Fistula on the gum in a child
If a child has a fistula on the gum, it cannot go unnoticed by the parents. There may be several reasons for such an education, but in any case, it is not worth delaying the referral to a doctor, since the fistula may cause serious complications.
The reasons
Fistula is a channel inside the gums of a child, which is formed due to purulent inflammation. Through this canal, the pus that has gathered inside the inflamed gums comes out. Such pathologies lead to the formation of a fistula:
- Periodontitis. This is one of the complications observed in a child with untimely detected and cured caries. Due to the anatomical structure of the jaw with such a pathology, a bright red connective tissue, called granulation, grows. It destroys healthy cells and under the influence of some external factors (hypothermia, viral infection, overwork) provokes the formation of a fistula.
- Osteomyelitis. If this infection affects the jaw bones, then due to weak immunity, it quickly spreads upwards with the formation of a fistula.
- Cyst. Such education may appear in the gums of a child in the process of teething, due to late treatment of teeth, as well as in violation of their normal development, for example, when baby teeth fell out early or in a child rickets. If an infection gets inside the cyst, it becomes inflamed and as a result a fistula appears.
- Sinusitis. If the disease develops in the maxillary sinuses and it is caused by a dental disease, sinusitis can be complicated by the appearance of a fistula. At the same time, the child will also have other ENT-symptoms, for example, a stuffy nose and deterioration of smell.
- Injury. If a child damages the gum during a fall, eating solid food or a sharp object, then when bacteria enter the wound, purulent inflammation begins, resulting in a fistula.
The most common fistula on the gum of the milk tooth occurs as a result of neglected caries. The first stages of the disease often pass unnoticed, as they are represented only by white spots or caries can develop between the teeth. Due to insufficiently strong enamel and feeding habits of children, caries in childhood spreads rather quickly.
If the child complains of pain, then the infection has already fallen into the pulp, which threatens purulent inflammation of the roots. Bacteria and their toxins cause inflammation with the formation of pus. When pus collects near the root, it tries to find a way out through the gum tissue, which is manifested by the appearance of an abscess on the gum. If you do not go with the baby to the doctor in time, who will open such an abscess and treat it, the pus breaks out on its own in the form of a fistula.
In addition, a medical error can lead to the appearance of purulent inflammation in an infected tooth decay, if the dentist during the treatment did not sufficiently clean the tooth from infected tissue or accidentally perforate the root. After closing such a tooth with a temporary or permanent filling inside, bacteria continue to develop, which causes inflammation with the formation of pus and the formation of a purulent lump first on the gum, and then fistula.
How does it look
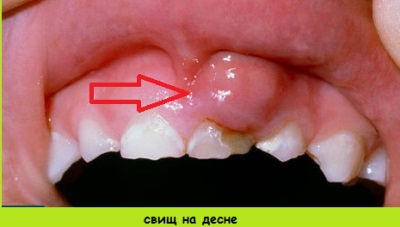
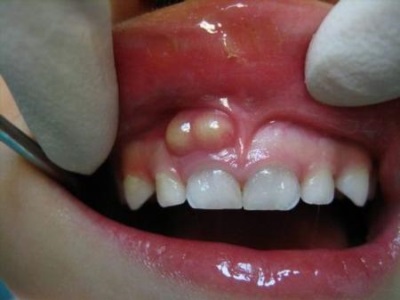
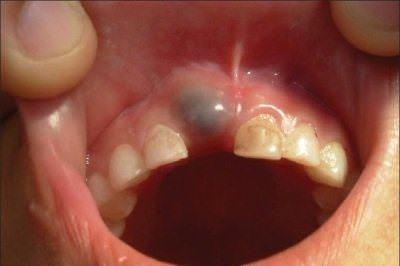
A fistula can form on the gum of a child of any age - both in the first years of life, and at 5 years of age or at school age. It is a small tubercle from which pus or blood is released (especially if you click on the sore area).Around it, the gums mucosa is usually reddened and swollen.
