Acute bronchitis in children
Respiratory failure occurs in babies at almost any age. Even newborn babies can get sick. Timely diagnosis and timely treatment lead to full recovery.
What it is?
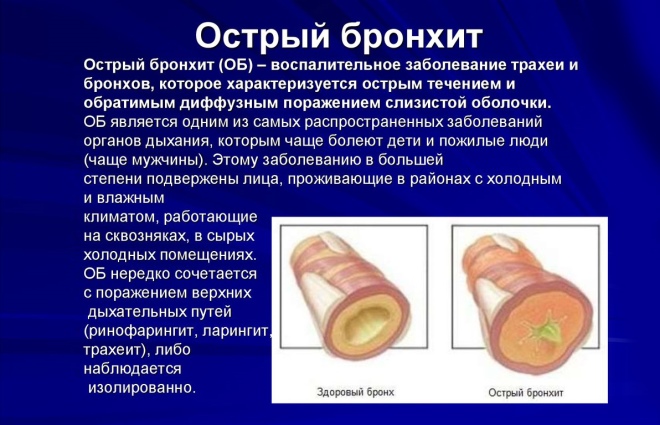
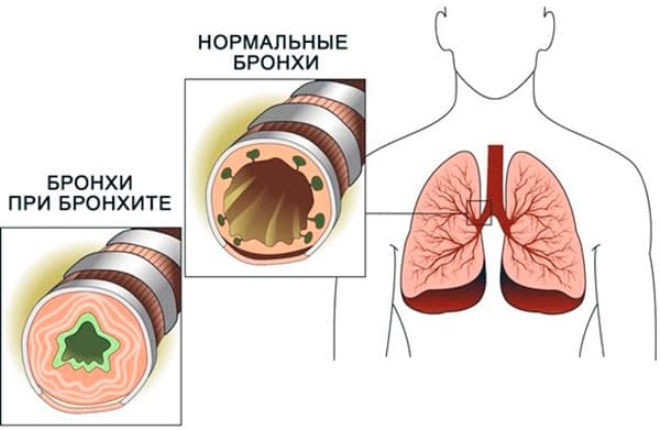
Inflammation of the bronchial mucosa caused by any cause is called acute bronchitis. The reasons that contribute to the development of the disease, a wide variety. The peculiarity of the structure of the bronchial tree contributes to the appearance of this disease in children.
The greatest number of cases of the disease is usually recorded during the cold season. There has also been an increase in the incidence of acute bronchitis during flu epidemics or infectious colds. Boys suffer as often as girls. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 4 - 10 years.
The reasons
Every child can get bronchitis. This is due to many reasons that cause this disease. In some cases, there are even several different provoking factors that act simultaneously and cause disease.
Acute bronchitis can cause:
Viral infections. Are the most common cause of the disease. Among the active pathogens are influenza viruses, parainfluenza viruses, adenoviruses, and PC viruses. They are well preserved in the external environment and are able to spread rapidly. Getting on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, microbes cause inflammation and the appearance of adverse symptoms of the disease.
Bacteria. Staphylococci, streptococci, moraccella, pyocyanitis, and anaerobic microorganisms are often the causative agents of bronchitis. Such forms of the disease usually go much harder than viral ones. Antibiotic prescribing is required.
Exposure to toxic substances. Emissions from industrial enterprises and factories contribute to bronchial damage and the development of bronchitis. The smallest components of toxic products for a long time can be in the air. When hit in the bronchi, they cause trauma and give impetus to bronchial obstruction.
Congenital defects of the structure of the bronchi. Respiratory organs are formed in the third trimester of pregnancy. The disease revealed at this time in the future mother contributes to the underdevelopment of the respiratory system in the child.
Foreign bodies. Sudden blockage of the lumen of the bronchus leads to the development of adverse symptoms of bronchitis.
Fungal infection. It occurs in weakened babies or children with immunodeficiency.
How does it come about?
