Iron deficiency anemia in children
Reduced hemoglobin is quite common in young children. Almost every second child with anemia suffers from iron deficiency.
What it is?
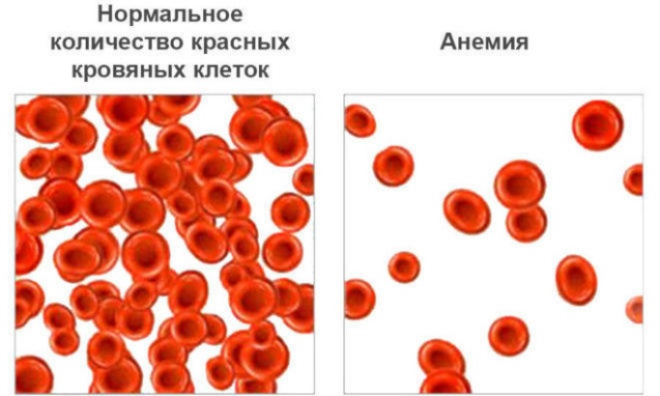
A pathological condition in which the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is reduced is called anemia. If the cause of the anemic condition was a decrease in iron intake, then such anemia is called iron deficiency.
The content of this trace element in the children's body in the first days after birth is 400 mg. If the baby was born prematurely, then the amount of iron is reduced by about four times.
Regular replenishment of this substance occurs during breastfeeding. Breast milk contains all the necessary nutritional components, as well as micro and macro elements. With full feeding and timely introduction of supplements, the amount of iron in the body is enough to carry out all vital functions.
Ferrum is a part of hemoglobin. Sufficient filling of red blood cells with iron leads to the fulfillment of the transport function. Hemoglobin allows you to carry oxygen to every cell of the body. To compensate for iron, babies need 1-2 grams.
The absorption of trace elements occurs in the small intestine. After that, most of the iron remains in the red blood cells. There is about 80% of the total ferrum. About 20% of iron remains in macrophages and liver cells. This reserve is called reserve, it is needed only in emergency situations. They usually occur with severe injuries and damage, accompanied by severe blood loss.
The reasons
The development of iron deficiency can lead to:
- Insufficient intake with food. Vegetable vegetarian food with the absence of animal proteins often leads to the development of anemic conditions. Meat products and poultry contain heme iron. It is more easily absorbed and well absorbed by the child's body.
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system. Pathology of the stomach and intestines contribute to the violation of iron absorption.
- Multiple pregnancy. Twins or twins - this is a higher risk of developing iron deficiency. If the expectant mother, who bears several babies during pregnancy, consumes an insufficient amount of iron-rich foods, then babies after birth often develop an anemic condition.
- Prematurity It leads to an underdevelopment of the blood-forming organs, which cannot perform their functions in the formation of erythrocytes in sufficient quantity for the organism.
- Pathology arising during pregnancy. Fetal hypoxia, placental insufficiency and violations of the structure of the placenta can lead to the development of anemic condition in the unborn child.
- Inadequate nutrition mom during pregnancy. If the expectant mother eats few foods that contain enough iron, then she may develop an iron deficiency. This leads to the development of anemia in the child.
- Late introduction of lure. The lack of puree made from beef or poultry in the diet can contribute to the development of an anemic condition.
- Pronounced growth during puberty. As a result of hormonal imbalance in adolescents, anemic syndrome is often observed. This disorder is transient in nature and disappears after the end of puberty.
- Excessively strong menstruation in adolescent girls. Long and too heavy discharge on critical days leads to severe blood loss.
- Functional disorders of the intestine. Persistent irritable bowel syndrome and dysbacteriosis contribute to the disruption of iron absorption from incoming food.
Classification
All iron deficiency states are divided into:
- Lungs. Diagnosed at hemoglobin levels from 90 to 110 g / liter. They are characterized by the appearance of small clinical symptoms or may remain unidentified for a long time.
- Medium heavy. The hemoglobin level ranges from 70 to 90 g / liter.
- Heavy. Occur with a decrease in hemoglobin below 70 g / liter. Require immediate treatment.
- Extremely heavy. Occur when hemoglobin decreases below 50 g / liter. Treatment may require blood transfusions or red blood cells.
For premature babies, a classification of iron deficiency states is applied by the time of appearance of anemic manifestations.
All iron deficiencies can be:
- Early. Arise in babies immediately after birth. Refusal of breastfeeding or the use of improperly selected adapted mixtures, hypoplasia of the blood-forming organs lead to the appearance of anemic symptoms.
