Staphylococcus aureus in newborns and infants
Infections in babies of the first months are quite difficult. Bacterial pathologies top the list of infectious diseases that occur in pediatric practice. The development of a huge number of dangerous diseases in newborns is caused by infection with Staphylococcus aureus.
Causes
Scientists have learned about these microbes many years ago. They were discovered at the end of the XIX century. These microorganisms got their name not by chance. When viewed through a microscope they resemble special clusters, which in Greek means "staphylos". The color of the colonies of these microbes is usually yellow or has a faint orange tint.
These microorganisms are quite stable in the environment. They are able to maintain their livelihoods even in the most extreme conditions.
Microbes can not die, even while in a solution of hydrogen peroxide. This chemical product can cause various rashes on the skin of a person, and does not pose any danger to staphylococci.
Many disinfectants and even certain groups of antibiotics cannot have a destructive effect on these microorganisms.
This feature is caused by a special cellular structure. Outside, the microbe is covered with a powerful capsule, which protects it from various environmental influences. It should be noted that even the inability to form spores protects staphylococcus from death in adverse environmental conditions.
These microbes have a whole arsenal of various toxic substances. One of the most dangerous are special bacterial components called hemolysins. They can have a devastating effect on many blood cells, including red blood cells and white blood cells. This ability also influences the development of adverse symptoms in a sick child.
Bacterial toxins, which secrete microbes in the course of their life, have a pronounced inflammatory effect. They activate the immune response, forcing the immune system to throw out a huge amount of a wide variety of biologically active substances.
For these microorganisms, there is not a single internal organ into which they could not fall. The spread of infection proceeds rapidly. Reaches the internal organs of the bacteria in the systemic circulation.
The prevalence of staphylococcal infections in children is extremely high. The predominant method of infection in newborn babies and infants - contact. In this case, dangerous germs get on the skin of the child through dirty hands.
Every year, outbreaks of purulent pathologies occur in our country in newly born children who are still in maternity hospitals. In this case, the babies are infected through insufficiently well-developed tools or the hands of medical staff.
Family cases of the disease also occur. They are mainly due to violation of personal hygiene.
If the towels used daily for the hygienic toilet for the baby are not washed and not ironed in a timely manner, then they often get a different mix-infection. Staphylococcus is perfectly preserved on textiles.
Only washing in hot water with the use of detergents, and then ironing with a very hot iron on both sides has a detrimental effect on these microorganisms.
There is an airborne infection. In this case, microbes get on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract of a healthy child from the patient. Infected newborn baby can and from the carrier of the disease.
In the high-risk group, premature babies, as well as babies with congenital immunodeficiency states. Anomalies of the internal organs also increase the likelihood of infection by various types of infection.
Infants often have symptoms of the disease in the first months after birth. This situation usually occurs with intrauterine infection. Staphylococcus aureus - small enough microbes that are able to enter the body of the fetus through the bloodstream of the placenta from an infected mother.
Placental pathologies present during pregnancy increase several times the risk of infection by staphylococcal infection in very young patients.
The provoking factors in babies in the first months of life include severe hypothermia or overheating. These causes often contribute to a decrease in immunity.
If, for some reason, the baby is bottle-fed, the risk of developing an infectious disease in it increases several times. Babies receiving mother's milk are more protected from staph infection. This is due to the presence of a sufficient amount of protective antibodies, which they receive from the mother during breastfeeding.
It should be noted that not all babies can become ill with a staph infection even if it gets into the children's organism.
Children with strong immunity and not having chronic diseases of internal organs, can only have a carrier. Usually this form occurs in every third child infected with Staphylococcus aureus. In this case, the disease develops only with a pronounced decrease in immunity.
Symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus is a universal microbe in its ability to penetrate into various internal organs. His colonies can be found almost everywhere.
The incubation period for staph infections may be different. Some pathologies develop already after 3-6 hours from the moment microbes get into the children's organism. The incubation period for other clinical forms can be 2-5 days.
In premature babies, adverse symptoms can appear fairly quickly. This is still not sufficiently effective work of the immune system.
The duration of the preservation of adverse symptoms of the disease also varies and is largely due to the localization of the inflammatory process. As a rule, most staphylococcal infections pass in 7-14 days.
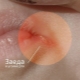
Quite frequent localization for these microbes are the skin. Getting on the skin, they cause a variety of manifestations. They are manifested by the appearance of multiple furunculosis formations, pimples, red spots, ulcers, purulent-necrotic changes on the skin.
The peculiarity of such skin rashes, as a rule, is in the presence of pus inside the cavity. Its quantity can be different and depends on the severity of the disease.
Purulent manifestations on the skin may be localized or common. Newborn babies have a rather unfavorable tendency for the spread of purulent rashes. This is due to the looseness of subcutaneous fat and good blood supply to the skin. Within a few days, the local process becomes generalized.