In childhood, the bronchial tubes are narrow and have a small diameter. This contributes to easier penetration of the infection, which causes a strong inflammatory process.
Outside, the epithelium of the bronchi is covered with cilia. They contribute to the purification of the bronchial tree from the various particles that can get inside. In babies, cilia are still not functioning well enough, which also contributes to the development of bronchitis.
Excessive sputum formation occurs during illness. This is largely due to the fact that the number of glands that produce mucus in the bronchi is much larger in babies than in adults. Inflammation activates their work, causing sputum and a strong cough.
Weak respiratory muscles cause a decrease in active respiration in the acute period of the disease.Small lung volume contributes to the active reproduction of pathogens and enhance the inflammatory process. The smaller the child’s age, the more severe the illness.
The incubation period may be different. It largely depends on the cause of the disease. For viral infections, it lasts 3-5 days. For bacterial bronchitis, it is usually 7-10 days. Toxic effects can manifest themselves in different ways: from several days to 1 month. In infants the disease is much more difficult, and the incubation period may be shorter.
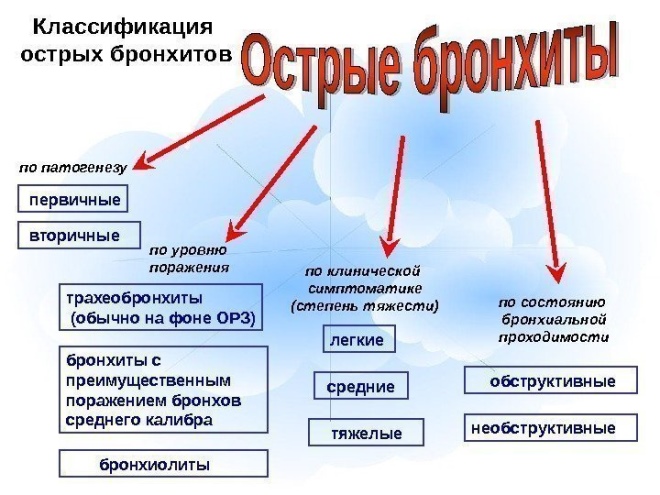
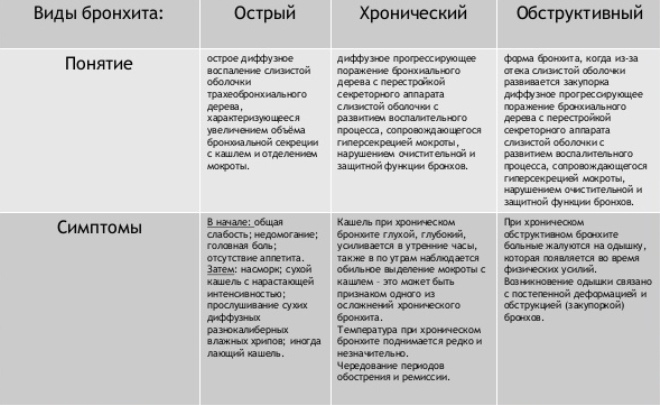
Classification
All forms of acute bronchitis can be classified according to severity and clinical forms. Such a division helps doctors to choose the right treatment, which contributes to the complete recovery of the baby in a short time.
Clinically, acute bronchitis can be bronchiolitis. In this process, the smallest bronchi and bronchioles are damaged. The disease is most severe. Most common in babies at 2 years. During an exacerbation of the disease, the baby is hospitalized in a hospital equipped with an intensive care unit and intensive care.
By severity:
-
Lungs. Proceed with mild symptoms. Complications do not cause. Lasts 7-14 days. Well treated. After a high-quality therapy, they pass without a trace.
-
Medium degree. Accompanied by a temperature increase of up to 38 degrees and the appearance of a hacking sweltering cough. The well-being of the child suffers greatly. The treatment is long, there are complications. With the ineffectiveness of the therapy required hospitalization in the pediatric ward.
