What to do if a child has insomnia?
Insomnia in children is common, but true insomnia rarely happens. The task of the parents is to understand in time when the situation can be corrected on its own, and when it is time to seek treatment by a doctor, because normal sleep is necessary for children for the harmonious development, growth, mental health.
About the problem
Difficulties in falling asleep are a widespread problem: from time to time both adults and children face it. But usually such cases have quite understandable reasons, obvious to parents - the child was overexcited, tired, slept too much during the day, was ill, was not well, etc. Such cases are not considered pathology, difficulties with falling asleep are harmless. As soon as the problem is resolved, sleep is restored, and nothing needs to be done about it.
There is another insomnia for which special terms are invented in medicine - insomnia or dissomnia. To understand why a child is not sleeping normally, one should clearly know what stages the dream consists of in general:
- superficial sleep - the process of immersion in sleep;
- transition to the deep phase - the movement of the oculomotor muscles stops, the electrical impulses of the brain decrease, the heartbeat slows down;
- deep dream - the recovery phase, in which we see dreams, delta waves gradually begin to predominate, and if a person wakes up at this stage, he cannot understand for a long time where he is and who he is;
- fast phase - the movement of the eye muscles is resumed, the body is preparing for awakening, the brain becomes active.
Childhood (as well as adult) insomnia is always associated with certain disorders occurring in the recovery or fast phase.
The state of insomnia is a sleep disorder associated either with its short duration or with a violation of its quality, which is observed in a child for a long time. Disorder can occur in children of any age, even in infants and newborns, but less often in babies.
How does it manifest itself?
Calling any insomnia violation is wrong. According to medical recommendations, the painful state of sleep disturbance can only be talked about when the child has significant difficulties with falling asleep for a long time, he cannot sleep well all night, often wakes up and cannot fall asleep again.
To make the appropriate diagnosis to the baby, the doctor takes into account the repetition of such manifestations with a frequency of at least three times a week for one month.
All symptoms of insomnia are divided into several groups according to the time of their occurrence.
Presumnic
It is difficult for a child to fall asleep (the process takes more than 30 minutes), while the crumb can look tired, he feels like to go to bed, but as soon as he is in bed at the appointed hour, he cannot fall asleep.
At this stage, the baby can search for a comfortable posture for a long time, “mess around”, may complain that it itches something, itches (psychosomatic manifestations or “mind games”).
Intrasomnic
Sleep is of poor quality, but deep sleep does not occur or it is insufficient in time. Anyone, even a quiet extraneous sound, can instantly interrupt the sleep of the child, after which it is again very difficult for him to fall asleep. Often, there are nightmares, the desire to empty the bladder, rapid heartbeat. This also includes "restless legs syndrome" - with him, the baby constantly goes over with his feet in a dream.
Postsomnic - symptoms that are essentially a consequence of insomnia. They appear after the child wakes up. This is lethargy, lack of tone, vigor, concentration and attentiveness. The child is drowsy, inhibited, he has sudden mood swings, headaches.
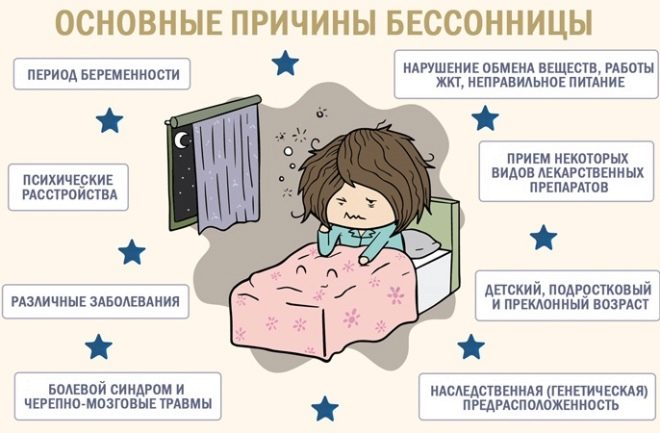
The reasons
If the symptoms of sleep disturbance appeared almost immediately after birth, it is likely a congenital physiological predisposition due to the organization of the child’s nervous system.
In all other children and adolescents, acquired neurological disorders, diseases of the nervous system, and diseases of the internal organs can also be causes.
Insomnia often develops as a reaction of the nervous system to severe stressThis is especially true for children in the "critical" periods of development and formation of the nervous system - at 2-3 years old, at 6-8 years old and with the onset of puberty - in girls from 10 years old, in boys from 11-12 years old.
