Symptoms and treatment of tuberculosis in children
Tuberculosis can cause every person. In children, this disease is quite difficult and can cause numerous complications. This article will tell you what parents should know about this dangerous pathology.
What it is?
Infectious disease of the internal organs, which is caused by mycobacteria, is called tuberculosis. This pathology occurs in both adults and children. Many parents believe that only children from socially disadvantaged families can become ill with tuberculosis. However, this is a big mistake. The risk of infection with this infection exists in each child.
The prevalence of this infection in different countries of the world is different. In economically developed countries, tuberculosis is much less common than in developing ones. This fact further confirms the importance of the influence of the social factor in the development of this disease. Every year, scientists spend hundreds of different scientific studies aimed at finding new drugs that will help to cope with the adverse symptoms of the disease.
The susceptibility of the child's body to various infections is quite high. This is due to insufficiently effective work of the immune system. WHO experts believe that coping with massive outbreaks of tuberculosis in the population can only be prevented by new cases of the disease in adults. They identify several countries that are most unfavorable for the development of this dangerous infection in them. According to statistics, in these states by adolescence, more than 70% of children are infected with mycobacteria.
Tuberculosis is a rather dangerous disease. Every year more than 1.5 million people die from this infection. Child mortality from tuberculosis is also quite high. This trend suggests that the incidence of this infection should be carefully monitored.
In the last decade, from 1 to 10 out of 100,000 babies fall ill with tuberculosis. More cases are found in Asia and Africa. In our country, pulmonary tuberculosis is a fairly common pathology.
Since Soviet times, various state medical programs have been conducted to reduce the incidence of this infection. At present, the situation with this disease cannot be called satisfactory. Doctors say that the disease in children is quite difficult and has an unfavorable tendency to develop an infectious process not only in the lungs, but also in other internal organs.
There is historical information that the first cases of tuberculosis were recorded in the ancient world. Scientists were able to determine from the remains and bones of some pharaohs that they had signs of tuberculosis. This infectious disease has worried doctors for many centuries.
During the Middle Ages, it was often called "consumption." This popular name accurately enough conveys the essence of the disease - a person, having become ill, begins to weaken (withers).
For quite a long time, doctors believed that tuberculosis affects only the lungs. However, this is not at all the case.Modern laboratory instruments allowed to establish other localizations of this dangerous disease. Even hair and nails may be involved in this pathological process.
Quite often, lesions of internal organs are combined. The inflammatory process in this infectious pathology is specific. It causes particular morphofunctional disorders that are not found in other infections. This type of inflammation also occurs during syphilis and leprosy.
In the development of the disease, scientists distinguish several stages. They differ significantly from each other, not only in the development of adverse symptoms, but also in the characteristics of morphological disorders that occur in the course of the disease.
More about the causative agent of infection
For the first time, microorganisms that cause this disease were identified at the end of the 19th century. An outstanding scholar of those years, Robert Koch, made this discovery. This scientific breakthrough and served the appearance of the popular name of the causative agent of the disease, which was also called "Koch's wand".
A few centuries ago, scientists knew only about one type of mycobacteria. Currently, scientifically confirmed information has appeared that they exist in 74 different forms. They are widespread not only among the human population, but also present in water, soil, and in some animals.
The pathogens that cause tuberculosis can be of different subtypes. The main causative agent of this infectious pathology in humans is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This subtype of mycobacteria includes several other types of microorganisms, which differ in each other mainly in the degree of manifestation of their virulent properties and their pathogenicity.
The virulence of microorganisms and the initial state of the child’s body determine how difficult the disease will be in a baby or everything will be limited to carriage. The causative agents of this infection are perfectly preserved in adverse environmental conditions. They are highly resistant to most acids.
Mycobacteria look like elongated sticks. In length, they do not exceed 10-12 microns. The ends of the body of the microorganism are slightly rounded, which makes them look like kegs or sticks.
In the external environment, mycobacteria remain immobile, but they do not form a spore. The special structure of cell walls that protect bacteria from adverse environmental influences allows them to maintain their vital activity for a long time without losing pathogenic properties.
Outside, these microbes are surrounded by a dense shell, which consists of several layers. Such cellular protection is like “armor”, protecting microorganisms from the effects of disinfectants.
