Hirschsprung disease in children: from symptoms to treatment
Hirschsprung's disease in children - the disease is not so frequent, but very serious, and therefore the confusion of parents who hear such a diagnosis is quite understandable. The name of the disease in most moms and dads is not even on hearing, and therefore there are more questions than this for questions about this disease than answers.
What it is?
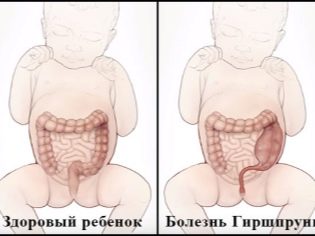
Hirschsprung disease got its name from the name of the pediatrician's doctor, Harald Hirschsprung, who first described the illness after the death of two of his little patients from severe chronic constipation. Also, this disease has other names - colon agangliosis or congenital megacolon.
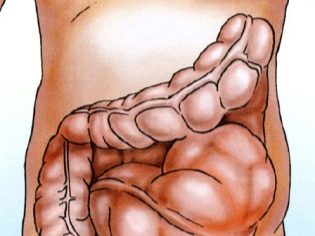
It should be noted that the disease is a congenital malformation of the colon, in which defecation is extremely difficult due to the fact that the innervation is impaired (neural connections or nervous structure) in one of the sections of the large intestine, usually the lower. As a result of the fact that the nervous activity in this department is impaired, a decrease in peristalsis develops, up to its complete absence, and in the intestinal sections located above the affected area, deposition of large amounts of feces.
According to the WHO, Girshprung disease in childhood occurs in one of 5,000 newborns. There are other data indicating that the disease occurs with a frequency of 1: 2000 newborns. Boys are more susceptible to congenital disease - there are four young men for each sick girl.
In 9 out of 10 children, according to statistics, congenital megacolon is detected at the age of 10 years. In almost every third case, an abnormal development of the colon is accompanied by some other malformations, and every tenth child with such an anomaly has Down syndrome.
Why it happens?
Defect is always innate, but the reasons that cause it are still the subject of study of physicians and scientists. Today, experts are inclined to believe that in the formation of an anomaly there is an influence of several factors at once, the main of which consider damage to several genes at once, which, in fact, are responsible for how correctly and in time the nervous structures of the colon walls will be formed. In genetics, everything is very difficult, and it can be difficult for parents to understand why a healthy baby was born to them, healthy. But try to explain.
Hereditary factor. Approximately one in five children with congenital megacolon experts detect marital genetic influence. At conception, a process of mutation is formed in the genes RET, GDNF, EDN3, ENDRB. At 7-12 weeks of gestation, when the fetus completes the formation of nerve cells in the walls of internal organs, the affected genes cannot ensure the transition of germ cell neuroblasts (from which neurons are formed) to the right place. In about 11–12% of cases, genetics detect aberrations (unexplained errors) in chromosomes. And for every fifth child with Hirschsprung's disease, the anomaly is closely related to some kind of hereditary syndrome.
Anomalies at the level of intrauterine development. They arise in children who at the time of conception had the above genes healthy, but the problem and error arose in the process of embryogenesis.The reason could be a viral infection, the flu transferred by the mother in the early gestational period, the effect on the pregnant woman's body during this period of high doses of radiation, the contact of the woman in the early stages with substances that can cause genetic mutations in the fetus. The distribution of germ cell neuroblasts was impaired.
Doctors have followed the statistics and confidently assert that the probability of Hirshprung disease in children increases if the pregnant woman suffers from various obstetric pathologies, gynecological diseases, as well as preeclampsia, diabetes, hypertension, heart failure or certain heart diseases.
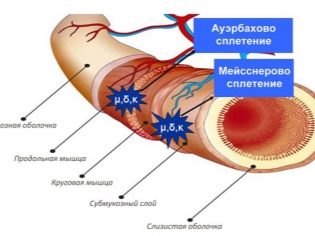
The period from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation is considered to be critical in terms of the probability of failure in the formation of nerve structures of the walls of the large intestine of the fetus. It was during this period that the so-called Meissner nerve plexuses were laid, which are found in healthy people in the layer of the colon under the mucous membrane. For the same period, the formation of nodes and plexuses of nerves called Auenbach plexus, located in the muscle layer of the intestine.
Since germinal neuroblasts do not arrive at the right place on time or in insufficient quantities, the nerve endings are formed there with errors — either their individual fragments or the undeveloped weak and irregular network. This area, deprived of normal nervous support, cannot cope with the main task of the large intestine - the removal of the contents out. Therefore, there are constant constipation, and then located above the intestinal sections begin to expand.
Classification and types of pathology
Doctors will speak about the type and type of the disease in a newborn, infant or older child, based on the anatomical and clinical features of the anomaly in a particular child.
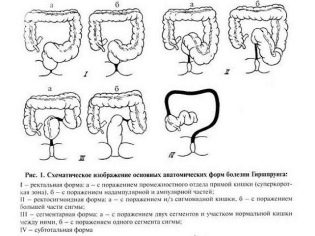
The main criterion is the length of the affected intestinal area.
