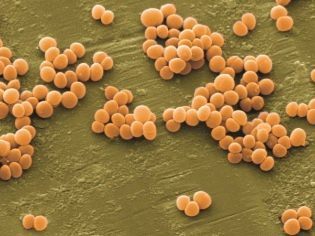
Staphylococcus aureus in the nose and throat of a child
Protracted rhinitis and sore throat are often caused by staphylococcal flora. The most dangerous forms of the disease are usually provoked by Staphylococcus aureus. This article will tell parents about what features such infectious diseases have in babies.
Symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus is very pathogenic microorganisms. Once in the children's body, they can cause multiple lesions. The severity of adverse symptoms may be different and depends on many factors. Staph infection in newborn babies and infants is quite difficult.
One of the favorite localization for Staphylococcus aureus is the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. Infection in this case occurs by airborne droplets.
You can become infected from any sick person or carrier of infection that has microorganisms in the nasal cavity and oropharynx. Even a simple conversation with him can lead to infection. Staphylococcus aureus have a whole arsenal of various toxic substances that lead to severe inflammation. Severe inflammatory process leads to the appearance of adverse symptoms in a sick child. These symptoms occur, taking into account the preferential localization of the inflammatory process.
Severe course of the disease is usually accompanied by severe intoxication syndrome. It is manifested by fever. With severe disease, it rises to 38-39 degrees. The sick child does not sleep well, often wakes up at night. Babies have reduced appetite. They become more capricious and lethargic.
In the nose
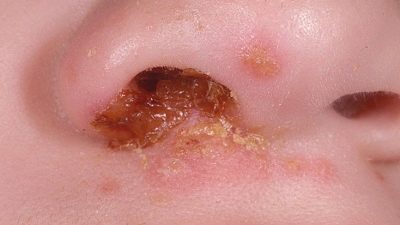
Staphylococci living in the nasal passages cause many adverse symptoms. A characteristic symptom of staphylococcal rhinitis is the appearance of a cold. Nasal discharge with yellow or green light. They are usually thick, poorly separated. In some cases, runny nose becomes protracted. Staphylococcal nasopharyngitis is an infectious pathology in which the mucous membranes in the nasopharynx become inflamed. This clinical variant of the infection can occur in babies at any age.
The incidence increases in the cold season. Mass outbreaks of the disease occur mainly in crowded groups. Toddlers attending preschool educational institutions have a higher risk of infection.
The development of staphylococcal rhinitis is caused by the influence of some provoking reasons:
- Weakening of local immunity. Quite often occurs after marked hypothermia.
- Injuries to the nose. Wounds of the mucous membrane contribute to easier penetration of any infection. Operations on the nasopharynx for the removal of adenoids or polyps also contribute to the active proliferation of microbes.
- Abuse drops for the treatment of rhinitis. Overly long-term use of these drugs contributes to the development of atrophic changes in the mucous membranes of the nasal passages. This leads to the fact that pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus easily falls into the nasal cavity.
In the throat
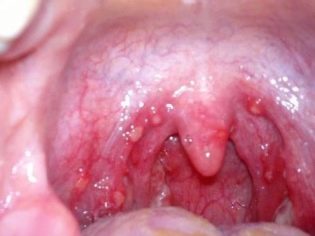
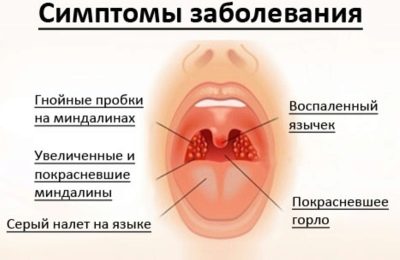
Airborne Staphylococcus aureus easily penetrates the oropharynx and pharynx. This contributes to the development of a strong inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract. Quite frequent manifestation of staph infection is bacterial pharyngitis.This pathology is manifested by the appearance of purulent plaque that covers the outside of the tonsil. The palatine arches with staphylococcal pharyngitis increase and hang heavily above the entrance to the mouth.
The neck of the sick baby becomes bright red. The tongue is coated with gray or yellowish bloom. During illness, the child has a strong pain in throatdecreased appetite. Infant babies may refuse breastfeeding or do not attach well to the breast.
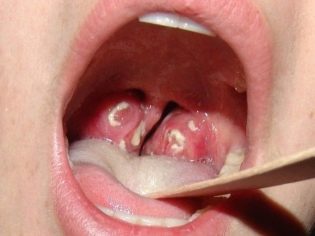
Acute Staphylococcal tonsillitis accompanied by the development of many adverse symptoms. Zev in this state becomes bright red, and in some cases becomes even glowing.
Palatine tonsils increase in size and loosen. Outside, they are covered with purulent bloom, which in some cases can solidify and form dense crusts. When you try to remove plaque yourself with a teaspoon or spatula, bleeding appears. Staphylococcal angina It is usually quite severe. In weakened children and children with chronic diseases of internal organs, acute tonsillitis can lead to the development of multiple complications and adverse long-term consequences.
Quite frequent manifestation - the development of bronchopneumonia.
It occurs in more than 10% of cases of acute staphylococcal tonsillitis.
Diagnostics
With the appearance of the first adverse symptoms in the nose or pharynx, it is necessary to show the baby to the attending doctor. A pediatrician or a children's otolaryngologist will be able to examine a sick child. After conducting a clinical examination, the doctor establishes a preliminary diagnosis. To determine the causative agents of infection requires additional laboratory tests. A complete blood count is performed for all babies with signs of bacterial diseases. Staphylococcal pathologies of the upper respiratory tract are accompanied by the appearance of leukocytosis - an increase in the number of leukocytes.
