What is the afterbirth? What are its functions and how does it look?
Postpartum separation is the final stage of labor. After that, the woman finally goes from the category of women in labor to the category of newly-made mothers. Everyone heard about the latter, but in practice there are a lot of questions about this. In this article we will talk about what the afterbirth is, how and why its birth occurs, and also open the veil of secrecy over the fate of the afterbirth after birth.
What it is?
What mothers and doctors call the placenta, in medicine, has a second, scientific name - the placenta. This body is temporary, it arises, develops, ages and is rejected in strictly limited periods. Need a placenta only during pregnancy. After the child is born, the need for a “childish place” is no longer there, it is born, completely ending its own existence.
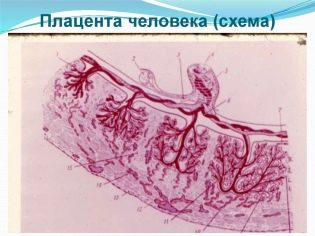
The placenta looks like a flat cake, a rounded disk. During pregnancy, its thickness and structure vary somewhat depending on the degree of maturity and some external and internal factors.
The placenta is located on the wall of the uterus, it is the link of two - mother and fetus. Through the placenta, the baby receives oxygen, nutrition, nutrients from the maternal bloodstream. Here, everything that becomes unnecessary for the baby is returned to the maternal organism: carbon dioxide, metabolic products. The placenta produces hormones that are important for the preservation of pregnancy and the induction of labor. During pregnancy, the “baby seat” serves as a reliable protection for the crumbs.
In the understanding of obstetricians, the placenta is not only the placenta itself, but also some other embryonic structures that depart from the uterus in the final birth stage. This is a part of the umbilical cord adjacent to the placenta, all shells and lobes of the placenta itself.
Formed "childish place" from the day of implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. The chorionic villi begin to grow into the endometrium, forming a complex structure. By the 12th week of pregnancy, the chorion becomes a young placenta. Normally, from 35-36 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta intensively ages, is depleted, and gradually loses its function. At the time of birth, the weight of the afterbirth on average is about half a kilogram.
The value of the placenta during pregnancy is difficult to overestimate. Considering its functions, it becomes an irreplaceable temporary body, without which or with pronounced pathologies of which it will be impossible to carry the child.
How is born?
The placenta in normal childbirth is born after the child. When the most difficult stage of childbirth is over, and the crumb was born, announcing the delivery room with the first cry, the third stage of labor begins for women. The mechanism of rejection of the afterbirth is laid by nature itself, and therefore the afterbirth, in the absence of complications, leaves itself. This happens within 20 minutes-1 hour after the birth of the fetus.
On the beginning of the birth of the placenta, the woman and the obstetrician announces the resumption of contractions. They are not as painful as pre-needy and fit. The placenta begins to exfoliate for quite physiological reasons - after the child leaves the uterus, the volume of the reproductive organ is significantly reduced, the walls of the uterus "sag". Holding on to them later becomes difficult. In addition, after cutting off the umbilical cord, the blood flow, which was fetoplacental, that is, connected the fetus and placenta, is disrupted.
At birth, a woman is asked to get pregnant at a time. This is enough for the placenta to fully come out of the womb. During the placenta detachment, obstetricians evaluate the signs of detachment from the uterine wall by specific signs:
- the uterus softens and changes the angle of deviation to the right side (Schroeder's diagnostic sign);
- the part of the umbilical cord that emerges from the genital tract after the birth of a baby, clamped with a clamp, begins to become longer as the placenta descends from its place down to the exit from the uterus (Alfred sign);
- an unconscious and strong desire to push, almost the same as a woman experienced at the beginning of the laboring period (the diagnostic sign of Mikulich).
There are other obstetric signs and methods for determining the separation of the placenta. The waiting time of separation is usually no more than two hours. If the last after this time does not depart naturally, it is removed manually.
This happens differently, depending on the method chosen by the obstetrician. A woman can have anesthesia or immerse her in a drug sleep. The fact is that the manual separation of the afterbirth is a very responsible and difficult stage, coupled with the risk of massive bleeding. The placenta in the first nine months of pregnancy is firmly growing into the uterine tissue, the blood vessels intertwine. Improper separation can lead to widespread injury to the uterine wall.
