What is preimplantation diagnosis in IVF and what does it show?
Women who go to IVF, are not always well aware of the main stages of this technique. And when the doctor is interested, patients would like to do pre-implantation diagnosis, there are even more questions. Some refuse, knowing that PGD makes the protocol more expensive, others simply do not know the purpose for which such genetic research is appointed and whether it is needed at all. In this article we will explain what PGD is about in IVF and what it can tell about.
PGD - what is it?
From the moment a woman’s egg merges with a man’s sperm cell, everything is predetermined at the genetic level - the child’s hair color and growth, intellectual ability and gender, as well as possible genetic abnormalities and diseases that the child inherited from parents, grandparents or other relatives .
Pre-implantation diagnostics is a complex of genomic studies, which makes it possible to identify in the embryo, which is only a few days old, various developmental deviations, diseases, syndromes and other troubles. PGD is able to identify about 150 hereditary genetic ailments, among which are fairly common - Down syndrome, Turner, and quite rare - cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, butterfly wing syndrome, etc.
Using special techniques and high-precision equipment, diseased embryos are determined and screened out. For transplantation into the uterine cavity, women use only high-quality, healthy and viable embryos.
Standard IVF does not include the mandatory stage of pre-implantation diagnosis. After fertilization and the cultivation of embryos for several days, only growth rates, crushing rates, and viability of embryos are assessed. After that, they are transferred to the uterine cavity of the woman. Which of them will take root and take root at all is a big question. The effectiveness of standard IVF is about 35%.
If pre-implantation diagnostics is performed, then future parents may not worry about the state of health of the baby, even if they themselves have certain genetic problems. In addition, the effectiveness of IVF with PGD is somewhat higher - about 40-45%. This is due to the fact that a large embryo, even if implanted in the uterus, has very little chance of development and survival. A healthy and examined embryo is more likely to gain a foothold and begin to grow and develop.
Purpose of the survey
PGD is strongly recommended to parents who have genetic diseases that can be inherited by a baby. Also, such a preliminary genetic examination of embryos would not hurt if there were hereditary diseases in the ranks of close relatives of the future parents.
Diagnosis before implantation is important and necessary for couples in which one of the parents carries the disease linked to the sex chromosome. For example, a woman carries a hemophilia gene, but a child will only be sick if it is a male baby. PGD in this case determines the sex of embryos that are only a few days old, and doctors select only embryos that are not threatened with hemophilia, that is, girls, for replanting.
A woman with a negative Rh factor and several pregnancies in the past (it does not matter how they ended), PGD is recommended, if the sperm of a husband with a positive Rh factor was used for in vitro fertilization. In this case, the doctors will select from all the resulting embryos only those who inherited the maternal Rhesus identity. In this case, pregnancy after IVF will proceed with less risk, and the baby will not be at risk of hemolytic disease.
PGD is recommended for a couple if a woman has had two or more miscarriages earlier, if there have been cases of missed abortion, and also if either of the spouses in the first marriage or together they have a child with chromosomal abnormalities or genetic pathologies. Diagnostics before transfer allows to exclude from the number of embryos considered for transplant those who are ill or have anomalies of non-genetic origin.
Pre-implantation diagnostics in the second or third IVF protocol allows to establish with high accuracy the causes of previous attempts failed.
And a completely non-standard, but, alas, the real situation - parents go to IVF to have a baby who can become a donor, for example, of the bone marrow, for their own elder brother or sister. In this case, relying on natural conception is too risky. A born child may not be suitable as a donor for a sick relative.
Pre-implantation diagnostics will help to select individuals from the resulting embryos with a certain combination of genetic information that guarantees genomic coincidence between children. This study is called HLA-typing.
What does the survey show?
Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis allows you to pre-identify various diseases and conditions in which a child may be unviable or disabled. It all depends on the recommendations given by the geneticist. If necessary, embryos are examined only for certain criteria and gene mutations, but in general there is the possibility of estimating all the parameters determined by the study.
For example, PGD with an accuracy of 97-99% determines blindness and deafness, congenital deafness, retinoblastoma, Fanconi anemia, neurofibromatosis, phenylketonuria, myopathy, torsion dystonia, muscular dystrophy of Duchene and several dozens of dangerous and incurable diseases and syndromes.
PGD also determines the karyotype of the embryo, its blood group and Rh factor, gender, the presence of mutations at the gene level, unusual for parents and manifested for the first time.
Who is prescribed?
Since the pre-implantation diagnosis itself is not cheap pleasure. Not every woman who has dared to in vitro fertilization, this additional step is recommended. It is offered to everyone, but there are categories of patients who are highly undesirable for refusing the preliminary genetic assessment of embryos before transfer to the uterus.
These patients include:
- "Age" women and couples. With age, the male and female sex cells age and lose their health. Under the influence of drugs, bad habits, unfavorable ecology and just past years, their DNA-set can mutate. Therefore, in “age-related” women and men, the risks of fetal chromosomal abnormalities are higher. PGD is highly recommended for women over 35 years old, as well as for couples in whom a man is over 40 years old.
- Rh-negative womenwho had abortions, miscarriages, childbirth, children were born with hemolytic disease. Diagnosis is relevant only if the spouse has a positive Rhesus blood factor. If donor sperm is used, then the male biomaterial is initially selected with a negative Rh factor, then the probability of obtaining Rh-positive embryos is zero.
- Women who already have an experience of 1-2 unsuccessful IVF attempts in the absence of objective reasons (the protocols were conducted correctly and without complications, there is no endometriosis and other barriers to implantation).