-
Heavy. Require mandatory treatment of the child in the hospital. Dangerous development of adverse and dangerous complications. Often occur with symptoms of respiratory failure.
Symptoms
After the end of the incubation period, the first characteristic signs of the disease appear. The severity of such manifestations depends on the child’s immunity, age, and the presence of chronic comorbidities. Younger children suffer the disease harder than schoolchildren.
The following symptoms are characteristic of acute bronchitis:
-
Cough. It can be hysterical and paroxysmal. In severe cases, it does not stop even at night. A prolonged cough may even contribute to the appearance of vomiting.
-
Increase in body temperature to 37-39 degrees.
-
Throat redness and runny nose. Characterized by viral and bacterial infections.
-
Dyspnea. Kids start breathing faster. The number of respiratory movements per minute is increased by 10% or more.
-
Noisy breathing. With the passage of air through the inflamed and tightly closed bronchi, resistance increases. This process causes noisy breathing, which becomes audible from the side. In some cases, you can hear even wheezing rales.
-
General weakness. Kids become lethargic, less active. They eat poorly, sleepy. A persistent cough makes the baby very anxious and easily excitable.
-
Chest tenderness when breathing. Frequent and prolonged coughing leads to pain during breathing.
-
Increased sweating. It is a manifestation of severe intoxication.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, be sure to show the baby to the pediatrician. The doctor with the help of a phonendoscope will be able to listen to specific rales that appear during bronchitis. After examining the child, the doctor will prescribe the full range of treatment.
Usually to determine the cause of the disease and the correct diagnosis is prescribed:
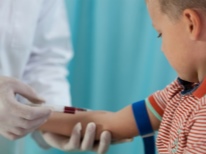
-
General blood analysis. The increased number of leukocytes during accelerated ESR indicates the presence of an infectious process. Changing the parameters in the leukocyte formula helps to establish the alleged cause of the disease: viral or bacterial.
-
Biochemistry. Conducted to clarify the associated complications.Helps determine the presence of damage to the kidneys or other internal organs during a severe course of the disease.
-
X-ray. It is conducted in children older than one year. The pictures allow to clarify the nature of the damage, as well as to conduct a differential diagnosis with other diseases.
-
Sputum analysis for pathogen detection. It is usually performed in the first days of the disease. Helps to establish the exact cause of the disease.
-
Sputum test for antibiotic susceptibility. The minus of the research is a long analysis period. Usually the result is ready only after 7-10 days. Allows you to accurately identify the pathogen and establish its sensitivity to various antibacterial drugs.
-
The definition of blood gases. Measurement of blood oxygen saturation is carried out in severe disease.
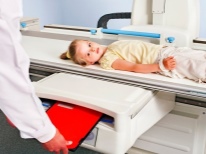
-
Computed or magnetic resonance imaging. These methods are used only in difficult cases when the diagnosis is very difficult to make. These studies are highly informative and allow you to accurately get the result. Conducted in older children who can not move during the entire survey.
Complications and consequences
Mild forms of the disease usually proceed calmly. After an adequate treatment, the baby can forget for a long time that he once suffered bronchitis. However, in severe cases, complications may occur. In some cases, they are quite dangerous.
The most common complication of viral or bacterial bronchitis is development of pneumonia. Usually it occurs in weakened and frequently ill children. Low immunity leads to the rapid spread of the inflammatory process in the lungs. Pneumonia can develop rapidly. This greatly violates the condition of the baby, and weights the course of the disease.
Another, no less dangerous complication is abscess formation - cavity in the lung, which is filled with pus. Usually they are formed with improperly selected antibacterial treatment, as well as with a strong depletion of the child's body during the period of illness. Treatment of this complication is carried out only in the hospital.
With an incorrectly chosen therapy, acute bronchitis can become chronic. This option happens with insufficient follow-up care. After prescription of medicines, the baby begins to feel much better already by 3-4 days of illness.
