Embryo transfer in IVF: features and sensations after the procedure
The birth of children conceived "in vitro", in our time is not something out of the ordinary - it is common practice in the case of family infertility. There are about 5 million people on the planet today who were conceived through IVF. This procedure consists of several successive stages. Embryo transfer is the final step of the IVF protocol and, perhaps, the most crucial. About how it passes and what a woman can feel after replanting, we will look at this material.
What it is?
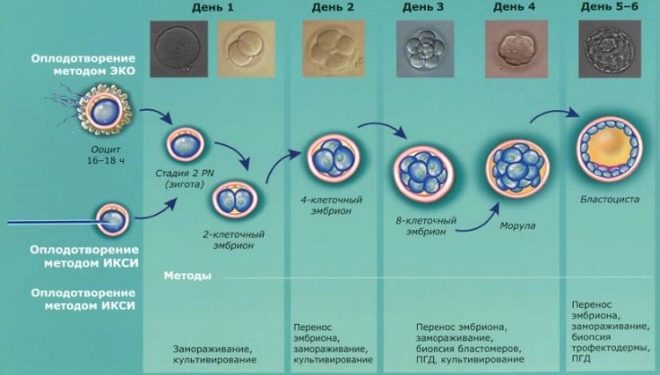
Fertilization itself in IVF is not done in a test tube, despite the well-established definition, but in a Petri dish - in a special container into which the sex cells of a man and a woman are placed. Sometimes the meeting of sperm and egg has to "organize" by hand - the method of ICSI. If fertilization took place, after 14 hours, initial metamorphoses are observed in the structure of the egg. Next begins the cultivation of embryos.
Growing embryos under the watchful supervision of embryologists takes several days. The transfer of “grown-up” embryos to the uterus is performed when, in the opinion of the reproduction specialist and embryologist, the most favorable time for this comes.
The transfer itself is standard, double and combined. In the case of standard transfer, the procedure is performed once on the designated day. When double replanting is carried out twice, an embryo is first planted, which was cultivated 2-3 days after fertilization, and then an embryo was planted, which reached the blastocyst stage (5-6 days after fertilization). Double transfer increases the couple's chances of a long-awaited pregnancy. But there is also a reverse side of the medal - the previously transferred embryo can “fall out”, it will be washed off with a solution. Also increases the likelihood of multiple babies.
Combined transfer increases the chances of conceiving with a repeated protocol after an unsuccessful one. With it, two types of embryos are introduced - fresh, obtained in the current protocol, and cryopreserved, which froze in the previous protocol or even earlier. Such replanting is most often done in the natural cycle, without prior hormonal stimulation of the ovaries.
If the protocol is successful, a few days later implantation transferred embryos to the uterus. The embryo takes root and begins a full, quite normal pregnancy.
Optimal time
Embryo cultivation is an interesting and painstaking process. The embryologist has practically no right to make a mistake - to transfer, one needs to select the strongest and most viable embryos. From this depends largely on whether IVF is successful.
The transfer date is determined individually. In this case, the age of embryos should be within 2-6 days from the day of fertilization. However, there are exceptions. What they can be connected with:
The number of embryos received
If you get a lot of embryos (more than 2-3), then choose the best for the second day of cultivation is quite difficult, it takes more time to assess the rate of crushing of the egg.In this case, the transfer may be slightly delayed. This is called prolonged cultivation, its purpose is to track the development of each of the embryos, because some may stop developing or slow down.
If few germs are obtained, then the dates can be shifted to the lower side, that is, the transfer can be carried out already on the second day after the start of cultivation. This is due to the fact that in the uterus, if the implantation takes place, the embryo will be better than in the nutrient medium, and in fact it has no choice - the quantity is limited. Either he or nothing.
The state of the endometrium of the uterus
The functional layer of the main female reproductive organ should be sufficient in thickness and structure. The looser the endometrium, the better for embryos - it will be much easier to attach to the membranes.
Therefore, a woman is prescribed progesterone drugs after the collection of eggs, this hormone contributes to the preparation of the endometrium for the upcoming implantation of embryos.
If the reproductive specialist according to the ultrasound results concludes that the endometrium is not ready, the embryo cultivation will be extended.