The main properties of mycobacteria are in tuberculoproteins. These are special proteins that cause a certain immunological reaction on the part of the child’s immune system. This systemic response of a child’s body is called delayed-type hypersensitivity. This is a very specific mechanism for the development of immune inflammation.
The presence of certain lipids in the cellular structure of bacteria makes them more tolerant to the effects of various external chemical substances and biologically active components, which the immune system releases in response to ingestion of these microbes.
The effect of alcohol and some strong alkalis also does not have a destructive effect on microorganisms. Infectious agents are well preserved in house dust. In it, they can exist for several months.
There are a huge number of scientific experiments showing that mycobacteria are perfectly preserved in milk. They can maintain their vitality for several months in soil and water.
It is important to note that boiling has a detrimental effect on microorganisms. However, to completely kill them, it is necessary to boil water or another liquid containing tuberculosis pathogens for 5-10 minutes.
In adverse environmental conditions, microbes pass into a certain “sleeping” state. At this time they are called the L - form of mycobacteria. When they enter the children's organism into conditions favorable for their vital activity, they quickly recover and begin to exert their negative effect.
Some external factors and chemicals still have a destructive effect on the microbes that cause tuberculosis. Disinfection using chlorine-containing products helps to reduce the concentration of pathogens in the room. Quartz, carried out in a special mode, also has a pronounced disastrous effect on mycobacteria.
The causative agents of tuberculosis infection can be attributed to microorganisms that multiply long enough. This morphological trait affects the peculiarity of the course of the disease, as well as the duration of the appointment of appropriate treatment.
The reproduction cycle of one mycobacterial cell is about 18-20 hours. For staphylococcal flora, this time period is much less - 8-10 minutes. The morphological feature of the cellular structure of microbes and a rather slow reproduction rate lead to the fact that in the affected internal organs, areas of inflammatory infiltration begin to form. This is a consequence of the granulomatous process.
Externally, these areas look like numerous bumps, which can be of various sizes. These formations are quite susceptible to decay.
How can a baby get infected?
The most frequent culprit in the infection of babies is a sick person suffering from an active stage of tuberculosis. During this period of the disease, it usually releases a large amount of mycobacteria into the environment, so direct contact with such an infected person significantly increases the risk of possible infection with tuberculosis.
The most common method of infection is airborne. A baby can become infected during a conversation or intimate communication.
It is fairly common infection of tuberculosis infection in public transport. The use of common dishes, toys and household items also contributes to the possible infection with tuberculosis.
Adults who suffer from tuberculosis infection in an active form and release mycobacteria into the environment can infect a child during a kiss or a warm embrace.
There are other ways of transmission. They arise in those situations when a person infected with tuberculosis has tuberculous lesions of some internal organs. So, during infection of the bones and lymph nodes, infection occurs through a household contact. In this case, mycobacteria get on the skin of a sick person through open fistulas.
In tuberculosis of the skin and nails, infection can occur when simple rules of personal hygiene are violated.
In some cases, a child may become infected with this infection by drinking contaminated water or milk.
Cattle is also a possible source of infectious diseases. Eating unboiled milk from farms can cause a baby to develop tuberculosis.
In infants, the alimentary (food) route of infection is most common. The habit of pulling dirty hands in your mouth outside or while playing with others in the sandbox can also lead to possible infections.
Cases of congenital tuberculosis are also quite common in pediatric practice.Infection in this case occurs even at the stage of intrauterine development: the baby becomes infected with a tuberculosis infection while in the womb.
But not always a mother infected with tuberculosis has a baby with signs of disease. If the pregnancy proceeds fairly smoothly and without pathologies, the risk of infection of the unborn child is significantly reduced.
Quite rarely there is a mixed infection. In this case, different mechanisms of infection lead to the development of the disease. In pediatric practice, this is mainly a combination of airborne and contact-domestic methods of transmission.
Clinical forms
Mycobacterium tuberculosis can affect a variety of internal organs. This causes the appearance of a huge variety of the most diverse clinical forms of the disease. The features of the course of the disease largely depend on the initial localization of the infectious process, as well as the state of the child’s immune system.