You can learn more about what a fistula is, how it forms and looks, you can watch the following video.
Other symptoms
Parents can notice fistula on the outside or on the inside of the gum with the naked eye, but the child will also have the following symptoms:
- Pain when the child touches the area of the fistula or food enters it.
- Increase tooth mobility.
- The appearance of bad breath.
- Increased body temperature (not in all cases).
Possible complications
When a child develops a fistula, as a rule, the symptoms preceding its appearance (fever, feeling of spreading, pain) decrease. But this does not mean that the disease can be ignored and wait for the fistula to close itself. If left untreated, the following problems are possible:
- Pus can get with saliva on the tonsils and cause their chronic inflammation.
- Ingestion of pus in the gastrointestinal tract can also cause inflammatory processes in the intestine.
- Because of the granulations that make up the walls of the fistula, the soft tissues next to them can collapse, resulting in purulent sinusitis or a hole in the cheek.
- Bacteria can spread into the jaw bones and cause flux.
What to do
Since the fistula is one of the symptoms of the inflammatory process in the mouth, it is very important to immediately show the baby to a specialist as soon as he is seen in the baby’s mouth. The doctor should exclude a wen or a cyst in the gum, as well as clarify how common the inflammation is, so the child is often sent for an X-ray examination. Only after this the dentist will decide how to treat the fistula on the gums.
Treatment
Depending on the cause of the fistula in a child, medical, therapeutic and surgical treatment can be applied.
- If a fistula is formed due to purulent inflammation of the root of the baby tooth, as a rule, the tooth is removed, even if the child is only 6 years old or 7 years old and the physiological change of this tooth does not occur soon. This helps prevent infection of the germ of a permanent tooth.
- When a fistula is formed due to a medical error or when the root of the permanent tooth is inflamed, an opening of the canals and the removal of pus, as well as all dead tissue, are shown. Next, the dentist will perform disinfection and close the tooth with a temporary filling. On the next visit, the doctor will assess whether new foci of infection have appeared, after which a permanent seal will be placed on the tooth.
Among the medicines prescribed for the fistula, there are:
- Antibacterial drugs.
- Antihistamines.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments or gels.
- Antiseptics for rinsing.
Treatment must include rehabilitation measures aimed at preventing fistula recurrence. They consist in local use of the laser, ultrasound or diathermoglagulyatsii, with the result that the fistula painlessly cauterized. Also used for the restoration of rinsing and irrigation.
In the course of treatment, the child must comply with all the recommendations of the doctor. The diet during the period of therapy and recovery should be gentle, therefore, it includes unsalted, unsharp wiped food, which will not irritate the diseased part of the gum. It is allowed to take it 3 times a day, and after each use the child must rinse your mouth.
Folk methods
Traditional medicine is used as an additional treatment and must be agreed with the doctor. They are aimed at reducing inflammation, as well as disinfecting the oral cavity and speeding up recovery. Replace the treatment at the dentist, such funds can not.
The most common and effective recipes are:
- A glass of warm water, in which you need to add a teaspoon of soda and 1 drop of iodine.
- A mixture of leaves of strawberries and calendula flowers (10 g each), brew in 200 ml of water.
- Poured over 100 ml of boiling water the herb of Hypericum taken in an amount of 10 g.
- 10 g of oak bark, chamomile flowers and sage leaves, brew 100 ml of boiling water.
- Boil 200 ml of boiling water with 50 g of chamomile flowers.
Prepared tools can be used for rinsing, and if the child has not yet learned how to perform such a procedure, then make applications with a cotton swab or irrigation. You can also grind these medicinal herbs in a coffee grinder, mix with sea buckthorn oil and apply such ointment on the sore spot.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of a fistula in the child’s gum, it is important:
- Pay attention to hygiene procedures that clean the mouth.
- Time to treat all dental pathology.
- Regularly go to the doctor for a checkup.
- Immediately show the child to the dentist if a purulent bump appears on his gum.