Epidural anesthesia for caesarean section
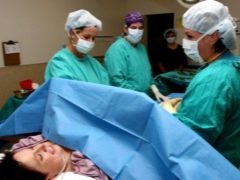
The vast majority of cesarean section operations in Russia today are performed using epidural anesthesia. She allows the woman to keep clear consciousness during the entire period of surgical manipulations and at the same time not to feel pain. The main thing that gives this type of anesthesia - the opportunity to see the moment of birth of the crumbs, enjoy his first breath and the first cry. These minutes are truly priceless. In this article we will talk about how epidural anesthesia is done, what effect it has, what complications can develop after it, and whether there are alternatives.
What it is?
Epidural anesthesia belongs to the category of modern careful methods of anesthesia. In medicine, there is a second name - peridural anesthesia, and women and doctors in everyday life often call it "epidural". With cesarean section, this method of anesthesia has been widely used in recent years. A large accumulation of nerves is concentrated in the human spine, and therefore the introduction of anesthetics directly into the spine allows one to achieve narrow goals - to anesthetize one or another part of the body for subsequent surgical actions.
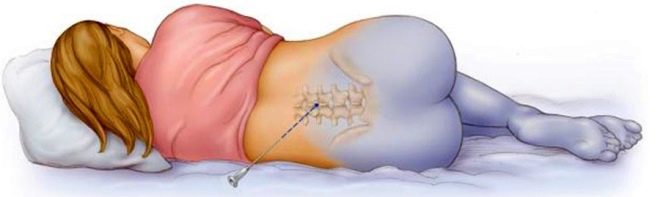
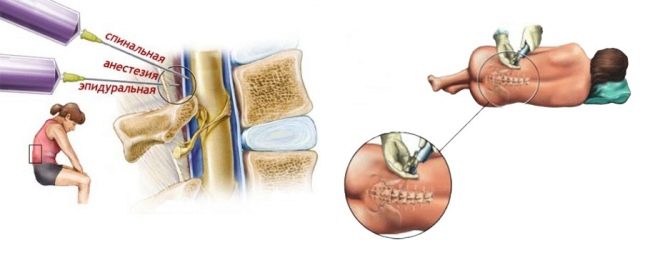
Epidural anesthesia refers to the delivery of drugs through the thin catheter to the epidural space of the spine. The anesthetic enters the gap between the walls of the spine and the pleura of the spinal cord. The nerve roots are washed with anesthetic and cease to transmit nerve impulses to the brain. Thus, the center of pain in the brain, thus, does not receive information about sensitivity in a blocked part of the body, which means that any manipulations in this part are permissible and the patient will not be hurt.
Epidural anesthesia is used in both natural childbirth and caesarean section. But in the first case, small doses of analgesics are administered, for example, lidocaine or ropivacaine. They allow to achieve partial anesthesia while maintaining the sensitivity of the lower body.
For caesarean section, which involves the penetration into the abdominal cavity, requires a longer and deeper blocking of pain. Therefore, opiates are added to analgesics - buprenofrin, promedol, etc. Ketamine can be used.
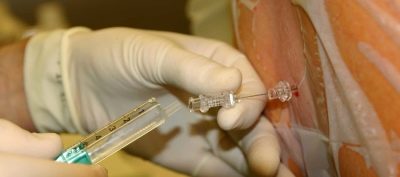
All solutions are pre-pharmacological cleaning, they are intended exclusively for spinal or epidural administration. When they enter the nerve root zone in the epidural space of the spine, the drugs act stronger and longer, and therefore the doses themselves are used less than with intravenous anesthesia.
What dose to enter a particular woman, decides the specialist anesthesiologist on the basis of analyzes, the general health of the future mother, her weight and height. Moreover, growth in this case is crucial: for each segment of the spine that needs to be numbed, an average of 2 ml of solution is used. The description of dose calculation methods is rather complicated, doctors use special algorithms and formulas.
How is it done?
