How is breast milk produced?
With the ability to produce milk in the breast of a woman, we can provide the newborn baby with the nutrients it needs. The production of breast milk in a female breast after pregnancy is called lactation.
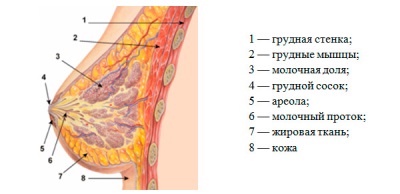
The internal structure of the mammary glands
Milk production occurs in the glandular tissue represented by the alveoli. So called small "bags" in the breast of a woman who produce milk. From such "sacs" ducts emerge, which are interconnected and merge into the milky sinuses next to the nipple. About ten to twenty ducts leave these sines to the nipple.
Many mothers with small breasts worry about the amount of milk that will be produced in their mammary glands after childbirth. However, the difference in the size of the mammary glands is mainly influenced not by the amount of glandular tissue, but by the content of adipose tissue. In addition, by the end of pregnancy, most expectant mothers are breast augmented.
Changes in the breast during pregnancy
Although milk production begins when the baby is already born, various processes and changes occur in the breast during pregnancy, designed to prepare it for lactation. This is primarily hormonal changes. Simultaneously with an increase in the number of estrogens in a woman's body during pregnancy, stimulation of the production of the hormone prolactin begins. It is this hormone that stimulates the breasts to start producing milk. Its amount increases by the end of the gestation period, but thanks to the circulation in the blood of pregnant progesterone and estrogen, milk is not yet formed.
Nipples, as well as areas of the breast around them (they are called areoles) become darker and increase. Small bumps appear on them, represented by glands secreting sebum. It will serve as a natural moisturizer that is responsible for the elasticity and softness of the nipples.
Breast augmentation
By the end of pregnancy, simultaneously with a decrease in the level of progesterone, as well as estrogen, the activity of prolactin increases, which is a stimulus for the mammary alveoli. The alveoli are filled with milk and stretched, so the woman’s breasts increase in size. However, milk often does not flow, but remains in the breast until the baby starts to suck it. Also one of the factors in the increase in the female breast in size during pregnancy is an increase in blood flow to the gland.
Colostrum
The first of the female breast begins to stand out a yellowish liquid called colostrum. This type of milk has a high content of proteins, but more valuable for colostrum is a significant amount of antibodies, as well as minerals. Due to this composition, colostrum will protect the baby from inflammatory and infectious diseases, as well as exert a laxative effect in order to clear the intestines of the infant from meconium.
Although colostrum does not stand out much, it is fully capable of meeting the needs of a newborn baby. In addition, this type of milk contains active substances that prevent the development of allergic reactions and stimulate the work of the children's intestines. That is why it is important that the crumbs are applied to the chest in the first minutes after childbirth.
Colostrum is released in the first few days after birth. Within three or four days after birth, milk begins to be released from the breast, which is called transitional. In it, the concentration of minerals and protein is reduced, and fat becomes more. The amount of milk also increases. Often, on the 3-4th day of the postpartum period, the woman has a strong milk rush.

Mature milk
This type of breast milk begins to be produced in the breast of a nursing mother from the second week after birth. Its composition is constantly changing to meet all the needs of a growing baby. On average, such milk contains about 1% protein, about 6-7% carbohydrates and 3-4% fat. Read more about composition and fat content of breast milk read in another article.
The formation of human milk in the postpartum period
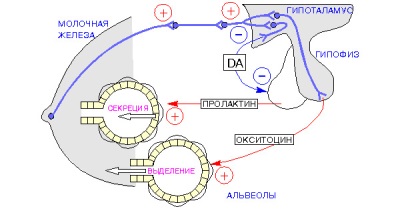
Both hormones and the reflexes formed with their participation affect the formation of milk in the female breast. Thanks to a certain hormonal balance, milk begins to be produced in the mammary glands, and the supply of this valuable liquid to the baby is provided by reflexes.
The role of prolactin
The main function of this hormone is to stimulate the formation of mother's milk in the breast. When the baby sucks the breast, the nerve endings located on the nipple are stimulated and send signals to the brain tissue of the mommy. It also produces prolactin. The peak of his appearance in the mother's body comes at a time immediately after the baby sucks the breast. It helps to accumulate milk inside the breast for the next feeding.
The process linking nipple stimulation by sucking and milk secretion in the breast is called the prolactin reflex. Note that this hormone is produced more at night, so sucking during a night's sleep is especially important for maintaining lactation. Another effect of prolactin is the suppression of ovarian activity and delayed menstruation in lactating women.
The role of oxytocin
The main function of this hormone is to stimulate the release of milk from the breast. When the baby sucks the breast and stimulates the nipple nerve receptors with this action, this affects not only the level of prolactin. Oxytocin is also produced at the same time. It is responsible for the contraction of the muscle cells inside the breast glands. These cells are placed around the alveoli, so milk begins to flow through the ducts to the sinuses and nipples. Another effect of this hormone is to reduce the muscle tissue of the uterus, which is especially important for stopping bleeding after childbirth.
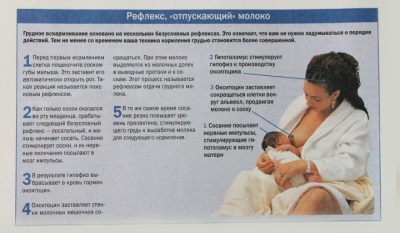
The process that binds the child to stimulate the nipple and release milk from the breast is called the oxytocin reflex. Since oxytocin "works" during feeding, it therefore ensures the release of milk to feed the baby during the breastfeeding process.
Such a reflex can be affected by the emotions and feelings of the mother, which can hinder or facilitate the production of milk from the breast for the baby. If mom is sure of success breastfeeding, relaxed and positive, oxytocin is actively produced. If mommy feels discomfort, pain, doubts, worries and worries, the reflex of oxytocin can be inhibited.

The relationship of the requirements of the baby and milk
It is important for the nursing mother to understand that more milk will be produced in the breast in response to sucking the baby. The more crumb will suck mother`s breast, the more milk production will occur. That is why the breast gives just as much milk as the baby “requests” from her. And if mother's goal is to increase lactation, then the child should be applied more often and longer, or express breast milkremaining after feeding.