Age of the woman and the number of IVF protocols in history
The younger the woman, the higher the probability of successful replanting. Therefore, during the first IVF at the age of 35, doctors try to transfer into the uterus embryos - “two-day” or “three-day”.
If a woman is over 35 years old, and already has several IVF attempts on her shoulders, the date of embryo transplantation is postponed to a later date. It is believed that "five-day" or "six-day" embryos attach more often.
The state and well-being of women
If the patient has suddenly caught a cold, she developed symptoms of ovarian hyperstimulation after collecting oocytes, if any chronic diseases worsened under the effect of the hormones taken earlier, the transfer will be postponed for an indefinite period of time. Quite often in this case, the protocol is interrupted. Two-day and six-day embryos are frozen and stored in a cryobank until the next attempt.
After recovery, a woman can be combined combined in a natural cycle or cryo-transfer.
Quite often, fertility specialists use a standard formula to determine the date of transfer (provided that the woman’s body is fully prepared for the procedure and there are no contraindications):
- if by the third day of cultivation more than 5 embryos of good and excellent quality are obtained, the transfer is carried out on the fifth day;
- if by the third day of cultivation less than 5 embryos were obtained that meet the “good” or “excellent” standards, transfer is carried out immediately on the third day.
In any case, the date of the procedure is set individually, taking into account all the factors listed above and the special circumstances that may arise.
Number of embryos
This question is not so much medical as ethical, and bioethics considers it. It is recommended to transfer as many embryos as the mother can bear and give birth if they take root. The method by which a large number of embryos are planted, and then, after the onset of pregnancy, resection (removal) of the “excess” is performed, from a moral point of view it is unpleasant.
From the position of most religions, resection is no different from abortion. Yes, and the woman who fought so long for the right to become a mother would be morally difficult to choose which of her children to kill and who to give life to. Preserving all embryos in the uterus can be dangerous for a woman, because carrying four or five babies is an extremely difficult task. Therefore, there are recommendations of the Ministry of Health, which state that for women who have not yet turned 40, no more than three embryos can be transferred with her consent, and for women older than that age - no more than four. Quite often, only two embryos are planted. According to the established practice, only 1–2 survive in 40% of cases when replanting 3-4 embryos. Overwhelmingly, one baby gets accustomed.
There are categories of women who are immediately recommended to transfer only one embryo, no more. The chances of conception are, of course, reduced, but the likelihood of a successful pregnancy, if everything goes well, increases immeasurably. In addition, there are no torments of conscience and moral and ethical problems. These women include:
- patients with scars on the uterus (after surgery, cesarean section in history);
- surrogate mothers, if biological parents do not want two kids;
- in vitro fertilization donor programs.
In most cases, only 1 egg can be obtained in the natural IVF protocol; therefore, without options, the woman also falls into the list of those who are transferred to only one embryo, provided that the quality of the embryo is good or excellent.
Training
Most often, women who have to undergo an embryo transfer procedure for IVF, care about how to properly prepare for this. Can I drink and eat, do I need to do an enema and empty the bladder. Since the procedure itself is quite simple, it does not require any specific preparation. But there are several important rules that should be followed before this important stage of IVF:
- in the morning before the procedure you need to take a warm shower, without using aggressive cosmetics;
- it is better to fill the bladder so that the uterus is better visualized on the ultrasound, and therefore you need to drink several glasses of clean drinking water a couple of hours before the manipulation;
- on the day of the procedure do not wear jewelry and jewelry, contact lenses, and do not use cosmetics and perfumes;
- Breakfast on the day of the procedure should be easy, easy for the digestive system.
Before manipulation, a woman should do a blood test for progesterone. The next time, the level of progesterone will be determined in the blood plasma of a woman as early as 7 days after transplantation.
In the days preceding the replanting, it is important for the woman to pay special attention to the prevention of SARS and influenza, not to be in crowded places to prevent infection with viral ailments. Sexual relations are contraindicated, as well as stress and excessive exercise. On the eve of the manipulation you need to go to bed early to get a better sleep and feel cheerful. There are no special recommendations regarding diets and regimen before this procedure.