- Late. They are found in babies 3-4 months after birth. Associated with the depletion of iron reserves and excessive destruction of hemoglobin.
Symptoms
In many cases, it is difficult to determine the signs of iron deficiency anemia. If iron deficiency is expressed slightly, then the symptoms of the disease are not very pronounced. Only in weakened babies or with long-term development of an anemic condition can the presence of iron deficiency anemia be suspected.
With anemia, the following symptoms occur:
- Pallor of the skin. Against the background of pale skin, the lips become blue. The skin becomes thinned, the veins are clearly visible.
- Fatigue and severe weakness. The symptom is well manifested in schoolchildren and adolescents. Children study worse at school, memorize learning materials poorly, and cannot concentrate well on the subject.
- Increased dryness of the skin. The use of special moisturizers does not improve. The skin becomes very dry and easily injured.
- The appearance of small wrinkles around the lips.
- Decreased blood pressure on the background of increasing pulse.
- Behavior change. Kids become more capricious, quickly tired. Infants may refuse breastfeeding.
- Chair disturbances. Constipation occurs most frequently. Diarrhea is much less common, usually with the development of intestinal dysbiosis.
- Frequent tooth decay. In some cases - bleeding gums.
- Increased brittle nails and excessive hair loss.
- Violation of taste preferences. Addiction to overly spicy foods may indicate a decrease in iron in the body.
- Lag in physical development. Insufficient weight gain or deviations from normal growth rates may indicate the presence of anemic syndrome.
- Exposure to frequent colds and infectious diseases. Prolonged oxygen starvation leads to a decrease in immunity.
Diagnostics
To establish iron deficiency can already in the early stages. A routine blood test can detect a decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin. Iron deficiency anemia is also accompanied by a reduced color index. Such states are called hypochromic.
In the prelativnom period of the disease, when there are still no changes in the general analysis of the blood, it is possible to detect iron deficiency only in the tissues. In the following stages of the disease, a decrease in the serum iron concentration is already observed. In the final stage of the disease, low levels of hemoglobin and red blood cells are recorded.
In some cases, additional consultations with a gastroenterologist, hematologist, nephrologist are required. A teenage girl should definitely show a gynecologist. To establish iron loss requires a primary diagnosis, which led to the development of an anemic condition.
To determine diseases and anatomical defects, doctors sometimes prescribe an ultrasound examination of the liver and spleen. This examination allows you to identify various pathologies of organs at the earliest stages.
Complications
Long-term oxygen deprivation, which occurs when iron deficiency in the body, leads to the development of adverse effects. The most dangerous such conditions for the brain and heart.
With a long course of the disease, myocarditis may develop. This condition is dangerous by the development of heart rhythm disorders, as well as a strong decrease in blood pressure. Arrhythmias and severe tachycardia cause marked discomfort for babies.
Treatment
According to the clinical guidelines that regulate the algorithm for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, disease therapy should be carried out at the first detection of a decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells.
For the treatment of anemia caused by iron deficiency, use:
- Medical nutrition. This children's menu includes a large number of foods high in iron. Daily inclusion in the diet of meat, poultry and offal will help to normalize hemoglobin levels. Such a diet should be followed for a long time.
- Appointment of iron. Such drugs are prescribed for course treatment. Normalization of hemoglobin and erythrocytes occurs only after a few months. Most often, babies are prescribed pills and syrups. In the presence of chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines, iron-containing drugs are prescribed as injections.
- Normalization of the daily routine. A good sleep, active walks in the fresh air, as well as a decrease in stress at school, help to quickly restore hemoglobin to normal values.
- In critical conditions - blood transfusion or red blood cell mass.
- Surgery. Conducted in cases where the pathological destruction of red blood cells. Removal of the spleen or bone marrow transplantation helps to restore hemoglobin levels and contributes to a marked improvement in well-being.
Prevention
To restore the normal level of iron in the body requires mandatory monitoring of sufficient intake of foods rich in this microcell. Timely treatment and prevention of exacerbations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract help prevent the development of an iron deficiency state in the future.
All babies who were born earlier or who have a low birth weight should get enough iron. To do this, Mom should be breastfed as long as possible. If for some reason lactation stops, you need to find the right adapted mixture with a high content of iron and vitamins.
How to determine the level of hemoglobin, and what to do if it has become low, see the next video.