The most common case is the rectosigmoid form. It is found in 65-75% of patients. In every fourth case, the rectal form of the disease occurs. Only in 3% of cases the subtotal form is detected, in 1.5% of cases the lesion is segmental. The total form, in which the entire large intestine is affected and deprived of nervous support, occurs in 0.5% of cases.
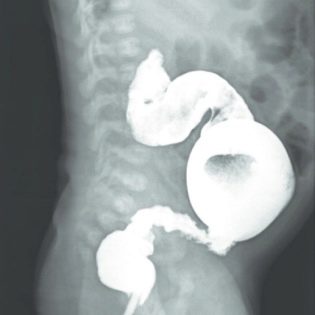
As already mentioned, the upper divisions expand due to the constant accumulation of fecal masses, and depending on the exact location of the pathological expansion, such designations of the expansion site as mega-rectum, megasigma, subothotal and total megacolon, etc., are added to the specific diagnosis.
The combination of symptoms and manifestations of developmental anomalies allows physicians to identify several types of disease.
- Typical children - occurs in 90-95% of cases. It develops quickly, is accompanied by very frequent constipation, when, without help from the outside, the child is practically not able to empty the intestines, and the first symptoms of intestinal obstruction quickly appear.
- Protracted children - first appears after infancy. This is usually due to the fact that a small section of the intestine is affected, and therefore the clinical picture develops slowly, prolonged.
- Hidden - for the first time, an agonizing constipation becomes a problem closer to the teenage period of child development. Intestinal obstruction rapidly increases.
Also isolated compensated, subcompensated and decompensated forms of the disease. If the body is able to partially compensate for the problem, for many years the child may empty himself, but gradually he will become prone to constipation, the duration of which can be from 3 days to a week. With subcompensated Hirschsprung disease, the child is able to empty the bowel, but only with the use of an enema or laxative. Without them - constipation.
In a state of decompensation, the child himself does not poke and does not even feel the urge to this natural cleansing process. Consolidation of feces in the intestine becomes stone-like, and laxatives and enemas do not help.
Symptoms and signs
It depends on how affected the large intestine is when it will be possible to determine the first symptoms of a pathology in a child. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the anomaly is determined after birth, but it is possible that a latent course with minor symptoms will make it possible to diagnose Hirschspring's disease only at school, adolescence or later.
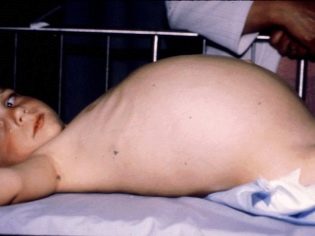
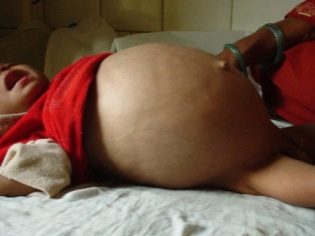
Manifested innervation of the colon chronic constipation. If the child has the urge to empty the intestines, but cannot do this, we are not talking about a congenital anomaly. With congenital megacolon the child does not usually feel the urge to empty the bowel. Almost half of the children with this diagnosis suffer from bloating and abdominal pain associated with the accumulation of feces and expansion of the upper intestine.
The long presence of the anomaly creates a visible asymmetry of the abdomen. On the stomach with the naked eye visible blue veins veins. The long course of the disease causes anemia in the child, his skin is pale, he suffers from frequent dizziness, gets tired quickly. Due to the accumulation of feces may be symptoms of intoxication, manifested by headache, nausea, and sometimes vomiting.
Different stages have different characteristics.
- Compensated - constipation in newborns, which becomes stronger with the introduction of complementary foods. If the parents monitor the frequency of bowel movements, they carry out enemas in time, then the general condition of the child is not disturbed. When the second degree in the child begins to suffer appetite.
- Subcompensated - constipations become more frequent, without an enema, it becomes almost impossible to empty the intestines, but with adequate treatment, the pathology has every chance of becoming a compensated form. The symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease are increasing slowly and gradually.
- Decompensated - Symptoms increase very quickly. When the first degree is markedly acute, the child has disrupted discharge of gases, there is no bowel movement, the abdomen swells like a frog. In the second degree, the disease becomes chronic.
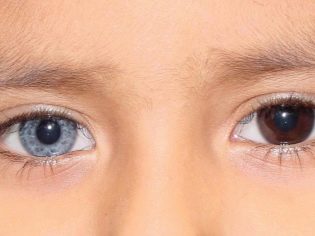
An interesting detail: often congenital megacolon is found in children with heterochromia from birth - different colors of the iris of the organs of vision.
What is the danger?
The agangliosis of the large intestine is dangerous because the digestive process is disturbed in the sick baby, nutrients are absorbed less than needed, and since all this happens against a background of decreased appetite, it is possible that the child will become hypotrophic or begin to suffer extreme exhaustion - cachexia.