Doctors distinguish several clinical variants of tuberculosis infection:
Respiratory organs
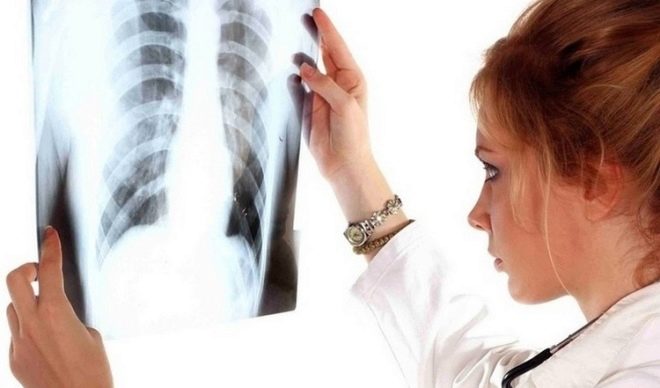
This form occupies a leading position in the structure of the incidence of this infectious pathology. Accompanied by the development of specific changes in the lung tissue, rarely bronchus and trachea are involved in the inflammatory process. As a rule, this form of the disease is established spontaneously - when carrying out radiography of the lungs and much less often at outpatient appointments with a doctor.
Lymph nodes
Also quite common pathology in children, in adults, this form of tuberculosis is much less common. There is a high risk of infection in babies with HIV infection. Most often, groups of cervical and axillary lymph nodes are involved in the infectious process, however, other peripheral lymph nodes can also be affected. Establishing a final diagnosis is not possible without puncture.
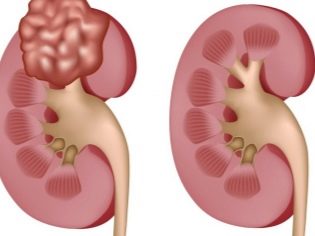
Kidney
This form of the disease is rare in babies. Characterized by involvement in infectious inflammation of the renal tissue. A long course of tuberculosis leads to the appearance of signs of functional disorders of the kidneys in the child. Delayed or incorrectly chosen treatment contributes to the appearance of multiple complications in the baby, one of which is the development of renal failure.
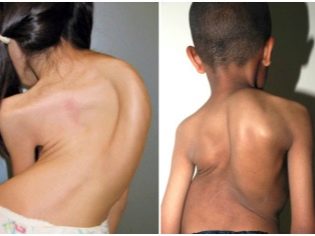
Bones
A fairly common clinical option in pediatric TB practice. Persistent tuberculosis of bones and joints often leads to the onset of a child's disability. Tuberculous changes can develop in almost all anatomical structures of the skeletal system. Quite often, the disease is detected in the late stages of development.
Intrathoracic lymph nodes
A fairly common form of the disease, especially in young children. Pathological process can be one - or bilateral. Enlarged intrathoracic lymph nodes exert a strong pressure on the adjacent bronchi, which leads to the appearance of the corresponding symptoms in the child. The first signs of the disease are often recorded already in children aged 2-3 years.
Nervous system
This clinical version of the disease, perhaps one of the most difficult. It is characterized by the development of a child's tuberculosis. meningitis or meningoencephalitis. The course of these pathologies is rather severe, characterized by the appearance of rather unpleasant symptoms that significantly disturb the baby’s well-being. Most often, this form of the disease occurs in infants.
Gastrointestinal tract
Another favorite localization for the vital activity of mycobacteria in the children's body is the intestine and mesenterial lymph nodes. This pathology occurs in children infrequently. Babies with AIDS are more susceptible to this form of the disease.In some cases, this clinical variant of tuberculosis occurs in children with pronounced immunodeficiency states, which are quite difficult.
Eye
In pediatric practice, cases of this type of tuberculosis are extremely rare. The development of tuberculous conjunctivitis or keratitis is often promoted by a marked decrease in immunity or multiple diseases of the internal organs. Kids with visual pathology are also in the high-risk area.
How does tuberculous intoxication manifest itself?
Doctors distinguish several periods in the development of this pathological condition. The early period of tuberculosis intoxication in children and adolescents is manifested primarily by pronounced disorders of the nervous activity. A sick child becomes more nervous, he has a nonspecific headache, fatigue, distraction of attention. Children attending school say that they cannot concentrate on the school curriculum and do not learn the material well.
Upon careful examination of the child, you can notice some changes in appearance. Ill child becomes more pale, apathetic.
As a rule, the child appears persistent subfebrile. The body temperature at the same time rises to 37-37.5 degrees. A long subfebrile condition significantly violates the general well-being of the child. The baby's appetite is sharply reduced, there may be problems with the duration of sleep.
In some cases, especially in skinny babies, you can easily palpate the liver and spleen. A sick child may experience stool irregularities, which are most often manifested by persistent constipation.
As a rule, by the end of the first month after the initial infection, a specific manifestation of tuberculosis appears - turn of tuberculin test. This reaction manifests itself as a positive tuberculin test and helps to recognize the disease at fairly early stages.
Another characteristic manifestation of the disease in the early period is the appearance of specific skin lesions. This pathological condition is called erythema nodosum. It is characterized by the appearance of bright red spots, which are localized mainly on the legs.
A rather high fever is usually preceded by these skin eruptions. Often this adverse symptom occurs in children aged 5-6 years.
The second period of development of tuberculous intoxication is its transition to the chronic form. This period is extremely unfavorable, as it is accompanied by the appearance of persistent morphofunctional disorders leading to the development of specific symptoms of the disease.
Long-term current illness leads to the fact that the baby is significantly behind its peers in terms of physical and mental development. A sick child looks rather pale, haggard.
Pathological changes in the lymph nodes lead to persistent functional disorders. Palpation of peripheral lymph nodes can determine the consolidation of their structure, as well as the change in size.
In some cases, the lymph nodules become similar in density to pebbles. Chronic tuberculous intoxication is accompanied, as a rule, by the defeat of 6-9 adjacent groups of lymph nodes. This pathological condition is called micropolyadia.
Establish the diagnosis of this condition, based on the persistence of positive tuberculin samples. In this case, from the moment of the first turn, one year must pass.
In some cases, there is marked increasing dynamics. Tuberculin tests every year in an infected child only increase. Such dynamics must necessarily be evaluated by a pediatric TB specialist.
In the chronic variant of tuberculous intoxication, numerous morphological abnormalities in the internal organs are already expressed.Quite often they occur in the bone marrow, peripheral lymph nodes, as well as the liver, spleen and gastrointestinal tract.
Chronic period differs from the early degree of severity of all symptoms. In the later stages, they proceed more clearly and strongly disturb the baby’s well-being.
Reduced appetite during chronic tuberculous intoxication leads to the fact that the baby loses pounds. This contributes to a pronounced lag in physical development. The child's muscle mass decreases markedly. Such babies look asthenic, quickly lose weight.
The skin of the baby loses moisture, becoming more dry to the touch. Skin turgor noticeably reduced.
The thickness of the subcutaneous tissue also decreases markedly due to a pronounced decrease in appetite.
The child’s well-being is markedly depressed by constant changes in body temperature. Usually its values in this period vary from 37 to 37.5 degrees. In some cases, there may be fever, chills.
The mood and behavior of the child in this period change markedly. Long-term current disease leads to the fact that the mental type of the child’s personality also changes.
Noisy active games with friends do not bring child satisfaction and joy. Sick kid tries to spend more time with himself. Even familiar activities can lead to excessively rapid fatigue.
A sick child can hardly practice sports and gets tired after a short walk.
The chronic period of tuberculous intoxication is quite dangerous, as it is accompanied by the development of numerous persistent disorders. To prevent it, timely diagnosis of the disease should be carried out. Only in time prescribed and carried out treatment will contribute to the regression of the disease.
If you suspect that your baby has signs of tuberculosis, you should immediately consult a pediatric TB specialist.
To determine the infection with tuberculosis, which is not accompanied by the onset of symptoms, or the latent form of the disease is possible with the help of special laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods.
Symptoms
During the incubation period, there are no specific symptoms of the disease. For tuberculosis infection, this time is usually ½ to 4 months.
In the scientific literature there is information that in some cases the incubation period was even a few years. The duration of this time is determined by the individual morphological features of the pathogen, as well as the initial parameters of the immunity of an infected child.
Tuberculosis has different masks. The variety of symptoms can be so huge that it can significantly complicate the clinical diagnosis of the disease.