Insomnia is often seen as a symptom of neurosis, psychosis, depression, panic disorder. Insomnia can cause any acute and chronic respiratory ailments in which free breathing is difficult at night.
Children with lesions of the central nervous system, brain tumors, schizophrenia, and epilepsy suffer from prolonged insomnia in about 75% of cases.
If such diagnoses are not established in the baby’s medical record, then possible external causes of sleep disturbance should be considered. These include:
- life in a big city, noise at night from the street, the light of signs, that is, insufficient blackout;
- frequent jet lag (if a child travels with his parents a lot);
- taking some psychotropic drugs;
- drinking strong tea or coffee, as well as a large amount of chocolate before bedtime;
- stuffiness in the bedroom and uncomfortable bed;
- overeating before falling asleep;
- abundance of impressions shortly before sleep, too active and mobile games;
- lack of normal physical activity;
- violation of the regime, when the share of daytime sleep has more time than necessary.
Insomnia can begin in a perfectly healthy child, who has all the conditions for a normal sleep, if the psychological climate in the family is tense (quarrels, parents divorce, violence).
Kinds
Harmless, physiological insomnia, which sometimes happens to everyone, is called transient, that is, passing, temporary. And indeed, it can last no more than a few nights. Then the healthy body will take its toll, and the child will begin to sleep normally. In some cases, transient insomnia is delayed up to 2-3 weeks, and then it is called short-term.
Sleep disorders for more than a month are a chronic form that necessarily needs treatment. Caused by objective causes, insomnia is called physiological or situational, and chronic forms are permanent.
There are also three degrees of severity of the disorder:
- the first - mild, episodes of sleep disorders rare, non-systematic;
- the second - average, symptoms are moderate;
- the third - heavy, repeated every night, the child’s well-being is significantly impaired.
Idiopathic is called insomnia if it is not possible to establish its causes. By the way, in 80% of cases the true root cause cannot be found, since it can be hidden in the emotional and psychological field, and therefore the problem is often considered psychosomatic.
What to do?
If a child has situational insomnia, nothing needs to be done. It will be enough to clearly understand what kind of situation caused sleep disturbance, and to take all possible steps to reduce its impact on the child’s psyche. But in the case of short-term and chronic insomnia, parents cannot do without medical help. It is obvious to which doctors to apply to a neurologist and a pediatrician.
Specialists will collect a detailed history, analyze the child's health, ask parents to keep a so-called sleep diary, in which parents will have to indicate how much time it took to sleep the child, how much time he slept before waking up, if he could sleep after waking up if it happened in the middle of the night whether sleep was restless, nightmares dreamed. By the way, such a diary helps to understand, “owl” is a child or “lark”.
Interesting fact: “Owls” and “larks” are philistine terms. In medicine, both the one and the other (early ascent and late climb) are considered a violation of the circadian rhythm, that is, an owl and a morning person are one hundred percent pathology, if after awakening a person experiences postomnic disorders.
According to the results of keeping a diary, EEG, polysomnography, consultation of a somnologist can be prescribed.
Treatment
First of all, parents of a child suffering from insomnia are advised to attend to sleep hygiene. It means that:
- the baby must go to bed every evening at the same time;
- daytime sleep should be kept to a minimum (up to 1 hour for a preschooler) and excluded completely for children of school age;
- increased daily activity;
- airing the bedroom before bedtime;
- elimination of active games and watching TV before going to bed;
- the use of soothing massage and water treatments before bedtime.
If all this does not help normalize the sleep and the duration of a night's rest, physiotherapy is prescribed - for example, treatment with high intensity white light.
Medicines are generally prescribed for the chronic form, as well as for the acute if the above measures had no effect. Sleeping pills seem simple and logical way out - he drank and fell asleep. But everything is not so simple. Hypnotics are addictive, have a lot of side effects. Therefore, for children they try to prescribe herbal remedies, for example, motherwort, preparations based on peony, mint, oregano.
In severe cases, the child may be assigned antipsychotics, antidepressants. With a tendency to allergies can be assigned and antihistamine "Dimedrol" but in strict individual dosages.
Often, the problem can be solved without drugs, with the help of work with the child psychotherapist, psychologist, psychosomat. Can also help and folk remedies, for example, "Sleepy bag" filled with dried herbs (lavender, lemon peel, chamomile flowers). It is fixed in the headboard, so that the child inhaled the smell of herbs.
Many mothers claim to help a glass of warm milk before bedtime, a cup of chamomile tea.
About insomnia in children, see the following video.