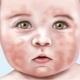
Why does a baby have skin on his fingers?
Peeling the skin on the hands and feet of a child is a phenomenon that causes the parents well-founded unrest and anxiety. The condition of the skin, as is known, reflects the state of the whole organism, and many pathological internal processes are manifested externally through the skin. Why does a child have skin on his fingers and toes, on palms and feet and how to treat a baby, we will tell in this article.
Desquamation - illness or norm?
The peeling of the skin on the medical language is a name little known to the masses - desquamation. In this process, desquamation of the scales of the epidermis occurs - the outer layer of the skin. It should be noted that this process is provided by nature, so that the skin can get rid of excess, dead cells, so that epidermis does not thicken and the skin is not coarse.
The epidermis consists of numerous layers. In the deep layers, cells divide, the new cells that are formed move to the surface of the skin and at the same time die because their life cycle is short. In the process of movement, cells produce and accumulate keratin. It is a strong protein that provides the skin with basic protective properties. On the surface, the peeling off of the epidermis cells that have worked out occurs. Thus, space is made available for new cells.
Desquamation is a completely normal physiological continuous process. However, sometimes the desquamation acquires a pronounced size and depth and becomes pathological.
Such desquamation occurs afterwards inflammation, damage to the outer skin layer, some internal processes. The death of keratocytes becomes widespread, and new cells are produced less than they die, and therefore unsubstituted fragments appear in the skin, the very places of peeling.
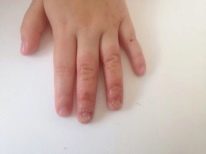
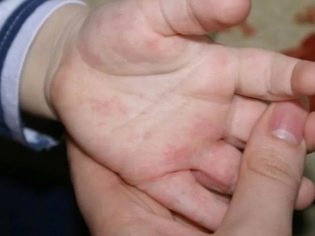
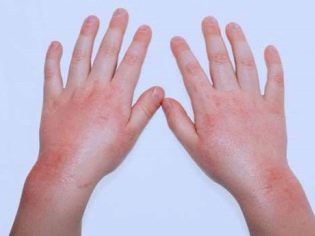
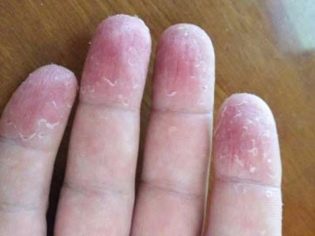
The flaking of epithelial scales during physiological normal desquamation is almost negligible. The skin gets rid of unnecessary cells gradually, replacing them with new ones. If a child’s skin peels off and is visible to the naked eye, then most likely it’s about pathological desquamationwhich requires an early clarification and elimination of the causes.
Peeling alone is not dangerous. Its consequences are dangerous, because the skin, deprived of a protective layer, becomes more vulnerable to pathogenic bacteria, various fungi, which can cause quite serious infectious diseases. In addition, there is always a certain external or internal trigger factor behind the peeling. If it is not eliminated, the negative impact on the body will continue and increase. Desquamation is often only the initial symptom of various pathological states and processes.
The reasons
The reasons that can lead to desquamation, a great many. That is why it is recommended not to engage in independent searches, and immediately visit with a child a pediatrician and a dermatologist. These experts will help narrow the search area and find the root of the problem.
Large-scale death of keratin cells of the epidermis can be caused by internal factors (occurring in the body) and external factors (aggressive action from the outside).
Internal causes:
- Vitamin deficiency. The most common cause of flaking of the skin at the fingertips, palms - avitaminosis. At the same time, one cannot say that there are not enough vitamins in the broad sense of the word.The child lacks completely specific vitamins that are involved in complex biochemical processes that make the skin supple and durable. These are vitamins E and A. They are popularly called “vitamins of beauty and youth”.
It is not necessary to prescribe a child with drugs with vitamins A and E, because the uncontrolled intake of these substances can cause severe overdose. It is better to entrust it to a specialist.
- Allergic reaction. The outer layer of the epidermis may also suffer due to inadequate response of the body to certain protein antigens. Allergy begins, the manifestations of which can be very different. Skin peeling, according to statistics, ranks second among all symptoms of allergic reactions. In this case, the child may be affected not only the skin of the hands. Often, when food or drug allergies can be noticed that skin is peeling off on the nose, on the chin, on the forehead.
- Fungal infections. Fungi that affect the epidermis, there are several dozen. In childhood, the most common diseases such as keratomycosis, pityriasis versicolor, erythrasma and actinomycosis. Superficial skin lesions can cause an anthropophilic fungus that causes trichophytosis. Most often, such a lesion is accompanied by additional pathological changes in the nail plates.
In the presence of a fungal infection, it is not only the hands that suffer, but also the scalp, legs, often flaking and painful reddening in the form of clearly defined areas can be found on the soles and nails of the big toes.
- Bacterial infection. Most often, problems with the skin of the hands are caused by staphylococci and streptococci. Peeling at the same time is only one of the stages, usually preceding the development of ulcers, papules, vesicles. The peeling itself quickly becomes deep, and cracks can form on the skin.