Children with such a congenital developmental anomaly slowly grow, lag behind their peers in height and weight, more often suffer from dysbiosis, inflammation of the intestinal mucous membranes.
The most dangerous complication is the development of intestinal obstruction, as well as the formation of pressure sores of the intestinal wall with fecal stones in violation of the integrity of the intestine itself. This is dangerous peritonitis and sepsis.
Diagnostics
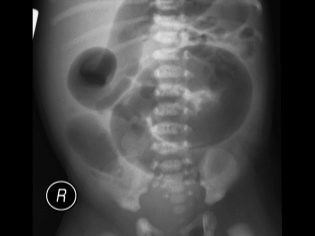
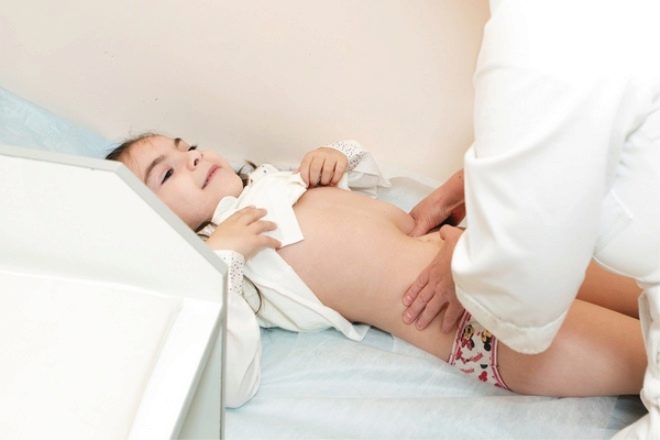
The doctor may, on the basis of parents' complaints of frequent abdominal distension, difficulty with defecation, and constipation, assume a bowel agangliosis in a child. When a medical worker touches the stomach, two tests are performed - a test for "swelling" and a test for "clay symptoms". In the first case, the doctor finds sealings with a finger examination of the abdomen, and in the second, signs of compression of the colon. In this case, the child is sent for examination, which is intended to confirm or deny the diagnosis. It includes:
- radiography of the large intestine with the filling of the intestine with a contrast agent;
- endoscopy of rectum and sigmoid colon;
- Swensen cytomorphology - histological examination of rectal and colon tissue samples;
- manometric tests.
In the analysis of the blood of a child with Hirshprung's disease, usually elevated leukocytes, ESR, and toxic changes in neutrophils are detected.
Investigate and establish the diagnosis proctologists, surgeons, infectious diseases, pediatricians.
Treatment and prognosis
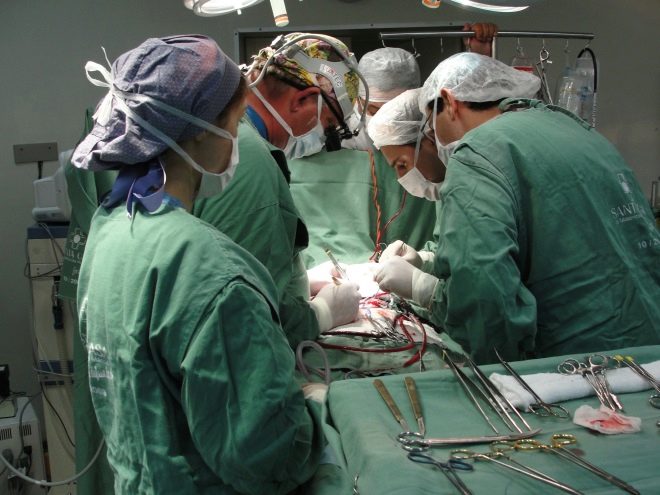
A child with such a diagnosis is usually recommended surgery. And parents should understand that if doctors advise to do this, it is better not to refuse, because Hirschsprung's disease is not conservatively treated by folk methods. During the operation, it will be possible to restore the intestinal permeability, as well as to remove the affected area, which creates so many difficulties in the work of the entire intestine.
There are two types of operations - one-stage and two-stage. To understand which one to recommend, the doctor takes into account the child's age, the degree of intestinal damage, the length of the innervated area.
A one-step operation is usually performed with a compensated disease and a small bowel injury. Simply remove the affected area, form an anastomosis. This method is less traumatic, judging by the reviews of doctors and patients.
A two-stage operation is performed for children with ailment in the stage of subcompensation and decompensation, with large affected areas of the large intestine. The first stage involves the removal of the affected area and the creation of a temporary colostomy. At the second stage, anastomosis is formed from it.
Emergency surgery for a child can be carried out in case of intestinal obstruction, pressure sores of the walls, violation of the integrity of the intestinal walls.
It’s pretty hard to predict. After all, it all depends on how early the child has identified a congenital developmental abnormality, what type it belongs to, whether all clinical recommendations have been followed in time. With early surgery, projections are favorable. If the baby is not treated, the probability of death of the child is estimated at 80%.
If you refuse the operation and form a subsequent obstruction, it is possible that after the operation the child will receive a disability, but even here everything is individual and depends on the amount of surgical intervention.
More information about the disease experts say in the next video.