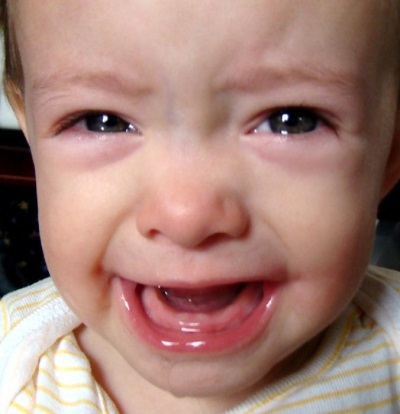
What does gum look like when teething?
In some babies, the teeth are cut with great discomfort for the infant, while in others, they “peck” painlessly and almost imperceptibly for parents. Wherein In all children, the main signs of the emergence of a new tooth are increased salivation and local changes in the oral cavity. Let us dwell on the changes in the gums that occur during normal tooth eruption, as well as on possible problems with the gums during the growth of teeth.
How does a tooth erupt?
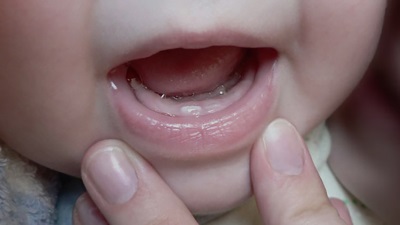
The gums of the child begin to change long before the appearance of the tooth. Their tissues become more loose and change color. The gum in the place where the tooth will soon appear, swells and slightly increases in size. As for the color change, in most cases there is redness, but in some babies the color may be bluish, burgundy or dark purple.
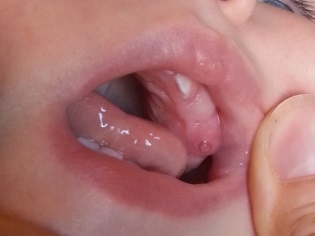
When the cutting tooth comes close to the surface of the gum, the parents see a white dot. It represents a clove translucent through a thinning gum. This is followed by the final stage of eruption, during which the crown of the tooth passes through the gum and the tooth is released from its tissues. This is assisted by the enzymes present in the baby’s saliva, which literally “melt” the gum and enable the tooth to appear on its surface.
When gum changes occur when teething
The process of teething through the gum takes from one to three days, however mild swelling of the gums and an increase in saliva can be observed 2-4 weeks before the moment when a clot erupts on the surface of the gums. The kid feels itchy and, in order to calm him down, begins to pull various objects into his mouth. During this period, the risk of injury and infection of the gums increases.
Why can the gum be blue?
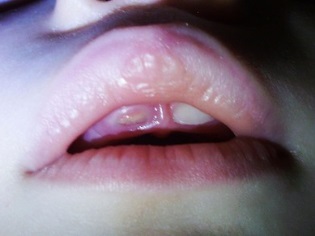
The acquisition of a gum in the place of the eruption of a new tooth of a blue tint is called cyanotic. Its appearance is associated with squeezing or tearing of small blood vessels when the tooth moves to the surface of the gum. If the blue area is small, usually this situation does not require any interventions.
For large sizes, the blue area of the child’s gums should be shown to the dentist, as this may be a sign of hematoma formation. You should go to the clinic with the baby so that the doctor can make a small incision and release the blood collected under the surface of the gum.
Why can the gums turn black?
The acquisition of a gum, through which a tooth is cut, of a dark color, which is sometimes blue, violet, purple or even black, is connected with the formation in her tissues of hematoma or cyst eruption. Such manifestations look rather frightening, but often do not give the child much discomfort and do not require medical intervention.
The appearance of a cyst or hematoma is most often observed with the eruption of chewing teeth, and a little less often when fangs or incisors are cut. In the oral cavity of the baby, parents notice a volumetric formation in the form of a dark ball on the gum.It appears when a tooth moves up through the gum and injures its tissues with a rupture of blood vessels.
The best way out after the discovery of such changes will be a visit to the dentist with the child. Independently trying to break through the gum or something to cut it is strictly prohibited.
Depending on the results of the examination, the doctor may recommend that the child bite hard objects that can speed up the breakthrough of the mucosa by the tooth and get rid of a hematoma, such as a teether toy, carrot or crouton. During chewing and physical impact on the gums, the mucosa breaks faster and the tooth goes to its surface.
In some cases, for example, if the hematoma is very large, the child has severe pain, infection or bleeding has appeared, they resort to surgical intervention. After local anesthesia, the child is cut through the gum with a special tool. This facilitates the appearance of the tooth and eliminates the accumulation of blood.
Cognitive video on how to help your baby in a difficult period of teething, see here:
What to do with inflammation of the gums?
To facilitate the condition of the baby, it is recommended:
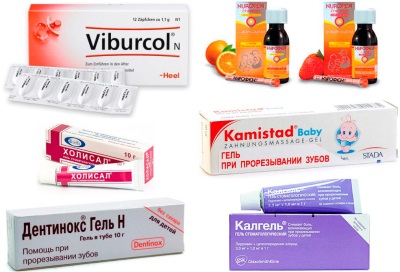
- Local anesthesia using specially designed preparations in the form of gels. They remove the inflammatory process and have an anesthetic effect.
- The use of teethers. Due to the possibility of nibbling such toys filled with water or gel, the child relieves itching in the gums, and the reduction of soreness and swelling is achieved by cooling the teethers in the refrigerator. Relieves pain and itching in the gums and a neat massage performed by mom with clean fingers, on which a sterile bandage is wound.
- Receive antipyretic drugs. Such drugs, often represented by ibuprofen or paracetamol, eliminate pain, reduce soreness of the gums and lower body temperature, if it rose during teething.
- The use of traditional medicine. Children with cutting teeth are recommended to wipe the gums with decoctions with anti-inflammatory action. Chamomile is often used to make them, but mint, lavender, and sageMelissa. Another popular way to help a child with teething is treating the gums with soda solution. In a glass of boiled hot water pour a teaspoon of soda and stir. Next you need to soak in the prepared tool gauze, wound on a finger, then wipe the gums.
When to see a doctor
Parents should constantly inspect the mouth of the toddler during teething and observe the general condition of the crumbs. Indications for seeking medical care consider:
- The appearance on the gum hematoma.
- Temperature increase of more than + 38 ° C.
- The appearance of severe diarrhea or repeated vomiting.
- Formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the mouth.
- The appearance on the mucous membrane of white spots or cheesy white plaque.
- Bubble rash appears in the baby's mouth.
- The appearance of pronounced cough.
- Constant crying baby.
- A runny nose with yellow or greenish discharge.

About the first teeth, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.