- Stress. Strong or prolonged stress can cause a variety of diseases in children. Peeling of the skin of the hands and feet is no exception. By the way, the neurological factor of dermatological diseases is the hardest to detect, because the presence of stress in young children who are not yet able to express their feelings and feelings in words is hard to guess even for an experienced pediatrician.
- Diseases of the digestive system. Desquamation of the skin of the hands may indicate the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Especially often on the skin there are problems with the pancreas. This organ, responsible for the production of enzymes and hormones, with pathological changes causes not only the peeling of the epidermis, but also a change in skin color. Cyanotic fragments may appear, or red vascular points may appear in different parts of the body.
- Pathological dry skin. We are talking about dryness caused by diabetes mellitus, hormonal disorders, atopic dermatitis. All these diseases and conditions reduce the production of lipids by the sebaceous glands of the epidermis, the skin is not moisturized, it is deficient in fluid. Even the slightest traumatic impact can cause a violation of the skin with further peeling of fairly large areas.
- Worms Many parasites that breed and feed on nutrients through the intestinal wall cause skin problems. Desquamation occurs with prolonged helminthic invasion with pinworms, ascarids, and giardiasis.
External causes:
- Contact dermatitis. The skin on the hands may peel off due to the fact that the child has been in contact with some irritating substances, household chemicals, poisons, toxins, alkalis and acids. Recognizing such a defeat will not be easy, but nothing is impossible. A lesion is limited only by the contact zone and does not extend to other parts of the body. There is a slight or pronounced redness, as well as a slight swelling and "glossiness" of the skin.Peeling usually does not begin immediately, but several days after contact.
- Temperature exposure. Heat or hypothermia can cause metabolic disturbances in the skin. If a child on the eve of a long time playing snowballs, then the next day there may be a slight peeling of the skin on the fingertips, on the palms. After a bath or sauna, the skin may peel off due to steaming and exposure to high temperatures. If a child often walks without gloves in the wind, desquamation occurs from dehydration caused by exposure to air currents.
Frequent contact with water, for example, during games in the pool, also affects the condition of the skin, and can lead to excessive scaly separation of epidermal cells.
- Improper hygiene. For children, not only the lack of hygiene is dangerous, but also its excessiveness. So, frequent hand washing with soap can lead to draining and desquamation. It is also dangerous to use adult detergents that aggressively affect the baby’s skin, disrupting the acid balance. Children with particularly sensitive skin can react in this way to chlorinated tap water.
- Medication. Desquamation often begins when the intestinal microflora is disturbed, which can be provoked by prolonged use of antibiotics, especially drugs of the sulfonamide group. Peeling may also be accompanied by hormonal drugs.
Symptoms
Even before the appearance of the first characteristic signs of desquamation, an itch may occur in a child. Often parents notice the already peeled skin only because they simply did not notice the previous stage. Not all children themselves pay attention to the fact that the pens are itching, and even more so they can inform mum and dad about this.
By the time of peeling, the skin looks somewhat edematous, although this, like redness of the integument, is not a mandatory symptom. For fungal lesions, instead of redness, there may be light, almost whitish spots, and for diseases of the digestive organs, light blue skin fragments. If the child is actively combing the skin, then it is injured and cracks, pustules appear, a white or yellowish crust appears. It may be dry or weeping.
Peeling most often begins on the tips of the fingers or on the toes, on the feet (for example, due to cramped and uncomfortable shoes), and then, with the continuation of the negative impact, skin disease spreads further - on the palm or heel.
It is important to evaluate the associated symptoms.. Peeling and digestive problems should be a reason to visit a gastroenterologist. Desquamation and simultaneous respiratory phenomena (runny nose without snot, dry cough) can be a clinical picture of allergies and a reason for contacting an allergist. Large-scale skin lesions may indicate contact dermatitis or fungal infection; this is an occasion to visit an infectious diseases specialist and a pediatrician.
Treatment
To treat such a seemingly simple problem as peeling of the skin on the hands or feet is not recommended by folk remedies, because the true reason can be quite dangerous, and the time needed for competent therapy will be missed.
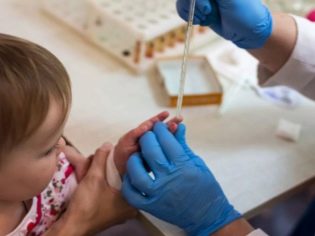
It is best to start with a detailed medical examination. To find out the reason, the child will need to pass a general and detailed blood test, which will allow to establish the presence of inflammatory processes, and also to find out if the baby has a deficiency of certain vitamins.
It is imperative to pass scraping samples of the epidermis on a microscopic examination, which will allow to detect fungi, as well as scraping on bacperic acid, in order to look for disease-causing bacteria.