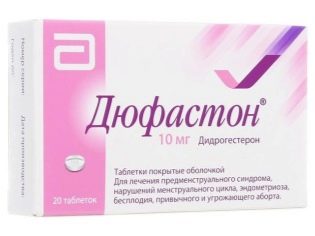
As already mentioned, the readiness of the endometrium of the uterus of a woman before transfer is an important component of a successful protocol. It is to ensure that the functional layer of the reproductive organ reaches the necessary requirements that progesterone drugs are prescribed - “Utrogestan”, “Duphaston”, “Proginova”, “Kraynon” and others in individual dosages. Often before the transfer prescribe anti-inflammatory drug "metipred."
The mucous membrane of the uterus under the action of these drugs begins to become more loose. This facilitates the stage of adhesion - sticking of the ovum. Progesterone preparations improve the endometrial filling of the blood; this facilitates the second implantation phase — invasion, in which the embryo's membranes go deeper into the endometrium and grow into it, connecting with the mother’s blood vessels.
The optimum value for transferring is the endometrial thickness of the uterus at the level of 9-12 mm.
Technique of
The procedure of embryo transfer should not frighten a woman - it is not painful, not scary, and not long. Manipulation is performed under sterile conditions, in the same small operating room, where the eggs were taken from the woman. Before the procedure, patients are usually offered to take a sedative drug to calm down and cope with anxiety. You can refuse it, because there will be no pain.
Before starting, with the married couple or the woman herself agree on the number of transferred embryos and decide what to do with the rest if there are “extras”. A woman by law can dispose of them at her discretion.
There are several options:
- to consent to cryopreservation and long-term storage in a cryobank (it can be useful if the protocol is unsuccessful and the pregnancy does not come, as well as a few years after the successful protocol if you want another child)
- give embryos as donor cryobanks of the clinic for use in programs of other infertile couples who need donor material;
- give the embryos to the needs of science for the study and experiments;
- Dispose of embryos by disregarding them until natural cessation of development.
Any decision of the patient is documented and signed by her personally. After that, the woman is escorted to the operating room, placed on a gynecological chair, and primary treatment of the external genital organs is performed.
Embryos will be inserted into the uterine cavity through a thin polymer catheter, which will be inserted through the cervical canal inside the cervix. The process is not very pleasant, but not painful. The material of the catheters is not toxic and does not harm the embryos.
After the introduction of catheters, the embryologist transfers a 1 ml syringe with a certain number of embryos in the nutrient solution to the fertility specialist. The syringe is carefully connected to the outer end of the catheter and its contents are slowly introduced into the uterine cavity. It is important that a slow and careful introduction take place.
The whole process is monitored by an abdominal ultrasound transducer. This allows you to see the location of the catheter inside the uterine cavity. It is important that the catheter reaches the bottom of the uterus (upper part), but in no case touches the endometrium, so as not to injure the mucous membranes.
After insertion, the catheter is carefully removed and immediately visited under a microscope to rule out a situation in which embryos could remain in it.
In severe cases, double-lumen catheters can be used, while antispasmodics are injected into the vein that will prevent spontaneous uterine contractions.
The procedure takes about five minutes. After that, the woman is recommended to stay in a horizontal position for about 40 minutes, then she is allowed to get up and go home.
What can you feel after replanting?
During the first day after the manipulation, the woman may feel that she is slightly weakly “pulling the belly” or there is a slight pain “as before menstruation.” This is a normal reaction to inserting a catheter into the cervical canal. Small mucous or spotting should also not embarrass and frighten. One should not expect that the sensations by day will differ significantly from those that the woman had before the transfer - most patients do not have any particular symptoms.
Small nagging pains may be the body's response to hormonal drugs, which were used in the first phase of the cycle and are now prescribed to increase the likelihood of implantation. It is impossible to feel the implantation itself, but some women have a so-called implant bleeding approximately 7-9 days after the transfer. It is manifested by the appearance of a brownish "daub" on the gasket. This is a good sign that may indicate that the implantation was successful.
It should be remembered that the implantation after the transfer may occur later - on the 10-11 day, and therefore it is too early to start to get upset from the absence of any "pregnant" sensations.
With a positive result on the 14th day after the transfer, you can do a blood test for hCG. Previously, there is no sense, as there is no sense in conducting pharmacy tests, because a woman was injected with an hCG injection to mature oocytes, and hormone traces are present in the blood plasma. A premature analysis done too hastily can give a false positive result and, consequently, a false hope of pregnancy.
