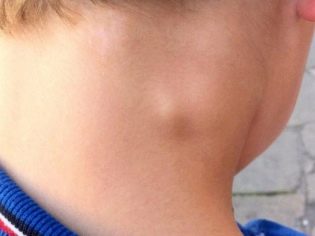
In some cases, streptococci enter various lymph nodes, contributing to the development of severe inflammation in them. Ultimately, this contributes to the development of lymphadenopathy.
The various groups of lymph nodes may be involved in the inflammatory process. They significantly increase in size, become available for palpation. The skin over the affected lymph nodes usually become red and hot to the touch.
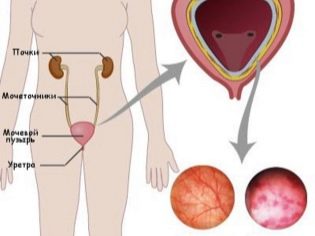
Inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system and genitals often occur due to infection with pathogenic streptococci. More prone to these pathologies girls. This is explained by the fact that the babies have a rather short urethra in size, as well as the close proximity of the external genital organs to the urinary tract.
A pronounced decrease in local immunity also contributes to the growth of conditionally pathogenic streptococcal colonies, which are representatives of the local flora.
Pediatric gynecologists believe that the overwhelming reason leading to the development of colpitis and other genital pathologies in girls is pronounced dysbacteriosis of the vagina. Such pathologies manifest themselves, as a rule, by a suddenly developed itch that can be quite unbearable.
In girls, urination may be disturbed, cramps or soreness appear during urine discharge. A large number of leukocytes are found in the urinary sediment, and in some cases red blood cells may appear.
Diagnostics
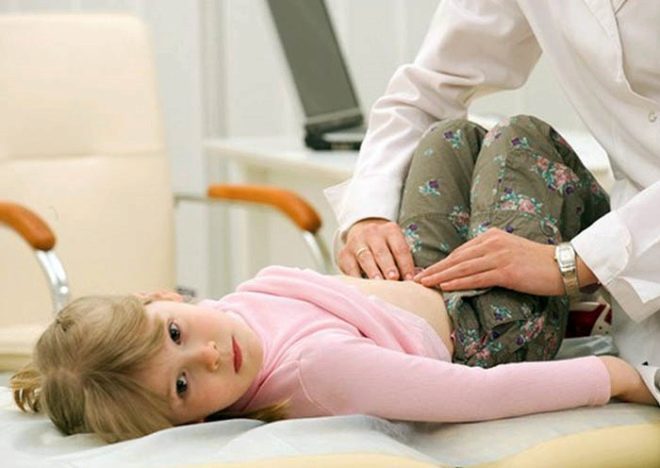
Pediatric doctors believe that you should not "carry out" treatment of tests, but you need to be guided by the initial well-being of the baby. If the child has the adverse symptoms of an infectious disease, then in this case he is prescribed complex therapy aimed at eliminating all clinical signs of the disease.
To identify the degree of deviations, various laboratory tests are used. They help to determine the limits of the norm, as well as to establish the pathology.
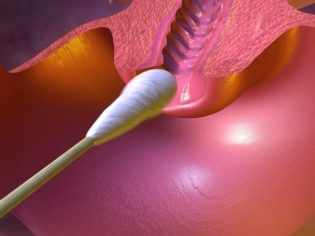
Streptococci can be detected in various biological fluids and materials: in blood, in urine, in a smear from the pharynx and nasopharynx, feces. The accuracy of the study in many cases depends on how well the material was collected.
With streptococcal lesions of the urinary tract and kidneys in the infant, it is very easy to identify the infectious agents in the urine.
There are methods of rapid diagnosis. They are used to quickly establish the cause of an infectious disease. These laboratory tests allow you to get the result after ½ hour.
This study should by no means be decisive in establishing the diagnosis. A positive result can only indicate a carrier. There are also false positive tests that require careful monitoring.
In the presence of rheumatological complications of the disease, various tests are conducted to identify specific markers of these pathologies.
The concentration of protein antibodies to streptococcal flora with glomerulonephritis usually increases several times and lasts for almost the entire period of the disease. These substances are determined by carrying out a specific neutralization reaction.