An allergist if an allergic reaction is suspected will conduct a study with special test strips to determine the specific allergen that caused changes in the skin. If there is a shortage of vitamins A and E, vitamin complexes will be prescribed, most often children are recommended “Aevit"In which both vitamins are presented in a certain amount. One by one, these vitamins are ineffective and poorly absorbed, so they should be taken exclusively in a complex. The doctor will advise you to include foods rich in vitamins A and E in your child’s diet:
- carrot;
- pumpkin;
- cabbage;
- plums;
- apricots;
- prunes;
- tomatoes;
- fresh greens;
- high fat dairy products;
- unrefined vegetable oil (olive, sunflower);
- Oatmeal and buckwheat porridge with butter.
Locally on the affected skin will be useful to apply ointment. Radevit, Aekol.
When treating an allergic disease, you will need to eliminate any contact with the intended allergen. If you could not find it, then the child is isolated from contact with all potential allergenswhich are traditionally household chemicals and chlorine, household dust, plant pollen, an extensive group of foods (nuts, milk, chicken eggs, sugar, red berries, etc.), and medicines. Along with a change in lifestyle, antihistamine medications are prescribed, and topically to the skin with severe damage and extensive desquamation, ointment and cream based on glucocorticosteroid hormones.
Fungal lesions of the skin are treated the longest and most difficult. Such treatment requires a mandatory purpose - the doctor to choose drugs must know which of the existing fungi is “guilty” of peeling the skin. Antifungal therapy in babies is often carried out in the hospital. Treatment involves taking antifungal agents topically, in the form of ointments and gels, as well as taking similar means by mouth.
After the first course of treatment, after waiting for 2-3 weeks, a second course is prescribed to avoid a new growth of fungal colonies.
Bacterial lesions are treated with antibiotics. There are a large number of antimicrobial ointments. Depending on the type of microbe belonging to one or another type, skin treatment is prescribed with ointments and antiseptics, as well as immunostimulating therapy, taking vitamins. Treatment usually takes from 7 to 14 days.
In diseases of the digestive system, a gastroenterologist prescribes a specific treatment, including sorbents, enzyme preparations, agents that increase or decrease the acidity of gastric juice, as well as choleretic drugs. Apply ointments with vitamins to the affected skin. Dryness and flaking with diabetes mellitus, HIV infections need the advice of narrow specialists, who will tell you how to correct the main drug support on which children are located so that skin manifestations are minimized.
In all cases of pathological desquamation, regardless of the cause, the child is shown:
- adherence to work and rest;
- normalization of the psychological background in the family, elimination of conflict situations;
- sufficiently humid air in the room (relative humidity - at least 50-70%);
- washing without the use of soap and other detergents, including children's products;
- moisturizing the skin with vegetable oils permitted for use in children (peach, apricot, olive, sunflower, petroleum jelly);
- careful trimming of the baby’s nails, since the bacteria and fungi contained under them can infect new wounds when combing, if desquamation occurs against the background of severe itching;
- avoidance of aggressive effects on the skin - heat, cold, chemicals.
From the arsenal of traditional medicine during desquamation, you can use hand baths with chamomile decoction. Water for the procedure should not be hot, but warm. It is useful to make lotions with calendula decoction.
But experts do not recommend using honey for spreading the skin of the hands - all beekeeping products are highly allergenic and can worsen the condition of the baby’s skin.
Useful bath with a string and celandine, adding to the water for bathing broth oak bark.The baby’s skin should be gently peeled off with a special baby mitten for washing. Rubbing of the affected skin is prohibited, this prohibition applies to hard towels.
Prevention
Desquamation can be avoided if you follow the basic rules for maintaining children's health:
- Care for the skin of the child should be without undue zeal. Bathing with soap is best done no more than 1 time a day, while for children up to six months it is better to use a soap solution prepared from baby soap. Children after the year should buy only hypoallergenic means for swimming. It is not necessary to wash hands after walking or before eating with the use of soap, it is enough to do it with ordinary running water for at least 30-40 seconds.
- Strengthening immunity from birth helps to avoid many childhood diseases, including skin problems. The best means for the formation of a strong immune defense are hardening, walking in the fresh air, playing sports, active games and a balanced diet, rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Do not use for baby products with strong drying effect - alcohol lotions, a large amount of talc. In total should be in moderation, and alcohol and all the means in which it is contained, are contraindicated in children until adolescence.
- It is important to protect the hands of the child from temperature effects. - In winter, be sure to warm them with mittens and gloves, preventing hypothermia, and in summer - lubricate with sunscreen, if you plan a long stay in the open sun. In the offseason, when the danger is wind, you need to lubricate your hands with protective creams ("Rescuer", "Bepanten") Before going out into the street and gently with warm running water, flush the protection after returning from a walk.
- All diseases must be treated promptly, first of all, it concerns colds and viral ailments, as well as helminthic invasions. In the treatment, you should always consult with your doctor, do not trust the child's health of traditional medicine, since no medicinal plant can kill all the pathogenic bacteria, fungi and in no way acts on viruses.
How to avoid problems with the skin of the child, see the following video.