Intracranial pressure in infants and babies
Changes in the brain are quite dangerous for newborn babies. Increased intracranial pressure is a very common pathology in neonatal practice.
What it is?
After the birth of each child, doctors must evaluate the performance of vital organs. Indicators intracranial pressure very important for the normal functioning of the brain in infants. The excess of normal indicators of cranial pressure indicates the presence of hypertensive syndrome. Doctors also call it intracranial hypertension.
Norm
Normal work of the brain and spinal cord is impossible without regular circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Normally, it is formed in special cisterns of the brain - the ventricles. They are also needed to ensure the cumulative function. Excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid can accumulate, leading to the development of hydrocephalic syndrome.
The resulting cerebrospinal fluid circulates freely between the lining of the brain. The brain is surrounded by several such formations at once: hard, arachnoid and soft. For better communication of the cerebrospinal fluid there are microscopic gaps between the meninges. This constancy is ensured by the continuous formation and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid between brain structures. This leads to the fact that normal intracranial pressure has strictly defined values.
Normally, in a newborn baby it should be in the range of 2 to 6 mm. Hg Art. In infants, cranial pressure can be 3-7 mm. Hg Art. As the baby grows and develops, the normal values of this indicator also change. High intracranial pressure for a long time leads to the development of resistant hypertensive syndrome.
Reasons for raising
Provocative factors that contribute to an increase in cranial pressure, a lot. It is no coincidence that neonatologists notice more and more cases of setting up such a syndrome after the birth of babies. Every day hundreds of babies are born around the world who have congenital intracranial hypertension.
The following causes lead to an increase in cranial pressure in newborns and infants:
- Anomalies of the structure of the placenta. Through this vital organ during the entire 9 months of pregnancy, the necessary nutrients get into the baby. Defects in the structure of the placenta or the supplying blood vessels lead to the development of venous outflow disorders in the fetus. After birth, this condition is manifested by the development of intracranial hypertension.
- Pathology arising during childbirth. Incorrectly chosen tactics of operational benefits or unexpected complications can lead to a traumatic brain injury. Often these effects also lead to damage and micro-ruptures of the meninges. With damage to the cerebral ventricles or head veins, the symptoms of intracranial hypertension in a baby increase several times.
- Intrauterine infection. The most dangerous 1 and 3 trimester of pregnancy. Viruses and bacteria that penetrate into the future mother's body at this time, very easily pass through the hemato-placental barrier.When they enter the child’s body through the bloodstream, they can cause damage to the brain, which in some cases contributes to the development of intracranial hypertension in a baby after birth.
- Traumatic injuries. When falling and hitting the head, the child often has various disorders of the meninges, as well as injuries of the anatomically close cervical vertebrae. Such traumatic defects significantly violate the outflow of liquor fluid from the brain to the spinal cord. Ultimately, this contributes to the development of intracranial hypertension in the baby.
- Neoplasm. There are no more than 1-2% of cases. Actively growing tumors in the brain significantly compress the cerebral ventricles. This leads to a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and the development of hypertensive syndrome.
- Hemorrhage in the brain. In newborn babies, they often occur with massive traumatic brain damage. In some cases, may be congenital, resulting from increased fragility of supply vessels due to hemorrhagic vasculitis.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain. Infectious meningitis leads to impaired venous outflow, which contributes to the development of intracranial hypertension.
All the factors contributing to the development of intracranial hypertension cause severe cerebral hypoxia.
This condition is characterized by an insufficient supply of oxygen and a high content of carbon dioxide in the body. Prolonged oxygen deprivation contributes to the disruption of brain activity and leads to the appearance of adverse symptoms characteristic of this condition.
Symptoms
With mild intracranial hypertension, it is quite difficult to recognize this condition. Usually, the baby does not really care about anything. Symptoms can appear quite insignificantly or be erased. Moderate course and severe intracranial hypertension usually manifest themselves very clearly. They are accompanied by the emergence of adverse clinical signs, for the elimination of which requires the appointment of complex treatment.
Among the symptoms of increased brain pressure in newborns and infants:
- Resizable head. She becomes several centimeters more than the age norm. This symptom is quite clearly detected in newborn babies.
- Eyelid bulging. In severe cases, the eyeballs protrude slightly beyond the orbits. At the same time, the upper eyelids cannot close tightly. This symptom can be defined independently. During sleep, the child's iris is visible.
- Permanent regurgitation. The most characteristic symptom for babies of the first 6 months of life. Even when fed in small portions, the baby can often regurgitate food. This condition leads to some loss of appetite and impaired stool.
- Rejection of breastfeeding. This is due not only to a decrease in appetite, but also to the appearance of a bursting headache in a child. A newborn baby cannot yet tell mom where it hurts. He only manifests it in violation of his usual behavior.
- Headache. It can be of different intensity and intensity. With a pronounced pain syndrome, babies start crying, asking for more on their hands. Usually the pain increases in a horizontal position. This is due to the greater filling of the veins with blood and increased intracranial hypertension.
- Change in overall behavior. A child with intracranial hypertension becomes moody. He may have increased nervousness. Newborn babies practically refuse any active games. Kids do not react to the smiles turned to them.
- Sleep disturbance. The increase in intracranial hypertension is noted mainly in the evening and at night.This leads to the fact that it is very difficult for a child to fall asleep. During the night, he can often wake up, cry and ask for his hands. In the afternoon, the child’s sleep is usually not disturbed.
- Swelling of the veins. In newborn babies, this symptom can be checked at home. Head veins become very inflated, well visualized. In some cases, you can even see their distinct pulsation.
- Lag in mental and physical development. The prolonged course of intracranial hypertension leads to disruption of brain activity. During regular examinations, the pediatrician will be able to identify these disorders, which will be clear markers of the possible development of increased intracranial pressure in the child.
- Blurred vision. Often this symptom can be detected only with long and fairly high brain pressure. Reduced vision and double vision are detected in babies by the year.
- Hand shake or finger tremor.
How to recognize?
Increased intracranial pressure can not always be suspected at home. Mild forms of hypertension are not accompanied by the appearance of bright symptoms.
Hypertensive syndrome is usually detected on examination by pediatricians. They may also conduct additional tests that will reveal the hidden signs of intracranial hypertension.
To establish this condition requires consultation neurologist, oculist. If traumatic brain damage has become the cause of hypertensive syndrome, then a neurosurgeon will also need to be examined. After examining specialists, additional analyzes and surveys are required.
To establish intracranial hypertension use:
- General blood analysis. Peripheral leukocytosis indicates the presence of various infections in the children's body. An increase in stab neutrophils suggests a possible infection by bacteria.
- Biochemical study of liquor. It is prescribed for traumatic injuries of the meninges, as well as for various neuroinfections. The ratio of protein and specific density is used to estimate the index. Also in the cerebrospinal fluid can detect possible pathogens and identify their sensitivity to antibiotics. The method is invasive and requires spinal puncture. Appointed only by a pediatric neurologist or neurosurgeon.
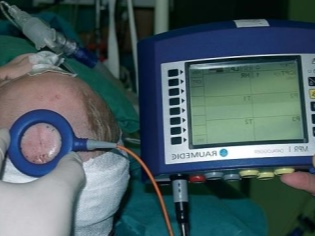
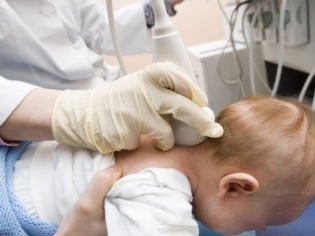
- Ultrasound of brain structures. Helps to establish anatomical defects in the brain and spinal cord. With the help of ultrasound, doctors measure intracranial pressure. In combination with neurosonography gives a fairly complete description of the existing pathology in the brain.