Some forms of the disease are almost asymptomatic. It is important to note that tuberculosis infections that occur without the appearance of adverse clinical signs occur in children quite often.
To help establish the correct diagnosis in this case can only alternative diagnostic methods.
The following symptoms are characteristic of tuberculosis infection:
- Persistent temperature rise. This feature persists in almost all stages of the disease. In most cases, the body temperature does not rise above 37.5 degrees. Febrile is found only in severe disease. Increasing the temperature exhausts the baby and significantly worsens his health.
- Great weakness and fatigue. The child becomes quite emotional, quickly irritated on trifles. Some babies have unmotivated outbursts of anger. Quite often, sick children have various depressive states.
- Loss of appetite. This symptom accompanies all periods of the disease.Decreased appetite leads to a strong weight loss, and ultimately leads to a lag in physical development. In severe illness, sick babies can lose up to 40% of their weight.
- Excessive perspiration. This symptom most often occurs at night. In TB practice, this clinical symptom is often called the “collar symptom”, since excessive sweating occurs mainly in the neck. In some cases, hyperhidrosis is profuse.
- Severe dry skin and pathological brittle nails. Quite frequent manifestation of tuberculosis infection is the appearance of areas with increased desquamation on the skin. In adolescence, this symptom often resembles seborrheic dermatitis.
- Enlarged and swollen lymph nodes. Almost all groups of peripheral lymph nodes are involved in the infectious process. They become firm to the touch and accessible to palpation. The affected lymph nodes increase in size several times. In severe cases, enlarged lymph nodes become visible when viewed from the side.
- Severe pallor of the skin. The skin of babies becomes thinned with easily visible blood vessels. Under the eyes appear "bruises" and dark circles. In some cases, acrocyanosis also occurs around the nasolabial triangle. A long course of tuberculosis leads to the fact that the child's fingers take the form of drum sticks, and the nails have the appearance of "watch glass".
- Cardiopalmus. Tachycardia occurs not only during physical exertion, but also in complete rest. Some babies have aching and tingling sensations in the chest.
- Soreness in the joints. This symptom is highly non-specific. Quite often, it occurs in tuberculosis of the musculoskeletal system. Pain in the joints can appear even at rest, without making active movements. Small children experience increased pain during getting up or crawling.
- Characteristic skin rashes, also called erythema nodosum. This form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of bright red spots that can itch and bring pronounced discomfort to the child. As the erythema nodosum develops, the specks change their color and become blue. Adverse symptoms usually persist in babies for 3-4 weeks.
How does it appear in newborns?
Tuberculosis can occur at any age. The first signs of the disease are sometimes found even in newborn babies. The appearance of symptoms in this case is highly non-specific. It depends on the initial localization of the tuberculous focus. In the presence of infection in the respiratory organs of a child, clinical signs associated with impaired respiratory function appear. Tuberculosis of the internal organs is accompanied by the appearance of a wide variety of symptoms, which can manifest themselves as the appearance of discomfort or pain in the abdomen, impaired stool or loss of appetite.
Diagnostics
Only phthisiatricians establish the final diagnosis of tuberculosis. Initially, for this, doctors conduct a clinical examination of the baby, which in some cases allows to establish signs of the disease. Confirm the diagnosis results of laboratory and instrumental studies. This examination is carried out in a phthisiological clinic. Laboratory tests are to conduct tuberculin tests. Tuberculin diagnosis helps to determine the increased sensitivity of the delayed type to specific mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins. By its chemical structure, tuberculin is a special substance that is a purified tuberculous toxin. The introduction of it into the children's body can not lead to infection of the baby with tuberculosis.
In many countries of the world, an enhanced reaction to the management of purified tuberculin is performed on babies from 4 to 14 years old. It helps to establish a variety of clinical options for the disease, including latent forms.
For Mantoux tests used tuberculin in a special dilution. It is administered intracutaneously in a dose of 0.1 ml or 2 TE. Introduce antigenic substance in the region of the middle third of the forearm.
Doctors use certain criteria to evaluate the results:
- Negative a reaction is the absence of a red bright spot in the needle insertion area.
- Doubtful sample - this is the appearance of a speck of hyperemia, up to ½ cm in size.
- With a positive reaction dermal papule exceeds in size 5 mm.