The diagnosis is carried out by doctors of various specialties. Streptococcal otitis media and nasopharyngitis are performed by pediatric otolaryngologists. Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are treated by gastroenterologists. Skin rashes are in the competence of dermatologists. Diagnosis and treatment of local purulent abscesses are conducted by pediatric or purulent surgeons.
Complications
Streptococcal infection is not harmless. Diagnosis, conducted in incomplete, or incorrectly chosen treatment leads to the development of a variety of dangerous complications and long-term effects of the disease in a sick baby. As a rule, the course of these pathologies is quite difficult. In most cases, treatment is carried out only in a hospital.
Inflammation of the lung tissue or pneumonia is a fairly frequent complication that usually occurs as a result of streptococcal bronchitis.
This pathology is characterized by the development of strong suppuration in the lungs. This disease is quite difficult. The body temperature of a sick child rises to 39-40 degrees. The baby can not fully breathe, over time, the crumbs of symptoms of respiratory failure.
The septic condition is a massive spread of microorganisms throughout the body. Failure to treat this condition leads to death. The treatment is carried out only in the conditions of the intensive care and resuscitation department.
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease, large concentrations of antibacterial drugs and physiological solutions, which are necessary for improving the microcirculation of vital internal organs, are administered to the child.
Meningitis is a serious complication of streptococcal infection. This pathology occurs with brain damage. It is characterized by the spread of pus between the meninges.
Streptococcal meningitis occurs with the development of a variety of severe symptoms. These include: severe excruciating headache, severe weakness, fever up to 39-40 degrees, complete loss of appetite. For the treatment of this condition requires a massive antibiotic therapy.
Some types of group A streptococci cause acute tonsillitis, which, in an unfavorable course, can turn into dangerous rheumatological diseases. These pathological conditions are dangerous by the development of heart defects, which are manifested by the formation in the child of the symptoms of heart failure.
Children's rheumatologists together with cardiologists deal with the treatment of these conditions in babies.
Treatment
Therapy of streptococcal infection is carried out taking into account the main localization of the inflammatory process. The basis of treatment is the prescription of antibacterial drugs.These funds are assigned to the exchange rate.
For 3-4 days from the first dose of the antibiotic, laboratory monitoring of the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy is required. For this complete blood count is performed. Leukocytes and ESR should decrease in this laboratory test.
The duration of the course of antibacterial treatment depends on the severity of the infectious pathology. Average, Therapy of streptococcal pathologies is carried out within 10-14 days. In some cases, the duration of treatment may be longer.
The frequency of taking medicines, as well as the dosage of prescribed antibiotic, is conducted by the attending physician, taking into account the age and weight of the sick child. Detrimental effect on streptococci have penicillin preparations.
Modern remedies, containing clavulanic acid in their composition, cause less possible side effects of damage to the stomach and intestines during the use of the drug.
If during the first control of the effectiveness of antibacterial drug has not had a positive effect, then it is canceled and replaced with another.
Also detrimental effect on various streptococci have cephalosporins. They exert their effect on growing colonies as well as on existing ones. Usually these funds are prescribed parenterally. Excess dose and daily dose can lead to increased side effects.
Symptomatic treatment also plays an important role in the treatment of streptococcal infection. Various anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce the symptoms of intoxication.
Helps to normalize high body temperature intake of antipyretic drugs. Most often in children's practice are used funds based on paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Immunostimulating interferon therapy is of secondary importance and is used for the combined infection with streptococci and various viruses.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene is necessary to protect the body from various infectious diseases.
During mass outbreaks of streptococcal infection in educational institutions, an emergency preventive measure, quarantine, can be introduced.
Family cases of infection will help prevent only careful implementation of all hygienic principles. To use someone else's towels, as well as personal hygiene products can not.
To identify carriers of certain forms of streptococcal infection requires mandatory medical monitoring of the health of babies. All temperate children attending educational institutions must necessarily spend an acute period of illness at home.
You should not attend school or kindergarten at this time, since such visits can lead to massive outbreaks of infectious pathologies.
Vaccinations for babies from streptococcal infections are not carried out. Preventing the disease will only help compliance with hygiene rules and hygienic regime.
See the next video for what diseases causes streptococcus.