A caesarean section lasts on average from 20 to 40 minutes. With epidural anesthesia, it lasts a little longer. Additional time is needed to gradually, gradually, correctly and accurately anesthetize the lumbar spine, which must be blocked, so that the sensitivity in the abdominal area and groin temporarily disappears.
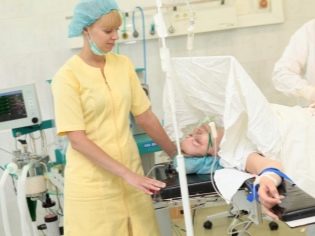
Before anesthesia, the anesthesiologist must make sure that the patient feels well. To do this, measure the pressure, temperature, pulse rate, be sure to watch the latest results of blood tests. A cuff is attached to the woman, which will directly monitor the level of blood pressure and pulse rate in direct mode.
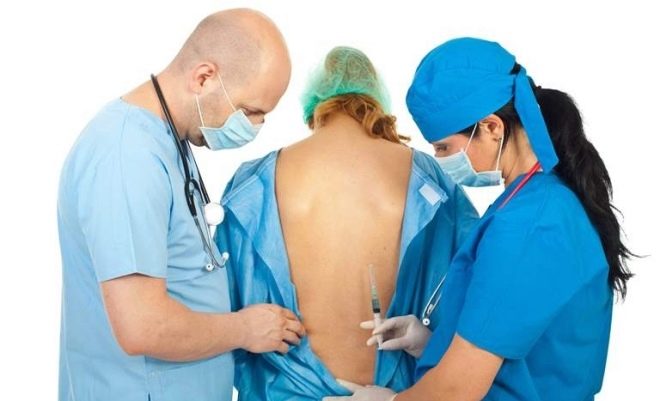
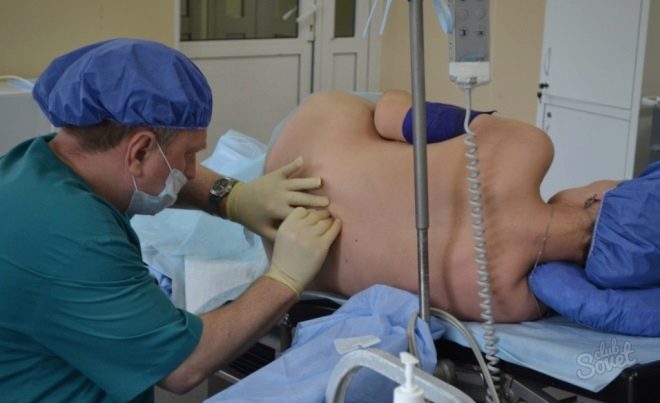
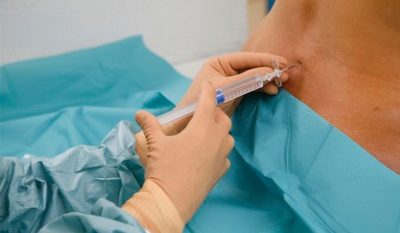
The mother is placed on the operating table so that it is on its side, the head is asked to be tilted as low as possible. The back is thus rounded, the vertebrae show through the skin better, which makes it easier for the doctor to find a place to insert the catheter. The anesthesiologist conducts the marking with a special pencil directly on the patient's back and proceeds to the introduction of the catheter.
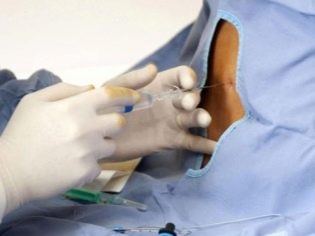
The skin is thoroughly disinfected. Next, the needle is inserted through the yellow ligament between the required vertebrae. There are several methods for checking the correctness of the introduction. The doctor can focus on spinal fluid entering the needle, and can use a syringe with air attached to the catheter. If the piston encounters resistance, the catheter is still in the bundle, if resistance disappears, this is a sign of falling into the epidural space.
