Cough Inhalation Solutions
Diseases that cause coughing are common in childhood.
One of the methods of their treatment is inhalation, which helps to moisturize the mucous membranes, reduce inflammation, make sputum more liquid and improve its coughing than speed up recovery.
Indications and contraindications
Children may be given inhalation for such diseases:
- When coughing caused by SARS.
- With acute bronchitis.
- With laryngitis and pharyngitis.
- In case of bronchial asthma.
- In the period of recovery from pneumonia.
- With tuberculosis or cystic fibrosis.
Inhalation can not be carried out:
- Children younger than a year.
- Babies with bacterial sore throat.
- At elevated body temperature.
- Children with otitis.
- In case of intolerance to the drug.
- With frequent nosebleeds.
- When coughing with discharge of pus or blood.
- In severe condition.
Why the procedure is carried out when you cough?
Inhalation has such an effect:
- Stimulate the secretion of mucus when dry cough.
- Soften sputum and facilitate expectoration when wet coughing.
- Prevent the spread of infection in the lower respiratory tract.
- Bacteria and dead leukocytes are removed from the respiratory tract.
- Reduce the risk of complications.
- Strengthen blood flow in the lung tissue.
- Activate metabolic processes in the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
Inhalation and bathing with a dry cough cause a lot of sputum, so these procedures should be careful. For more on this, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.
Inhalation rules
- Procedures are carried out one hour before meals.
- For therapeutic effects on the throat, you need to inhale through the mouth and exhale through the nose.
- The duration of one procedure is from 5 to 15 minutes.
- Inhalation is carried out in the course of 5-10 procedures.
- Before using for inhalation of any drugs should consult with a pediatrician.
Steam inhalation
For such procedures, you can use a steam inhaler or a container of boiling liquid. These inhalations provide for the use of only those solutions that are able to withstand heat. Often it is water with the addition of soda, salt, essential oils or medicinal herbs.
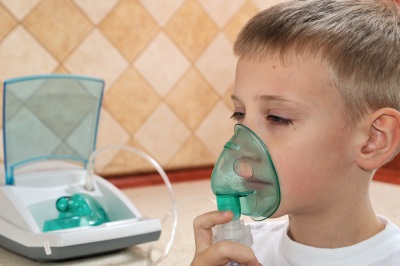
Nebulizer inhalation
Using a nebulizer for procedures allows you to spray medicinal substances into the smallest drops and deliver them to the respiratory tract in the place where their action is important. For its work, such a device can use ultrasound, a compressor or a special membrane.
Depending on the particles formed in the apparatus, nebulizing inhalations may be directed to different sections of the respiratory tract. The medicines transferred to the smallest particles will quickly get into the tissues of the respiratory system, and will also act on them longer and more efficiently than with other routes of administration.
Inside the nebulizer pour specially designed for use in this apparatus solutions. Most often, they are diluted in saline, and decoctions of herbs and oil solutions in most nebulizers use is prohibited. In some models, there are restrictions for drugs, such as corticosteroid hormones.
Preparations
The following substances are used for inhalations when coughing:
- Means to help moisturize and soften the mucous membrane. These include salt and mineral water, saline, water with soda. Such moisturizers are especially often prescribed for dry cough.
- Means with a bronchodilator effect, helping to eliminate cramps in the respiratory tract. This group of drugs include Berotek, Atrovent, Berodual and Ventolin. They are recommended for dry and allergic coughs.
- Means with mucolytic action. These drugs are Ambrobene, ACC, Bronchipret, Lasolvan, Mukaltin other. They are shown in both wet and dry coughs.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling and inflammation. This effect is given Tonsilgon N, Pulmicort, Cromohexal, Rotokan and other drugs. They are recommended for barking, allergic and wet cough.
- Means with antitussive effect. These include Lidocaine and Tussamag. Such drugs are prescribed for barking cough.
- Means with antiseptic action to cleanse the mucous membranes. This group includes Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin, Miramistin and Dioxidine. Their purpose is shown in a wet or barking cough.
- Medicinal herbs with mucolytic, anti-inflammatory and softening effects. These herbs include sage, chamomile, mother and stepmother, St. John's wort, mint, thyme and others. Their decoctions are used for dry cough.
- Essential oils with anti-inflammatory and softening effect. Such action is noted in oils of pine, sea buckthorn, eucalyptus, almond and others. Inhalation with them is recommended for dry cough.
On why you should not do inhalation with boiled potatoes, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.
Dosages of solutions for inhalation
What is the procedure or drug? | Dosages for different ages |
With saline | Use 3-4 ml of solution for one procedure. |
With Dry Cough Syrup | One procedure requires 3-4 ml of solution prepared with 1 sachet and 15 ml of water. |
WITH Miramistin | For children under 12 years old - 1 ml of the drug + 2 ml of saline. For children from 12 years and older - 4 ml of the drug without the addition of saline. |
With Lasolvan or Ambroxol | For babies under 6 years old - 2 ml of the drug + 2 ml of saline. For children over 6 years old - 2-3 ml of the drug + 2-3 ml of saline. |
With Borjomi | Use 3-4 ml of mineral water for one procedure. |
With Berodual | From 6 years of age to 10-60 drops, depending on the severity of the disease. Add saline to a total volume of 3-4 ml. |
S ACC | Children over 12 years old 3 ml of the drug. Dilute with 1 to 1 saline. |
With calendula tincture or Rotokan | For one procedure, you need 4 ml of the solution prepared from 1 ml of the preparation and 40 ml of saline. |
With lidocaine 1% | For children 2-12 years old - 1 ml of the drug + 2 ml of saline. For children over 12 years old - 2 ml of the drug + 2 ml of saline. |
With Tussamag | At the age of 1-5 years - 1 ml of the drug + 3 ml of saline. Children 6-16 years old - 1 ml of the drug + 2 ml of saline. |
With dioxidine 1% | The drug is diluted with saline 1: 1. For one procedure, use 3-4 ml of solution. |
With Furacilin | Use 4 ml of an aqueous solution per procedure. |
WITH Mukaltin | One procedure requires 3-4 ml of the solution obtained from 1 tablet and 80 ml of saline. |
Before inhalation, watch the following video, which describes the many important nuances during the procedure.