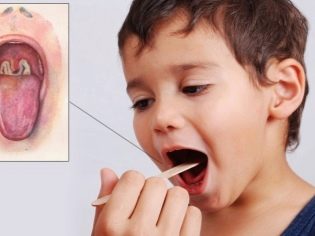
Severe inflammation accelerates ESR. There are also changes in leukocyte formula. A blood test can detect any abnormalities in the earliest stages. Detect pathogens can also be in the pathological secret. Staphylococcal nasopharyngitis or tonsillitis can be determined using bacteriological examination.
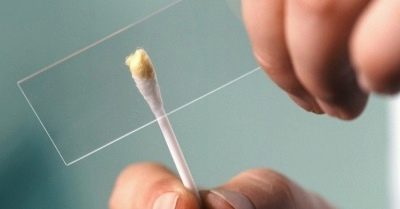
Biological material for carrying out such examinations is discharge from the nasal cavity or mucus from the back wall of the pharynx. Studies are conducted in a special laboratory. The effectiveness and specificity of these tests are quite high. A marker study to identify dangerous microbes is a smear test. After applying the biological material on a glass slide - it is placed in a thermostat.
The result of bacteriological examination is usually ready in a week. For research, in some cases, sputum is taken, which the baby coughs during the acute period of the disease. To establish the complications of staphylococcal acute tonsillitis that have arisen, an additional instrumental study is carried out - lung radiography. This method allows to identify pneumonia in the very early stages of the disease.
Complications
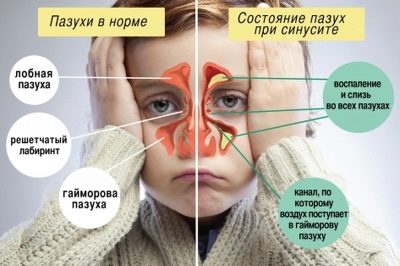
Protracted staphylococcal rhinitis often leads to the development of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses. Especially often this disease develops with untimely prescribed treatment. Golden staphylococci, falling into the sinuses, contribute to the development of strong inflammation in them. Ultimately, this leads to the development of acute bacterial sinusitis or frontal sinusitis. These pathologies are accompanied by the development of a strong debilitating rhinitis. The discharge from the nose in this condition is rather thick, yellow or brown in color.
A baby suffering from sinusitis feels constantly stuffy. Nasal breathing is severely disturbed. A child has a headache that is arching and permanent. Staphylococcal pneumonia is also a fairly common complication that occurs as a result of the unfavorable course of acute tonsillitis, which turns into bacterial bronchitis. Accompanied by this pathology pronounced intoxication syndrome. Younger babies may develop symptoms of respiratory failure. Therapy of staphylococcal pneumonia is carried out only in a hospital.
Treatment
Therapy of staphylococcal infections includes the appointment of a whole complex of different medicines. The main goal is to eliminate bacterial foci and normalize the beneficial microflora that lives in the upper respiratory tract. For this, various antibiotics are prescribed. The recalls of the parents of babies who took these drugs indicate that these drugs have a pronounced positive effect. Cons with the use of antibiotics - the development of side effects, which in some cases can be very unpleasant.
Staphylococcus aureus is particularly sensitive to penicillin and cephalosporin antibacterial drugs. Dosage, frequency and duration of use are determined individually, taking into account the age and weight of the baby, as well as the severity of the course of infectious diseases in a particular child. The duration of the treatment regimen may be different. On average, therapy for staphylococcal nasopharyngitis is 5-10 days. Acute tonsillitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus is treated in 1.5-2 weeks. In some cases, an alternative method of treatment is applied using specific bacteriophages. These drugs have a narrow action and cause the death of pathogenic microbes.
Treatment with bacteriophages has fewer side effects than with antibiotics. This therapy is quite successfully used to treat staphylococcal infections in the youngest patients. Various solutions of sea salt are used to improve nasal breathing. They are used for irrigation of the nasal passages. These remedies help flush the nose in babies and help soften too thick secretions. It is possible to use these solutions 3-4 times a day.
In some cases, vasoconstrictor nasal drops are used, which are prescribed by a doctor according to the indications with regard to the age of the baby.
The nasal cavity can also be treated with special medicines. For the treatment of inflamed nasal passages, Chlorophyllipt is well suited. This remedy reduces inflammation and has a detrimental effect on pathogenic staphylococci. For washing the patient's neck fit a variety of decoctions of medicinal herbs. These affordable herbal remedies will always be found in every home medicine chest. To rinse the throat, you can use a decoction of chamomile, sage, calendula. Rinse the neck should be 3-4 times a day one hour after eating. Only warm solutions can be used for rinsing.
Many bee products also have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. For carrying out rinsing of a pharynx usual propolis will approach. Conduct such rinses should be 2-3 times a day for 10-14 days. This treatment can be applied only to babies who do not have allergic reactions to bee products. For rinsing the throat is also suitable and ordinary honey. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretic agents should be used.
Medicines based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are quite successfully prescribed for children. These funds are taken in the age dosage.
Doctors do not recommend taking acetylsalicylic acid during an acute period of an infectious disease in infants, as this may lead to the development of dangerous side effects of this drug. During the height of the disease, the baby should be at home. If the disease in a child proceeds with severe fever, then the crumb must always comply with bed rest. Such a forced and simple measure will help to significantly reduce the risk of the development of dangerous complications of an infectious disease. During massive outbreaks of staph infections in educational institutions, quarantine is introduced. All babies who have been in contact with sick children are given prophylactic treatment.
To restore the lost strength during the illness, the baby is prescribed fortifying therapy. For this, multivitamin preparations are prescribed. The vitamins and microelements contained in them help restore immunity and improve the child's well-being. They should be applied for at least 30 days. Children with pronounced impairment of immunity are assigned immunomodulating therapy.
Whether the detected staphylococcus in the nose is dangerous, see the following video: