Stomatitis in children on the gums
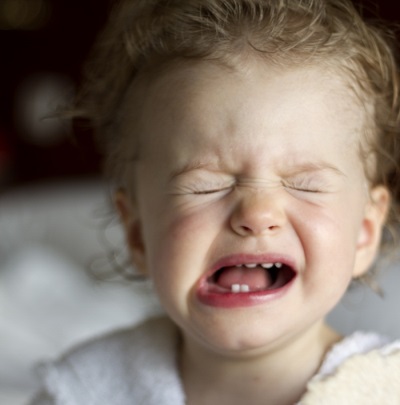
If the baby complains of pain in the mouth, and the mother discovers that the crumbs of the gums are bleeding or inflamed, you should immediately show the child to the doctor. These can be symptoms of stomatitis, which often affects the gums and causes severe discomfort and pain in children.
What is it
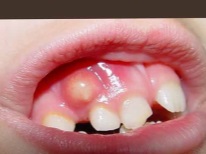
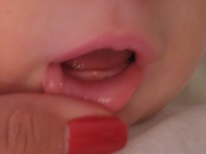
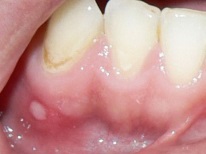
This is the name of inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth of a child, which often looks like an sore or a spot, but it can also be pustules, vesicles or plaque. If the lesion on the gum is represented by a white-yellow-gray sore, often the only one, this stomatitis is called aphthous. With the appearance of a bubble rash on the mucous membrane of the gums, herpes stomatitis is often detected. White spots that itch and hurt most often represent the candida form of stomatitis.
The causes of ulcers on the gums
The defeat of the gums with stomatitis most often can be caused by:
- Bacterial infection. If the baby’s saliva is not enough, the bacteria in the mouth become more active and cause wounds to the gums. In addition, their activity is associated with a weakened immune system or a course of antibiotics. Among the bacteria that cause stomatitis, staphylococci are more common.
- Viruses. The most common occurrence of stomatitis can provoke herpes viruses.
- Fungi. Such a pathogen often becomes the cause of stomatitis in children younger than a year, getting into the infant's mouth from the mother, through toys or nipples.
- Poor oral hygiene. The remaining food particles in the mouth are a good substrate for bacteria.
- Trauma. Gums can be damaged by a hard object, such as candy, crackers, or the sharp edge of a toy.
- Allergies. The cause of stomatitis on the gum may be an allergen from a toothpaste, drug, or food.
- Poisonous substance. The appearance of ulcers on the gums is due to varnish, paint and other harmful substances that due to an oversight could get into the child's mouth at an early age.
Symptoms
The elements of inflammation on the gum of a child are usually quite painful, and the mucous membrane is swollen. In addition to ulcerative lesions, vesicles or plaque, the child will also have such manifestations of stomatitis:
- The rise in body temperature. In some babies this symptom is absent, but it happens that the temperature during stomatitis can reach + 40 ° C.
- Refusal of food.
- General weakness.
- Bleeding gums.
- Unpleasant smell from the mouth.
- Insufficient excretion of saliva or its products in excess.
- Crying and anxiety if the disease appeared at an early age.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
What to do
If the baby's gum has a sore, painful spot, rash or other symptoms of stomatitis, you should immediately show the crumbs to the specialist. Since different types of stomatitis are treated differently, the doctor must determine what kind of disease the baby has developed, and only after this can the disease be started.
You can learn more about the causes of stomatitis, treatment and prophylaxis in the following video. The popular doctor Komarovsky will tell you what to do if your child has stomatitis.
Treatment
Only in cases where stomatitis on the gums is caused by bacteria or the herpes virus, the doctor will prescribe antimicrobial or antiviral medications to eliminate the cause. For other forms of the disease, it will be treated symptomatically:
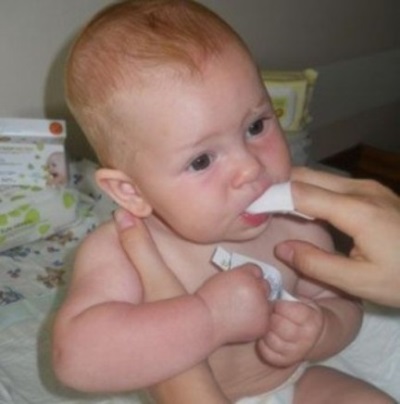
- Anesthetize the gum mucosa. For this purpose, usually used gels used in teething, for example, dentinox, calgel or kamistad.
- Clean the gums with antiseptics, for example, chlorhexidine, infusion of calendula, chamomile decoction, miramistin or furatsilinom. The child should rinse his mouth with warm remedy 6 times a day and always after meals.
- Reduce the temperature if it is elevated. To do this, the child is given fever-reducing antipyretic drugs at his age.
Tips
- When a baby sores or rashes appear on the gums, the baby should be isolated from other children, since the disease can be contagious.
- A child with stomatitis should definitely select individual hygiene items and dishes.
- Food for a baby with stomatitis on the gum should be fluid and warm. It is important to exclude irritation of the oral mucosa, so no cold, sour, sharp or hot dishes should not be given to the child.
- Give your child a lot of drinking and air the room regularly.
- When the child recovers, purchase a new toothbrush for him.
Prevention
To prevent the child from stomatitis on the gums, it is important:
- Regularly go to the dentist and treat bad teeth.
- Brush your teeth twice a day and rinse your mouth after meals.
- Buy high-quality toothpaste.
- Eliminate the effect on the child allergens.
- Teach your kid to wash his hands after a walk, before eating and after using the toilet.
- Limit the sweetness in the baby’s diet, give enough fruits and vegetables.
- Strengthen the child's immune system.