After the anesthesiologist has come to the right place, he injects the first dose, which is called the test dose. Assessment of the state takes about three minutes. After that, the rest of the prescribed drug solution is introduced gradually, step by step and slowly, the support stretches as much as the time it takes the surgeons to complete the operation.
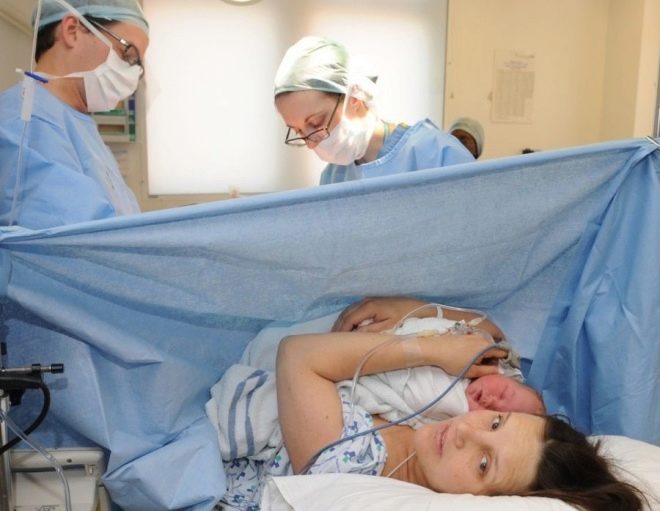
After the test dose, it is usually possible to attain the pain relief needed to start the operation within 10–15 minutes. The condition of the woman is carefully monitored and, if necessary, can add a new dose of drugs. When the baby is born, and the stitches (internal and external) are applied, the catheter is removed. The woman is transferred to the intensive care unit to monitor her during the period of recovery from anesthesia.
The operation takes place, as already mentioned, with the full consciousness of the patient. So that she does not see the surgeons' manipulations, they put a screen in front of the face, and when the baby appears, it must be shown to the mother and can be left next to her while the second phase of the surgery is in progress, during which the surgeon manually removes the placenta and stitches.
Pros and cons, possible consequences
Such anesthesia is considered one of the safest, but absolutely safe to call the "epiduralka" can not.
- In 1 case, there are various complications per 50 thousand deliveries. In about 17% of cases, after the drug has been injected into the epidural canal, it is not possible to achieve complete blockade. The woman retains a certain degree of sensitivity, which is undesirable neither for the woman in labor nor for the surgeon who would like to perform the operation on a patient relaxed, not straining muscles.
- If the expectant mother has problems with blood clotting, a hematoma can develop at the puncture site, and blood can enter the cerebral fluid.
- Much depends on the qualifications and experience of the anesthesiologist himself. Incompetent or negligent actions when inserting a needle can cause injury to the dura mater. This is often dangerous leaking of cerebrospinal fluid, which can lead to the development of severe headaches, as well as disruption of the normal operation of the central nervous system.
- If the subarachnoid space is injured, the consequences can be more severe - cramps, spasms, loss of consciousness, paralysis of the lower limbs.
- Quite often you can hear the opinion that epidural anesthesia does not harm the child, in contrast to general anesthesia. This is not entirely true. The development of weakness in respiratory activity, the occurrence of postpartum hypoxia, and cardiac rhythm disturbance under the influence of drugs in the fetus after birth are not excluded.
The exit from anesthesia, carried out through the epidural space, takes about 2 hours. The sensitivity of the lower body returns gradually, with it comes pain. It is stopped by injections of painkillers intramuscularly. At the same time, uterine-reducing drugs are administered, for example, oxytocin. And in this recovery period is not much different from the same period after general anesthesia.
With epidural anesthesia, the condition of the woman remains more stable - the vessels and the heart work without interruption. A significant minus of the method is the psychological unreadiness of many women in labor to “be present” at their own operation. This scares, the understanding of what is happening now, can cause a sharp rejection.
If not all nerve endings are blocked, then the woman will feel a limited range of unpleasant moments, but she will not feel sharp pain.