On the 21st day after the transfer, you should visit the doctor and make an ultrasound to make sure that the pregnancy has come and develops.Signs of pregnancy may appear not earlier than 14 days from the moment of embryo-transfer - usually they appear as engorgement and sensitization of the mammary glands, change in taste preferences, drowsiness or insomnia.
The basal temperature is not a very good method for diagnosing pregnancy after in vitro fertilization, because a woman takes progesterone, and this hormone causes the base temperature to remain at elevated values even in the absence of pregnancy.
Possible complications
Embryo-transfer rarely causes any complications. If the manipulation is carried out by experienced doctors, everything should go without negative consequences for the woman's body. Very rarely are recorded medical errors associated with the introduction of embryos that are too fast, as well as with the wounding of the end of the uterine mucous membrane catheter.
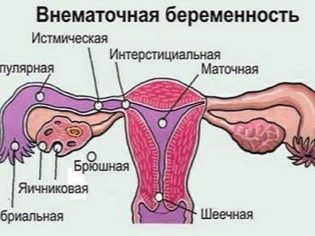
It is impossible not to take into account such possible complications as ectopic pregnancy - tubal or cervical. After the introduction of embryos, they are “in free flight” for several days, freely floating in the uterus, and therefore their penetration into the fallopian tube or cervix is not excluded. If the implantation takes place outside the uterine cavity, the pregnancy is doomed to interruption - there are no chances to survive in the embryo, and for the mother, the ectopic location of embryos can be deadly. Ectopic pregnancy after IVF occurs in 1-2% of cases. At the same time, approximately in half of these cases, a heterotypic ectopic pregnancy is recorded, in which one embryo attaches correctly - in the uterus, and the other - in the tube or neck.
The probability of infection of the uterus with the introduction and the development of the inflammatory process after it is not more than 0.02%.
Calling an ambulance for a woman is necessary when, after a transfer, the temperature lasts for several days, vomiting or diarrhea appears, the stomach hurts severely, and there is an abundant bleeding from the genitals.
Recommendations
An embryo is implanted in the uterus or not, no one knows - neither the doctor, nor the scientists, nor the woman herself. Therefore, it is quite difficult to increase the chances of implantation. General recommendations for women after embryo transfer are as follows:
- Take medication on a schedule without a pass. If your doctor prescribes progesterone, do not forget about the dosage and frequency. Missed admission can lead to a decrease in hormone levels relative to the norm. This will make implantation impossible. Low progesterone can also lead to the rejection of the ovum after successful implantation.
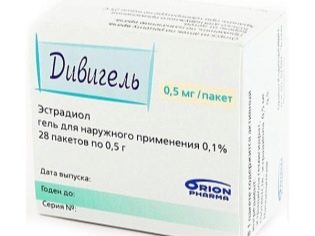
- To support pregnancy at the very initial stage, Dekapeptil, Diferelin, and Divigel are often additionally prescribed. If D-dimer is elevated in the blood, the use of Clexan is recommended. Schemes are purely individual, do not self-medicate and follow the scheme assigned to you.
- Avoid physical exertion, weightlifting, jumping, running, sharp squats.
- Exclude sex and masturbation.
- Do not take a hot bath, swim or sunbathe.
- Give up smoking and alcohol.
- Tune in positively because stress hormones disrupt the production of progesterone and by themselves can be a significant obstacle to the implantation and successful development of the fetus.
- The diet should be complete, for diets time is not suitable. Try to eat more animal protein.
- Take a walk every day in the fresh air.
It is important not to "wind up" yourself and not look for signs of pregnancy ahead of time. It is also desirable to clearly understand that the success of IVF is estimated at only 35-40%, and the probability of failure is higher than the probability of a successful protocol. This should be treated adequately to avoid depression and frustration, if you still begin monthly.
Reviews
According to women, the transfer takes place without complications, there is no difference in sensation when replanting fresh embryos or thawed after cryopreservation.
Many say that after replanting, secretions did not stop for two weeks or even more. There are also complaints of sleep disturbance and dizziness.
How the procedure takes place, how to prepare for it and how to behave after embryo transfer, will be told by obstetricians-gynecologists, fertility specialists of the Mother and Child Infertility Treatment Center of the Mother and Child Clinic Gary Zelimkhanovich Dostibegyan and Ekaterina Rurenkova.