Minimal brain dysfunction (MMD) in children
The diagnosis of MMD in a child confuses parents. The decoding sounds rather frighteningly - “minimal brain dysfunction”, the most joyful word here is “minimal”. What to do if a child has found a small dysfunction of the brain, how it is dangerous and how to cure the child, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
In neurology, there are several duplicate names of what is hiding behind the abbreviation MMD - mild encephalopathy, hyperactivity syndrome and lack of attention, minor brain dysfunction, etc. Whatever the name, the essence of it is approximately the same - behavior and The psycho-emotional reactions of the child are disturbed due to some “failures” in the activity of the central nervous system.
Minimal cerebral dysfunction first came to medical reference books in 1966, previously it did not attach importance. Today, MMD is one of the most common anomalies of early age, its signs may appear as early as 2-3 years, but more often by 4 years. According to statistics, up to 10% of primary schoolchildren suffer from minimal brain dysfunction. At preschool age, it can be found in about 25% of children, and a particularly "talented and corrosive" neurologist can also find ailment in 100% of active, active and unruly children.
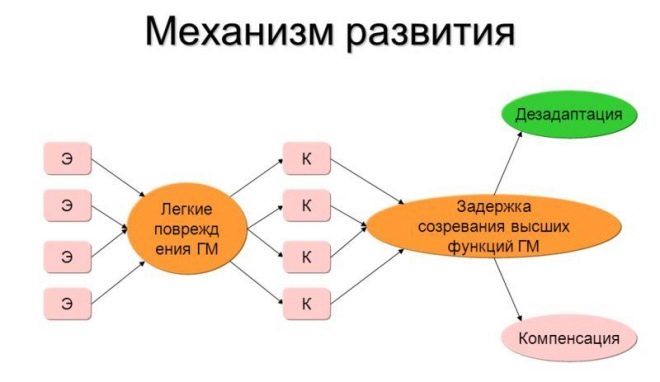
What happens to a child with minimal CNS dysfunction is not so easy to understand. If simplified, certain central neurons die or experience problems with cellular metabolism due to negative internal or external factors.
As a result, the child’s brain works with certain abnormalities that are not critical to his life and health, but affect his behavior, reactions, social adaptation, and ability to learn. Most often, MMD in children is manifested as a violation of the psycho-emotional sphere, memory, attention, and also in increased motor activity.
MMD in boys is four times more common than in female children.
The reasons
The main causes of minimal brain dysfunction are the defeat of the cortex and abnormal development of the central nervous system of the baby. If the first signs of MMD have developed after the child has turned 3-4 years old and older, the reason may be the insufficient participation of adults in the upbringing and development of the child.
Fetal causes are most common. This means that the baby’s brain was adversely affected while the baby was in the womb. Most often, infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy lead to the minimal dysfunction of the central nervous system in a child, and her use of medications that are not allowed for future mothers. The age of a pregnant woman over the age of 36, as well as the presence of chronic diseases in her, increase the risk of a negative impact on the baby’s nervous system.
Improper diet, excessive weight gain, edema (gestosis), as well as the threat of miscarriage can also affect karapuz neurons, especially since neural connections during pregnancy are still being formed. From this point of view, both smoking and alcohol intake during the period of gestation are dangerous.
Disturbances in the nervous system can also occur during childbirth due to acute hypoxia, which a baby may experience in rapid or prolonged labor, for a long anhydrous period if the fetal bladder opened (or was mechanically opened), and then the weakness of labor forces developed .It is believed that the cesarean section is stressful for the child, because he does not go through the birth canal, and therefore this type of operation is also referred to as MMD triggers. Quite often, minimal brain dysfunction develops in children with large weights during childbirth - from 4 kilograms or more.
After birth, the child may be exposed to toxins, as well as get a cranial injury, for example, when he bumps his head during a fall. This can also cause disruption in the work of the central nervous system. Quite often, the cause of the disease is flu and acute respiratory viral infections that were transferred at an early age if neurocomplications have arisen - meningitis, meningoencephalitis.
Symptoms and signs
Signs of cerebral dysfunction may occur at any age. In this case, the symptoms will be quite typical for a particular age group.
In children under one year, so-called minor neurological signs usually occur - sleep disturbances, frequent strong winches, diffuse hypertonus, clonic contractions, trembling of the chin, arms, legs, squint, and abundant regurgitation. If the baby cries, the symptoms intensify and become more noticeable. At rest, their manifestation may be smoothed out.
Already in half a year, a delay in mental development becomes noticeable - the child reacts little to familiar faces, does not smile, does not shake, does not show much interest in bright toys. From 8–9 months, a delay in object-manipulative activity becomes noticeable — the child is unable to take objects. He lacks the patience to reach out or crawl up to them. They quickly bother him.
In children under one year, MMD is accompanied by increased irritability and sensitivity of the digestive organs. Hence, first problems with regurgitation, and later with alternation of diarrhea and constipation, which can replace each other.
