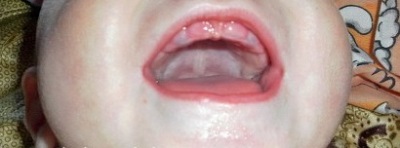
Blue gums in a child
Changes in the child’s mouth always alarm the parents, especially if mom or dad noticed that the gums have turned blue. Why gums in a child can get a bluish color, is it dangerous and how to help a toddler?
Why gums can turn blue
At an early age, the most common cause of the bluish color of the gums is the eruption of the baby tooth. Such manifestations are associated with squeezing or damage to the blood vessels at the site of the advancement of a new tooth, as a result of which a small hematoma may appear.
Another common cause of the blue gums is trauma. A bruise may appear if the child bangs on his gum as he falls on some kind of hard surface. A strong blow provokes the rupture of small vessels in the gum, because of which it turns blue.

What to do
A small hematoma formed in the process of teething does not require treatment if it does not bother the child. Let's gnaw teething toys or hard foods (carrots, apples) to the baby, which will help the tooth to peck up and get rid of the hematoma more quickly. If it is painful or too large, the child should be taken to the dentist. The doctor will reveal the formation, giving the outflow of blood collected in the gum tissue, which will also help in the appearance of the tooth.
If the child has hit the gum to bruise, the baby should be immediately taken to the doctor, especially if the teeth have also suffered from a fall. The doctor will carefully examine the toddler, prescribe an x-ray if necessary and tell you how to care for the oral cavity until the bruise resolves itself. If a large hematoma is detected due to a fall, it will be opened to prevent infection.