Most often obstetricians use the following emergency methods of expelling a placenta.
- By Abuladze - massage of the uterus through the abdomen and through the vagina with the subsequent seizure of the abdominal wall by the longitudinal fold and the simultaneous request to tighten.
- According to geteru - massage the bottom of the uterus with fists with a gradual pressure and placenta downward displacement.
- By Creed-Lazarevich - the bottom of the uterus is wrapped with the right hand so that one finger remains on the front wall, the palm is on the bottom, and the other fingers clamp the back surface of the reproductive organ. After, thus, "squeeze out" the remnants of the afterbirth.
A prerequisite for all types of manual separation is the independent separation of the “children's place” from the uterine wall with the subsequent difficulty of exiting the placenta. If detachment of the placenta does not occur, the woman is anesthetized and manual cleaning of the uterine cavity is performed with detachment and removal of the afterbirth.
Complications of the third stage of labor can be very different. The most common - the increment of the placenta, the total increment, the remnants of parts of the placenta in the uterus.
In order to avoid postpartum hemorrhage, which can be fatal for a woman, as well as for the prevention of inflammatory diseases of the uterus and genital tract after birth of the afterbirth, the doctor treats the uterus and vagina with antiseptic solutions.
The latter is placed on a special tray and inspected carefully from two sides - from the mother, adjacent to the uterus, and from the nursery - from the side of the umbilical cord attachment. If there are tears on the placenta, its integrity is broken, the doctor folds it piece by piece to make sure that nothing is left in the uterus.
What happens next?
This is the most mysterious moment. Usually a woman in labor is not up to it, she rests in the postpartum ward, the fate of the “baby seat” rarely worries anyone. The placenta in some nations was previously emphasized. In Russia, for example, she was buried under a sapling so that this tree would grow and grow strong with the child, give it strength in difficult life circumstances. Some tribes of Africa to this day have preserved the tradition of eating the placenta, as a product of incredibly valuable in its biological and chemical properties.
It is unlikely that a modern Russian woman will give an afterbirth with her after giving birth, even according to a preliminary statement, although in some regions, for example, in Chechnya, this is a common practice. The fact is that the afterbirth is nothing more than a biological tissue, exactly the same as amputated limbs.Therefore, it is customary to do with the placenta born as the law prescribes to deal with biological material.
There may be several options. It is considered legal to destroy it by cremation or burial in a common burial ground for biological waste materials. By law, the maternity hospital has the opportunity to transfer the afterbirth for scientific research, with the consent of the woman in labor is not required. The latter can serve as science and become material for laboratory experiments. Rules for the disposal of biological waste are usually spelled out in the documentation of a particular medical institution.
It is mandatory that the doctor saves the afterbirth and sends it for histological examination in the case of abnormal delivery, the birth of a sick or dead baby. This is necessary to establish the true cause of malformations, genetic abnormalities, causes of death of the child. The information obtained will be extremely important when planning a woman's subsequent pregnancy.
If there are no grounds for histology, the woman’s relatives theoretically have the right to request the delivery of the placenta for subsequent burial or other purposes, but the maternity hospital has full legal grounds for denying this request.
As for the vaunted healing properties of the afterbirth, according to which some nations recommend that women in labor have it, from the point of view of modern medicine, this is nothing more than wildness. The temporary organ has all the signs of human tissue, it even has a karyotype, identical to the karyotype of the child (46 XX, if a girl was born, or 46 XY, if the boy was born). Eating afterbirth - cannibalism in its pure form, since there will be nothing but human flesh.
Today there are many different false theories about the useful properties of the afterbirth, about its mystical and other properties. Experts advise women less to believe such theories, and certainly not try to repeat what some of them recommend.
If burial of the placenta is crucial for the relatives of the newly-born mother (there are fears that someone will extract stem cells from it and it will be enriched, or this is a religious conviction), you must first write a statement about the desire to pick up the last after birth. Relatives will need to come to the maternity hospital by the end of the birth and wait for the issue of the afterbirth, if, of course, they do not leave it for histological examination under strict medical indications.
On the birth of the afterbirth and the third stage of labor, see the following video.