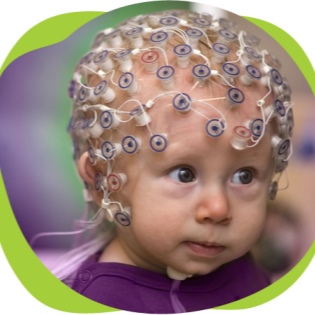
- Electroencephalography. This method is used as an auxiliary. It helps to establish cerebral disorders.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. High-precision descriptions of all brain structures are given. Using these methods, even the smallest traumatic injuries can be detected. These studies are safe and cause no pain in the child.
Effects
A prolonged increase in intracranial pressure is a condition that is very dangerous for a growing baby. Persistent hypertensive syndrome is accompanied by a strong hypoxia. It leads to disruption of the work of vital organs. With such a long state, various pathologies appear in the body. These include mental disorder, development of epileptic syndrome, lag in physical and mental development, visual impairment.
Treatment
It is possible to cure intracranial hypertension only after eliminating the causes of the underlying disease that caused this condition. Dr. Komarovsky believes that if they have not been eliminated, the symptoms of intracranial hypertension can recur in the baby again and again. The treatment regimen is built up by the attending physician after the full range of necessary examinations.Typically, the course of therapy is calculated for several months.
For the treatment of intracranial hypertension are used:
- Diuretic. These drugs contribute to the active removal of urine, and, consequently, a decrease in the total volume of fluid in the body. According to parents, such tools significantly improve the well-being of the child. Diacarbum, furosemide, lingonberry leaf, decoction of parsley, glycerin have a diuretic effect. Apply drugs should be based on the age of the child.
- Nootropics and medications that improve brain activity. These include Actovegin, Pantogam and other means. Prescribe medications for exchange. With regular use, they help to normalize cerebral activity and significantly improve the well-being of the baby.
- Relaxing massage. Helps to improve venous outflow, remove an increased tone, and also has a restorative effect. Therapeutic massage is used in babies 2-3 times a year for 10-14 procedures.
- Healing water procedures. Specially selected treatment programs adapted for newborns have a positive effect on the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the children's body. With regular water procedures, the child’s immunity and defenses to various infections are also strengthened.
- Antibacterial and antiviral agents. They are prescribed for the detection of infections. Drugs are usually prescribed for 7-10 days. Monitoring the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment is assessed by improving overall well-being and by changes in the overall blood count.
- Antiemetics. Assigned as an auxiliary treatment. It is used to eliminate vomiting with severe intracranial hypertension.
- Multivitamin complexes. These funds must necessarily contain a sufficient amount of vitamins of group B. These biologically active substances have a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
- Sedatives. Appointed with increased irritability and nervousness in a child. As a sedative, you can use herbs that have a sedative effect. These include: motherwort, Valerian, lemon balm. For newborns, warm baths with lavender are also suitable.
- Full nutrition. For babies it is very important to get breast milk. This natural product is very well absorbed and provides the children's body with all the necessary nutrients. Together with the mother's milk, the baby gets all the vitamins that are needed for the full operation of his nervous system.
- Ensuring proper day regimen. A kid suffering from intracranial hypertension should regularly walk outside. Walking with a child in the fresh air has a positive effect on the circulation of spinal activity.
- Surgery. It is used for traumatic brain damage, which provoke the development of hypertensive syndrome. The restoration of the integrity of bone structures and the elimination of intracranial hematomas are performed by a neurosurgeon doctor.
Prevention
In order to intracranial child pressure remained within the age norm, the following recommendations should be used:
- Organize your baby the right day regimen. Infants must rest during the day and fully sleep at night.
- Regularly walk with your child in the fresh air. The intake of large amounts of oxygen is very helpful in eliminating hypoxia.
- Favorable atmosphere in the house. Positive emotions are very important for babies of the first year of life. For normal functioning of the nervous system and full mental activity, the child must feel completely safe.
- Keep breastfeeding for as long as possible.
Mother's milk is a vital and fully adapted food for any baby.It contains all the vital nutrients and vitamins the child needs.
- Pay attention to any changes in the child's behavior. If the baby becomes more sluggish and capricious, and also begins to refuse the breast - be sure to show the child to the pediatrician.
More information about intracranial pressure in infants can be viewed in the next video.