- When hyperergic reaction the size of the red spot at the injection site exceeds 17 mm or a bubble (vesicle) is formed, filled from the inside with serous fluid.
All positive and hyperergic reactions require the mandatory conduct of additional diagnostic methods to eliminate the signs of tuberculosis in a child. These studies are necessary to determine the norm or pathology.
In difficult clinical cases, it is necessary to PCR diagnostics. This method has a high sensitivity and specificity, which allows you to determine the presence of mycobacteria in the child's body quite accurately.
The most modern method of examination, which is used to diagnose tuberculosis, is called spot study. This immunological test has been carried out in Russia since 2012.
The material for the study is venous blood. The duration of its holding usually takes 3-4 days. The information content of this test is from 95 to 98%, and the sensitivity varies from 85 to 98%.
Modern and accurate alternative to the usual diagnostic tests for tuberculosis - conducting Diaskintest. Using this method allows you to identify both active and latent forms of the disease. The essence of the study - the introduction into the skin of protein allergens to determine the specific immune response. A positive result of this test indicates that the children's body is already familiar with the infectious agent introduced into it.
Parents are often mistaken, considering Diaskintest vaccine. It's not like that at all. This study is conducted only for diagnostic purposes and is necessary to establish the correct diagnosis. Evaluate the result for 2-3 days from the date of entry of the allergen.
A child who has not had a previous tuberculosis infection does not have any red spots or swelling at the injection site.
Treatment
For the treatment of the disease, various combinations of anti-TB drugs are used. These funds are prescribed for permanent admission: passes and short-term cancellation of these drugs are not allowed. The duration of treatment is usually from 6 months to several years.
Therapy of tuberculosis is carried out in a special TB hospital. Multicomponent treatment is prescribed for the treatment of tuberculosis infection. It includes the appointment of several drugs at the same time.
The first treatment regimen, which was used to eliminate the adverse manifestations of the disease in our country, was three-component. It included taking three first-line drugs: streptomycin, isoniazid, and para-aminosalicylic acid. For quite a long time, such treatment was successfully used in phthisiology and brought a positive result.
Due to the fact that microbes mutate rather quickly and change their properties, the three-component treatment for tuberculosis was replaced by a four-component one. Currently, it is used to treat babies infected with sensitive strains.This treatment regimen includes the use of streptomycin or kanamycin, rafabutin or rifampicin, isoniazid or ftivazid, as well as pyrazinamide or ethionamide.
In some cases, the four-part treatment regimen does not bring the desired result. In such a situation, phthisiatricians add fluoroquinolone derivatives to the treatment. This scheme of therapy is used in the most difficult cases of tuberculosis, when there is a pronounced resistance of microbes to the effects of various drugs.
The use of five-component treatment can cause the child the appearance of numerous side effects, as it includes a lot of strong antibiotics last generations.
Hormonal agents for the treatment of tuberculosis are rarely used. These drugs have a strong immunosuppressive effect, which significantly worsens the further prognosis of the disease.
Usually, prednisone is prescribed only to eliminate the dangerous complications of tuberculous intoxication, which is accompanied by the development of meningitis or meningoencephalitis. As a rule, hormones are prescribed only for exchange intake for 5-7 days.
For centuries, doctors have been talking about the importance and effectiveness of sanatorium-resort treatment young patients with tuberculosis.
The combination of various physiotherapeutic methods, balanced caloric intake and fresh air help to significantly restore the children's organism, which was weakened during the illness.
It is desirable that the child undergo such treatment every year: this is an excellent prevention of disease progression. With the ineffectiveness of drug therapy, doctors may recommend surgical treatment.
Indications for surgery sets the attending physician. Most often, operations are performed when the baby has pathological lumps in the lungs that occur in pulmonary tuberculosis and are called caverns. After the operation, the child is prescribed a restorative treatment.
Clinical examination of children with tuberculosis is carried out taking into account their distribution into groups of dispensary registration. Currently, there are 7 groups. Toddlers and teenagers are monitored by a pediatric TB specialist until they are 18 years old. For each dispensary group, there is a certain multiplicity and timing of tests for the secretion of mycobacteria and prophylactic treatment.
Watch the next video show “Live Healthy” with Elena Malysheva on tuberculosis.