The expansion of the ventricles of the brain in infants
Quite often in babies after birth, the ventricles of the brain are enlarged. This condition does not always mean the presence of the disease, in which the prescription of treatment is required.
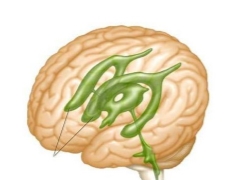
Ventricular system of the brain
The ventricles of the brain are several interconnected reservoirs in which the formation and distribution of liquor fluid occurs. Liquor washed the brain and spinal cord. Normally, when there is always a certain amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles.
Two large liquor fluid collectors are located on both sides of the corpus callosum. Both ventricles are interconnected. On the left side is the first ventricle, and on the right - the second. They consist of horns and body. The lateral ventricles are connected through a system of small holes with a 3 ventricle.
In the distal brain between the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata is located 4 ventricle. It is quite large in size. The fourth ventricle has a diamond shape. At the bottom of the hole is located, which is called the diamond-shaped fossa.
Proper ventricular function ensures the penetration of cerebrospinal fluid into the subarachnoid space, if necessary. This zone is located between the solid and spider shells of the brain. This ability allows you to save the required volume of CSF under various pathological conditions.
Newborn babies often have dilatation of the lateral ventricles. In this condition, the horns of the ventricles are dilated, and an increased accumulation of fluid in the area of their bodies can also be observed. This condition often causes both an increase in the left and right ventricle. In differential diagnosis, asymmetry is eliminated in the area of the main brain collectors.
The size of the ventricles is normal
In infants often the ventricles are enlarged. This condition does not mean that the child is seriously ill. The sizes of each of the ventricles have specific values. These indicators are shown in the table.
Anatomical structure | Depth in mm. |
The first and second ventricles (lateral) | 4 |
Third ventricle | 5 |
Fourth ventricle | 4 |
To assess the normal performance is also used to determine all the structural elements of the lateral ventricles. Side tanks should have a depth of less than 4 mm, front horns from 2 to 4 mm, and occipital horns from 10 to 15 mm.
Causes of ventricular enlargement
Premature babies may have dilated ventricles immediately after birth. They are arranged symmetrically. Symptoms of intracranial hypertension in a child with this condition usually does not occur. If only one of the horns increases slightly, then this may be evidence of the presence of pathology.
The following causes lead to the development of ventricular enlargement:
Hypoxia fetus, anatomical defects in the structure of the placenta, the development of placental insufficiency. Such conditions lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain of the unborn child, which may cause him to expand intracranial collectors.
Head injuries or falls. In this case, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disturbed. This condition leads to stagnation of water in the ventricles, which can lead to symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Pathological labor. Traumatic injuries, as well as unforeseen circumstances during childbirth, can lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. These emergency conditions often contribute to the development of ventricular enlargement.
Infection with bacterial infections during pregnancy. Pathogenic microorganisms easily cross the placenta and can cause various complications in a child.
Prolonged labor. Too long time between the discharge of amniotic fluid and the expulsion of the baby can lead to the development of intragener hypoxia, which causes a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the dilated ventricles.
Oncological formations and cysts that are located in the brain. The growth of tumors exerts excessive pressure on intracerebral structures. This leads to the development of pathological expansion of the ventricles.
Foreign bodies and elementsthat are in the brain.
Infectious diseases. Many bacteria and viruses easily penetrate the blood-brain barrier. This contributes to the development of numerous pathological formations in the brain.
How does it manifest itself?
Expansion of the ventricles does not always lead to the appearance of adverse symptoms. In most cases, the child does not have any uncomfortable manifestations that would indicate the presence of a pathological process.
Only with marked violations begin the first adverse manifestations of the disease. These include:
Gait disturbance. Toddlers begin to tiptoe or step on the heels.
The appearance of visual disorders. They often manifest in children in the form of strabismus or not enough good focus on various subjects. In some cases, the child may appear double vision, which is enhanced when viewing small objects.