From year to year, children with minimal brain dysfunction show increased motor activity, they are very excitable, they continue to have problems with appetite - either the child is constantly eating or it is completely impossible to feed him. Often children are slower than their peers, gaining weight. Most up to three years peculiar restless and disturbing sleep, enuresis, inhibited and slow development of speech.
From the age of three, kids with MMD become more awkward, but at the same time they are very quick-tempered and sometimes negatively disposed towards the criticism and demands of adults. A child at this age can usually do something alone for quite a long time; children with minimal brain impairment are not capable of it. They constantly change the type of activity, abandon the unfinished. Quite often, these guys painfully perceive loud sounds, stuffiness and heat. Very often, according to the observations of neurologists, it is babies and teenagers with MMD who hitch to vomit when traveling in transport.
But the brightest of all MMD begins to manifest itself when the child enters the company of his peers, and this usually occurs at the age of 3-4 years. A heightened sensitivity, hysteria, a baby produces a huge amount of movements, it is difficult to calm him down and carry away with something, for example, with exercise. At school, children with such a diagnosis have the hardest time - it is difficult for them to learn to write, read, it is very difficult for them to sit in class and observe the discipline instituted in the classroom.
Further more. Self-esteem decreases, communication skills are violated. Often, such children move away from the team or become informal leaders of not the best companies.
Diagnostics
At the age of one and a half years, an ultrasound of the brain is performed, the rest of the children can be assigned with CT, MRI, and EEG. These methods allow us to estimate the structure of the cortex and subcortical layer of the brain. The cause of the manifestations of small brain dysfunction is not always possible to establish. A neurologist in relation to children under three years old makes his decision based on the results of examining reflexes.
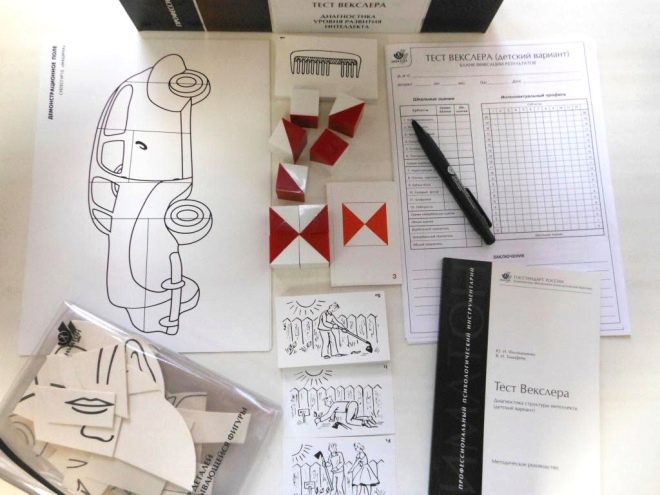
In the senior preschool and school age psychodiagnostics is carried out, the tests used are "Test Wexler", "test Gordon", "Luria-90".
Treatment
Therapy in all cases combined - it includes medication, physiotherapy, gymnastics and massage, as well as educational and developmental activities with kids or psychological classes with schoolchildren. A special mission in the matter of therapy is given to the family, because most of the time the child spends in it. It is recommended to talk with the child calmly, focusing on successes, and not on the shortcomings of his behavior.
Parents should get rid of the words "can not", "do not you dare", "to whom they say", "no" and establish a more trusting and good relationship with the child.
A child with MMD cannot watch TV for a long time or play at a computer. He necessarily needs a daily regimen to go to bed and get up on time. Outdoor walking and active outdoor sports are welcome. Among the quiet home games, it is better to opt for those that require concentration and patience from the child - puzzles, mosaics, and drawing.
Depending on the specific symptoms, sedatives or hypnotics, nootropic drugs, tranquilizers and antidepressants may be recommended. Dr. Komarovsky, whose opinion is listened to by millions of mothers around the world, argues that medications for MMD do not exist, and most of the drugs prescribed by neurologists are prescribed completely unreasonably, because the child does not treat the child, but the love and participation of adults.
Among the sports that are recommended for such hyperactive children, we can recommend those that require focusing on the second event, as well as improving the coordination of movements. These types include skiing, biathlon, swimming, cycling, tennis.
Forecasts
Despite the terrifying name, minimal brain dysfunction is far from being so terrible. So, about 50% of children with MMD successfully “outgrow” the violation, by their adolescence no deviations are detected. Treat MMD nevertheless necessary. If medications are not taken into account, then massage, sport, adequate upbringing and developmental activities with a child give a very good result. Only in 2% of children does pathology persist until adulthood and is not amenable to correction. In the future, it creates a lot of problems for a person in matters of contacts, work, interpersonal relations. It is difficult for a person with MMD to create a prosperous family, to maintain normal relations in it.
Reviews moms on the Internet show that with timely treatment, the symptoms disappear within a year. However, parents emphasize that very often doctors do not know how to distinguish a child with MMD from just an active and mobile baby, and therefore the treatment is prescribed for "safety net".
See the following video for more on minimal brain dysfunction in children.