Contraindications
Women have the legislative right to choose the method of anesthesia during cesarean section. If, despite all the advantages of regional anesthesia, the woman is firmly focused on general anesthesia, it will be enough just to write the appropriate refusal of epidural anesthesia. Contraindications general anesthesia has not. If a woman, on the contrary, wants to take the most active and direct part in what is happening and insists on epidural anesthesia, the doctor cannot always allow this, since the method has certain limitations.
- In severe preeclampsia or obesity, injuries or spinal deformities, systemic infections, local inflammation of the skin in the area of the intended introduction of the needle of the catheter, allergies to drugs used in such anesthesia, lesions of the central nervous system and low pressure, suspected bleeding or opened bleeding, in conducting epidural anesthesia is denied.
- The issue of epidural anesthesia is not considered in case of emergency caesarean section, if there is a need to remove the baby from the womb as soon as possible.
If a cesarean section involves removal of the uterus after the baby is born for medical reasons, general anesthesia will also be recommended.
Alternative
The main alternative to epidural anesthesia today is general (endotracheal anesthesia). When it is injected, drugs are injected intravenously, and after the woman falls asleep and the tube is inserted into the trachea, the patient is connected to the ventilator and begins to operate. During the operation, the woman is unconscious, the quality of anesthesia is higher than the epidural, any sensitivity during surgical procedures is completely excluded.
The impact of drugs on the baby is not excluded, while its central nervous system is also suppressed. But the likelihood of serious consequences and complications is small. Many women have heard that there is also spinal anesthesia. It is a type of epidural, only the differences lie in the depth of the introduction of drugs into the spine. Epidural differs from spinal less deep blockade.
Lumbar puncture occurs not in the epidural, but in the subarachnoid space of the spine. Spinal or spinal anesthesia is performed with a thinner needle, and doses of painkillers are required slightly less than with epidural anesthesia. The effect of spinal anesthesia occurs much faster, almost immediately after the administration of medicines. For the rest, epidural and spinal anesthesia are almost the same.
Patient Reviews
Many women note that after the epidural the back hurts badly, and the pain does not go away even after discharge from the maternity hospital and persists for several more weeks. Women who have done more than one cesarean section with different anesthesia, argue that after epidural anesthesia, the process of recovery from anesthesia is easier.
About a third of women in labor complain of headaches, which start after surgery and can last for quite a long time. There are reviews on the Internet for those who have been affected by such anesthesia “wrongly”: there was a feeling of numbness in the legs, but the abdominal wall remained sensitive. Such women in labor had to do general anesthesia at the last moment so as not to cause a painful shock.
Almost all moms say that epidural anesthesia is scary in itself. And then even more than half an hour to lie on the operating table, listening to the conversations of doctors and the sound of instruments, is too hard for the psyche.
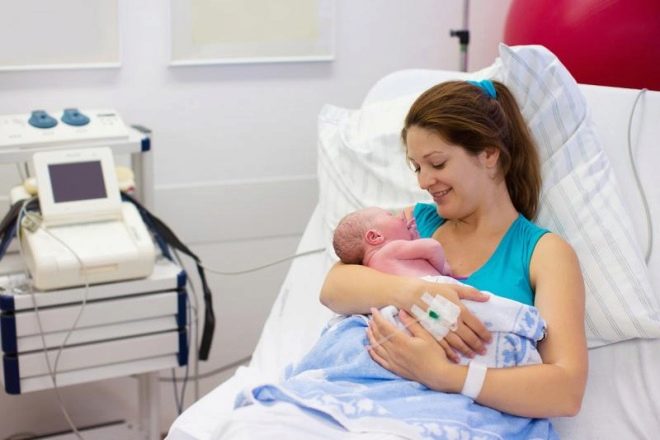
But the moment of birth of the baby, who will never see under general anesthesia, is not forgotten. Often, for his sake, one can suffer all other fears and inconveniences.
About methods of anesthesia for caesarean section, see the following video.