- If male sperm is used for fertilization with low sperm quality indicators (teratozoospermia, azoospermia, asthenozoospermia). With the natural conception, low quality sperm cells die, have no chance of fertilization, with IVF they may well fertilize the egg, because natural selection is impaired, which can lead to the development of various pathologies in the fetus.
Types of diagnostics
There are several types of genetic diagnosis of embryos. They differ in terms of research, technical nuances, equipment and methods of research. We list the main ones without going into laboratory and genetic details:
- FISH - This is a method of fluorescent hybridization. This is a fairly standard study, the cost of which is low compared with other methods of pre-implantation diagnosis. But its accuracy is somewhat lower than that of other methods. This method is widely used in clinics in Russia, Ukraine and Belarus. Foreign clinics practically abandoned it due to the fact that more accurate studies appeared. Plus the fact that the study takes place quickly - within a few hours. The downside is that many chromosomes are not even being investigated.
- CGH - comparative genomic hybridization method. Very expensive way. And both financially and temporarily. But the list of identified pathologies is greater than that of the method described above, and the accuracy is immeasurably higher. Among other things, this method of diagnosis prior to replanting allows you to determine which embryos have higher chances of implantation.
- PCR - polymerase chain reaction method. It reveals the Rhesus identity of the embryo, its blood group, as well as a rather large list of genetic problems. The study requires a mandatory preliminary examination of biological parents for genetic mutations. If a woman gets a donor embryo or donor oocytes are taken for fertilization, the PCR method cannot be used.
- Ngs - sequencing method. This is a modern method of pre-implantation diagnosis, which combines the best of all listed above. It gives the most complete picture of the health status of embryos, however, and its cost is higher than that of other methods.
How is the research going?
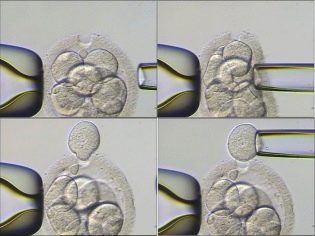
In order for embryologists and geneticists to have the ability to do PGD, a sufficient number of eggs must be obtained through prior hormonal stimulation. If less than 3-4, then pre-implantation diagnosis is usually not carried out. After the doctors “arrange” a meeting of the eggs with purified sperm, the development of embryos is monitored for 2-5 days. Then the embryologist can select the most viable. On the fifth day, the blastocysts already have about 200 cells. It is possible, without prejudice to the embryo, to take about 5-7 cells from each embryo for genetic research.
Modern high-precision lasers are used to collect cells, cell shells are biopsied, and other methods are used. A DNA strand survey provides comprehensive information on whether the embryo is healthy. After which it is recommended for transfer.
If the pair agrees on the preliminary genetic diagnosis of embryos, the embryo transfer itself may be delayed. If with the standard IVF protocol it is carried out for 2, 3 or 5 days from the moment of fertilization, then PGD results can be expected from several hours to 5-6 days. Thus, the IVF cycle is extended by at least a week. The cost of the protocol may increase in case of consent to the preliminary diagnosis of embryos by 40-240 thousand rubles.
It all depends on how many embryos you plan to examine, which method of the above will be tested.
To reduce costs, a couple can use quota tools, diagnostics is included in the list of services that can be provided by the OMS, but each clinic should clarify this issue separately. Some do PGD at the expense of the budget, others - not.
Possible complications
As already mentioned, the material for the study of genetics is obtained by biopsy. Despite the ultramodern precision equipment, there is still a chance of injury to the fetus during this procedure. Most often injured are subject to "three days". It should be noted that the probability of injury is quite low - about 3%, and the benefits of the study will be much greater. Otherwise, the complications with this IVF may be the same as with IVF in a standard protocol.
Any of the stages of in vitro fertilization can be associated with certain risks, and this will not go anywhere. It is important that all risks are low.
The couple needs to be well aware that even modern and precise instruments with which doctors of the highest qualification category work do not guarantee 100% that the baby will be healthy. Thus, with extensive mosaicism, biological errors can occur, and a diseased embryo can be transferred to a woman. This probability is, but it is very small - no more than 0.05%.
Reviews
According to official information from the World Health Organization, IVF with PGD increases the chance of protocol success by about 7-10% relative to the base 35%. However, there are not so many positive reviews in the Russian segment of the Internet about pre-implantation diagnostics.
Some women note that the survival rate of embryos from which cells were taken for analysis is somewhat worse, and therefore there are quite a few reviews of unsuccessful IVF protocols with preliminary genetic diagnosis of the fetus. The medicine does not confirm this popular opinion, and the official statistics of the statistics do not indicate a reduced percentage of successful implantation after the examination of embryos.
Often, women ask if it is possible to make an IOP to choose the sex of a baby, because besides the fact that I really want children, I still want either a son or a daughter. There is no technical ability to determine the gender, but no doctor will sift out the embryos of the “unnecessary” gender, unless there is a specific indication of the genetics (for diseases linked to the sex chromosome). Discrimination of embryos by gender is prohibited by law in Russia.
According to reviews, the process of diagnostics itself, which can last several days, delivers many experiences to a woman, because she doesn’t know to the last how many high-quality embryos turned out and whether they turned out at all. In addition, she needs to maintain the state of the endometrium in the right form — take prescribed medications, donate blood for progesterone, and do several ultrasounds to determine the thickness of the functional layer of the uterus. It is important that the transfer is carried out as successfully as possible and the fertilized egg can be implanted.
It happens that while the diagnosis is in progress, the “good” time for the transfer passes. In this case, the protocol can be interrupted, and the embryos that have passed the test are frozen and sent to the cryobank. Transfer them will be in the next protocol.
About the intricacies of preimplantation genetic diagnosis, see the following video.