Pustules may appear on many different areas of the skin. Staphylococcus aureus are very fond of living in the sweat and sebaceous glands. This causes the fact that with the development of a staph infection, symptoms of furunculosis or hydradenitis are quite common. In this case, purulent formations appear in the growth of hair follicles.They look like pustules, rounded or elongated, with yellow or greenish pus inside.
For purulent formations rather unfavorable. In case of late diagnosis and absence of treatment, this contributes to the development of a number of dangerous complications in a sick child. In this case, a mandatory consultation of a pediatric or purulent surgeon is required.
Purulent rashes on the skin can burst, in the process of pus expires. In this case, ulcers usually remain in place of the former pustules, which heal over time, with the formation of small scars.
Staphylococcus aureus is a fairly frequent uninvited “guest” on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. He gets there mostly by airborne droplets. Quite often this happens during a normal conversation with a patient or carrier of infection.
If parents have Staphylococcus aureus in the nasal cavity, they can easily infect their newborn baby with it.
Getting on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, staphylococci cause the child a variety of adverse symptoms. The most common of them is resistant rhinitis, manifested by a strong cold.
Discharge from the nose is usually thick, abundant, yellow or greenish. Without treatment, staphylococcal rhinitis leads to the development of inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses, which are manifested in the baby by the appearance of sinusitis or frontitis.
Staphylococcal infection quickly moves to nearby organs. The presence of bacteria in the nasopharynx leads to the development of inflammation in the throat and throat. This contributes to the formation of bacterial pharyngitis in the baby, and then tracheitis. These pathologies occur in newborn babies quite hard. They are accompanied by the appearance of cough, strong intoxication syndrome, severe pain when swallowing.
The danger of these conditions is that they can lead to the development of dangerous complications - bacterial bronchitis or pneumonia.
Lesions of the gastrointestinal organs are also very common in this infectious pathology. Staphylococcus aureus through the systemic circulation falls into this anatomical zone.
Gastrointestinal forms of staphylococcal infections, according to statistics, have the shortest incubation period.
Infection can also occur as a result of the use of fermented milk products or ready-made mashed jars that kids eat as the first complementary foods.
Once in the intestine, pathogens lead to a pronounced disruption of the normal biocenosis of the intestinal flora. This contributes to the development of a child with strong dysbiosis.
This pathological condition is manifested in babies, as a rule, by various disorders of the chair. A sick child may develop diarrhea or persistent constipation. In some cases, it may be alternating.
Staphylococcal infection in the gastrointestinal tract the appearance of a sore child in the stomach is also quite often manifested.
The babies of the first months of life still cannot tell their parents about their pain. Suspect pain in the tummy of a baby can only be watching his behavior. If, after eating, the child begins to cry or more often asks for his hands, then this symptom should seriously alert the parents. In some cases, the sick baby tries to limit its active movements, as this contributes to increased pain.
Any staphylococcal infection, regardless of the initial location, leads to a pronounced deterioration of the baby's well-being.
The child becomes more pale, lethargic. In sick children, appetite is noticeably reduced. This is usually manifested by the fact that infants begin to refuse breastfeeding.
With this bacterial infection, body temperature rises rapidly. The severity of this increase may be different and depends largely on the severity of the infection.
Usually staphylococcal infection in newborns leads to an increase in temperature to 38-39.5 degrees. High numbers can persist in a baby for several days, and without prescribing treatment for much longer.
The presence of pronounced intoxication syndrome aggravates the situation. It is usually manifested by the appearance of severe dryness of the skin and visible mucous membranes in a baby, an increase in severe thirst, a decrease in skin turgor, as well as behavior changes. Kids start to act up, fall asleep badly. During sleep they may wake up many times and even cry.
Diagnostics
When the first adverse symptoms appear, the child should be immediately shown to the doctor. If the baby has a high temperature, then you should not go to the clinic yourself. In this case, it is better to call the doctor at home.
The doctor will examine the baby and be able to establish a preliminary diagnosis. Accurately say what caused the disease, the doctor during the clinical examination can not. This requires a range of different diagnostic methods to accurately identify the infectious agents. These laboratory tests allow physicians to distinguish the rate from pathology.
All babies with signs of bacterial infection are required to undergo general clinical tests. In the blood, leukocytes and ESR increase, as well as normal indicators in the leukocyte formula.
In some cases, Staphylococcus aureus can be detected in the urine. This is possible mainly with urinary tract infections. In order to establish a diagnosis in this case, it is necessary to conduct a bakpossev urine on special nutrient media.
Quite often, feces are analyzed to identify pathogens. This simple and absolutely painless for the child examination allows you to identify various microbes that become sources of infectious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract in sick children.
The presence of pathogenic bacteria in the feces may indicate carriage or infection of this infection.
The presence of Staphylococcus aureus may be in the analyzes, but not accompanied by the appearance of adverse symptoms.
Thus, the microbial titer 10 to 3 degrees usually does not manifest itself by any visible clinical signs. It only indicates that when exposed to factors leading to a decrease in immunity, the infant may develop this infectious pathology.