At this time, some mothers stop giving the child antibiotics or antitussive drugs, or reduce their dosage on their own. This leads to a chronic process and the development of possible exacerbations in the future.
Acute bronchiolitis can also turn into chronic. This form of the disease is most dangerous in the development of persistent respiratory failure. As a result of the disease there is a strong and permanent narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi. Air with oxygen dissolved in it practically cannot get into the lungs. This leads to development of respiratory failure. The treatment is carried out in the surgical department.
Treatment
According to the clinical guidelines, which provide a detailed description of how the treatment of acute bronchitis is carried out, a whole range of different medicines is used to eliminate the adverse symptoms.
For the treatment of acute bronchitis prescribed:
Antitussive and expectorant drugs. They help make sputum more fluid and improve its discharge. "Ambroxol"," Lasolvan ","Flamed"," Sinekod "," Gideliks "will help eliminate the cough, and normalize breathing. They are usually prescribed for 7-10 days, 2-3 times a day. The dosage and frequency selects the attending physician, taking into account the age and condition of the child.
Antipyretic. Apply when the temperature reaches above 38 degrees. Paracetamol-based drugs are prescribed.With prolonged use may cause adverse side effects.
Antiviral. They can be given in the form of suppositories, nasal drops or pills. Interferon is used to activate local immunity. The drug is available in the form of nasal drops or aerosol.
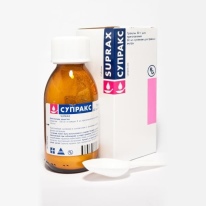
Antibiotics. Usually used drugs with a wide spectrum of action. It is most effective to prescribe antibiotics only after carrying out bakposeva sputum to determine sensitivity to them. The most commonly used are: "Suprax", Cephalosporin drugs,"Sumamed"," Flemoksin solyutab "and others. The course dose and the duration of treatment are chosen by the attending physician taking into account the severity of the disease.
Bronchodilators. Used for obstructive acute bronchitis to eliminate obstruction. Salbutamol-based drugs quickly relieve bronchial spasm and improve breathing. Combined means "Berodual"Helps to cope with even the most severe obstruction.
Hormones. Used only for allergic bronchitis. Appointed usually by inhalation. Systemic administration may contribute to side effects. If hormone therapy is prescribed, spirometry is recommended to be performed regularly to evaluate the functions of respiration.
Plentiful warm drink. Promotes faster removal of toxins from the body. Fruit and berry compotes, as well as fruit drinks and decoctions are perfect as drinks. During the day, the baby should receive at least a liter of fluid. Grudnichkov recommended soldered with boiled water.
Percussion massage. Light tapping and vibrating movements in the chest improve sputum discharge and improve breathing. You can perform a massage when the child is lying on the bed with his head down. This situation contributes to better expectoration of sputum and a decrease in cough.
Breathing exercises. It improves breathing and helps reduce bronchial obstruction. Recommended to conduct daily. The duration of the exercise is 10-15 minutes.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of the disease, you should remember to observe the following preventive measures:
-
Strengthen the immune system of the baby. Active walks in the fresh air and nutrition, enriched with vitamins and microelements, will improve the immune system.
-
Treat chronic diseases. Frequent exacerbations of sinusitis or otitis media ultimately contribute to the development of bronchial inflammation in the child. Early treatment of the upper respiratory tract will help prevent bronchitis in the future.
-
Use special moisturizers. Too dry air in residential areas causes dry mucous membranes and may even contribute to the development of bronchitis. Humidifiers help to create the right humidity and microclimate in the room. Such devices are simply necessary for all babies suffering from diseases of the bronchi.
-
Avoid excessive exhaustion and overwork of the child. A weakened child’s body is simply not able to resist infections. Proper day regimen and proper sleep will improve the immune system and prevent illness.
With a well-chosen treatment, acute bronchitis is completely cured. After a couple of weeks, babies become healthy and more active. Timely therapy allows to cope with the disease in a short time.
More information about acute bronchitis, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.