Trembling of hands and feet.
Behavior disorders Kids become more sluggish, drowsy. In some cases, even apathetic. A child is very difficult to carry away with some kind of games or entertainment activities.
Headache. Manifested with increased intracranial pressure. At the height of the pain, vomiting may occur.
Dizziness.
Decreased appetite. Babies of the first months of life refuse to breastfeed, eat poorly. In some cases, the child spits more.
Sleep disturbance. Toddlers may have difficulty falling asleep. Some babies walk in their sleep.
The disease can be of varying severity. With minimal symptoms, they talk about a mild course. With the appearance of headache, dizziness, as well as other symptoms indicating high intracranial hypertension, the disease becomes moderately severe. If the general condition of the child is severely disturbed and treatment in inpatient conditions is required, then the disease becomes severe.
Effects
Late diagnosis of pathological conditions that led to the appearance of extensions in the ventricular region of the brain, may affect the further development of the child. The first persistent symptoms of ventricular dilatation are observed in babies at 6 months.
Violation of the outflow of liquor fluid can lead to a persistent increase in intracranial pressure. With severe disease - it contributes to the development of disorders of consciousness. Visual and hearing impairment leads to the development of a hearing loss and impaired vision in a child. Some babies have epileptic seizures and seizures.
Diagnostics
In order to determine the exact size of the ventricles, as well as to know their depth, doctors prescribe several methods of examination.
The most informative and reliable are:
Ultrasound procedure. Allows you to accurately describe the quantitative indicators of the ventricles, as well as calculate the ventricular index. Using ultrasound, it is possible to estimate the volume of liquor fluid that is present in the brain sewers during the study.
CT scan. With high accuracy allows to describe the structure and size of all the ventricles of the brain. The procedure is safe and does not cause the child painful sensations.
Magnetic resonance imaging. It is used in difficult diagnostic cases where the establishment of a diagnosis is difficult. Suitable for older children who can not move during the whole study. In small children, MRI is performed under general anesthesia.
Examination of the fundus.
Neurosonography.
Treatment
Therapy of pathological conditions that led to the dilatation and asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain, usually conducted by a neurologist. In a number of cases, when the cause of the disease is a mass lesion or the effects of traumatic brain injury, a neurosurgeon doctor joins.
The following methods of treatment are used to eliminate the pathological symptoms:
The appointment of diuretic drugs. Diuretics help reduce the manifestations of intracranial hypertension and improve baby's well-being. They also contribute to the normalization of the formation of CSF.
Nootropics. They improve the functioning of the brain, as well as contribute to a good blood supply to the blood vessels.
Drugs with sedative effect. They are used to eliminate increased anxiety and agitation.
Potassium preparations. Positive effect on urine excretion. This helps to reduce the increased amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the body.
Multivitamin complexes. They are used to compensate for all necessary microelements involved in vital processes. They also help strengthen the body and contribute to better disease resistance.
Soothing and relaxing massage. Allows you to reduce muscle tone, and also helps to relax the nervous system.
Physiotherapy. It helps to normalize the outflow of liquor fluid and prevents its stagnation in the cerebral ventricles.
Purpose of antibacterial or antiviral drugs for indications. They are used only in cases when viruses or bacteria become the cause of the disease. Assigned to the course reception.
Surgery. It is used in case of presence of various volume formations or for the removal of bone fragments as a result of a skull fracture due to craniocerebral injuries.
Forecast
If the condition develops in infancy and early infancy, then the course of the disease is usually favorable. With appropriate treatment, all the uncomfortable symptoms quickly pass and do not bother the baby. High intracranial pressure is normalized.
In older children, the prognosis of the disease is somewhat different. Unfavorable symptoms are much more difficult to treat. A prolonged course of the disease can lead to persistent visual and hearing impairment. If the treatment was not started on time, then in most cases the child has persistent disorders that negatively affect his mental and mental development.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell about the expansion of the ventricles of the brain in infants and its consequences.