The content in the feces of microbes 10 to 4 degrees is accompanied by the appearance of symptoms, expressed slightly. Such test results are found in babies with localized and limited skin purulent rashes or a mild course of infectious staphylococcal infection of internal organs.
Usually, doctors do not prescribe a specific treatment, but they only manage by prescribing fortifying and mild immunostimulating drugs. In some cases, Staphylococcus aureus appears in the feces along with Klebsiella.
The content of microorganisms 10 to 5 degrees is already accompanied by the development of adverse symptoms in the child. The degree of their severity may be different. Quite often, in this case, diarrhea occurs with the release of frothy fetid fecal.
The excreta are usually greenish. The child usually feels extremely bad. His weakness increases, his appetite decreases. In this case, pediatricians have already prescribed specific anti-bacterial treatment.
In some cases, instrumental studies are required. They are appointed to clarify the degree of functional impairments that have occurred, and also help in timely detection of complications that have developed during the course of the disease.
As such studies, as a rule, radiography of the lungs and chest, as well as an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and kidneys, are appointed.
Complications
Staphylococcus can be very dangerous. The peculiarity of the course of this infection is that it can quite easily lead to the development of multiple complications. They significantly worsen the general well-being of the child and can form long-term adverse effects in later life.
A common complication is the formation of purulent abscesses in the internal organs.
Primary localization is lung tissue. Late diagnosis of pneumonia and late treatment helps to limit the inflammatory process and lead to the development of a local abscess.
This pathology occurs in children rather hard. Treatment of this pathological condition is carried out only in conditions of the pediatric surgical department of the hospital.
Bacterial meningitis - also quite dangerous complication. In the high-risk group there are babies born much earlier than the established time or children with various anomalies of the nervous system after birth.
Staphylococcal meningitis - a very serious disease, accompanied by the development of multiple adverse symptoms. These include: an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees, the appearance of severe headache, the possible appearance of epileptic seizures and seizures.
The treatment of this condition requires the mandatory appointment of a massive course of antibiotic therapy and the introduction of special physiological and colloidal solutions that have anti-inflammatory and regenerating effects.
Treatment
Therapy of various forms of staphylococcal infections is complex. It may include the appointment of various drugs. In most cases, treatment of babies with signs of a staph infection is carried out in a hospital. Late hospitalization or refusal of it can lead to a pronounced deterioration in the well-being of the baby.
Local local forms that occur on the skin are well treated by using aniline dyes that are simple and familiar to many parents. Surprisingly, these aggressive microbes are very sensitive to the effects of ordinary brilliant green.
Treatment of the affected pustules with a solution of brilliant green, iodine or furatsilina have a positive therapeutic effect. In some cases, doctors prescribe Vishnevsky ointment, which should be applied to purulent skin.
The main goal of treatment is to eliminate pathogenic microbes from the baby’s newborn baby’s body.
This can be done only by prescribing a course of antibacterial drugs.
Such treatment is carried out in the hospital, as there it is possible to inject antibiotics mainly parenterally. This introduction allows you to somewhat reduce the toxic effect of these drugs on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines.
The choice of an antibiotic remains for the attending physician. Staphylococci have a rather high sensitivity to various groups of penicillins and cephalosporins of the latest generations. The course of treatment may be different: from 5 to 10-14 days.
Antibacterial agents from the reserve group, as a rule, do not apply. Such use contributes to the development of high antibiotic resistance.
The complex of treatment necessarily includes anti-inflammatory drugs. They help to eliminate inflammation and lead to an improvement in the well-being of the baby. With a pronounced increase in body temperature above 38 degrees, antipyretic drugs are used. They help reduce febrile in the first few days after their appointment.
To improve the immune system, immunostimulating drugs are prescribed for sick children.
Restorative therapy also plays an important role in the treatment of infectioncaused by Staphylococcus aureus in newborn babies.
In stationary conditions, various physiological solutions are introduced for this purpose, which help to improve microcirculation and blood supply in all internal organs. These funds also have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
For an easier course of the disease, doctors may resort to treating the infection with specific bacteriophages. The need for such therapy is determined only by the attending physician and depends on many different factors.
The decision on the choice of bacteriophages or antibiotics must be made taking into account the localization of the inflammatory process, as well as the severity of the disease.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene is a very important component of the preventive direction.
To reduce the risk of contact-domestic method of infection, you should definitely use your own towels for the baby. These textiles need to be washed and ironed.
Even accidental use of baby towels can lead to infection of the crumbs.
You should also avoid any contact with feverish or febrile family members. If one of the parents is sick, then he should wear a gauze bandage or mask, which should be changed every 3-4 hours.
During an illness, all possible contact with a newborn baby should be limited. If there are pustules in the nipple area of nursing mothers, doctors recommend stopping breastfeeding and putting the baby on feeding with artificial adapted mixtures.
You can also read another article that thinks Dr. Komarovsky about Staphylococcus aureus.
For information on how staphylococcus manifests in children, see the next transfer of Dr. Komarovsky’s school.