How is the caesarean section: the stages of the operation
Caesarean section is a real salvation when independent delivery is either impossible or dangerous for the woman and her baby. This operation allows the baby to appear not through natural physiological paths, but through two incisions. Laparotomy - opening of the abdominal wall, and hysterotomy - dissection of the uterine wall. These two artificial holes and become an outlet for the baby and the placenta.
In this article, we will talk about how surgical delivery is carried out in stages, what the doctors do before the operation, during the operational delivery and after it. This information will help women to be more knowledgeable in the process of preparing for a planned operation.
Terms of hospitalization and preparation
In modern obstetric practice, caesarean section as a method of delivery occurs in about 15% of all births, and in some regions the number of operative births reaches 20%. For comparison, in 1984, the proportion of surgical deliveries was no more than 3.3%. Experts are inclined to associate such an increase in the popularity of the operation with a general decline in the birth rate, with an increase in the number of women who think about their first child only after 35 years, and the prevalence of IVF.
Approximately 85-90% of all chest sections are allocated to the share of planned operations. Emergency operations are carried out quite rarely, only for health reasons.
If a woman has a caesarean section, then the decision on the timing of the operation can be made both in the early stages and at the end of the gestation period. This is due to the reasons for which independent delivery is impossible. If the readings are absolute, that is, unremovable (narrow pelvis, more than two scars on the uterus, etc.), then the question of alternatives is not raised from the very beginning. It is clear that there can be no other way of delivery.
In other cases, when the basis for the operation is detected later (large fetus, pathological presentation of the fetus, etc.), the decision to conduct operative delivery is taken only after 35 weeks of gestation. By this time, the size of the fetus and its estimated weight become clear, some details of its location inside the uterus.
Many have heard that children who are born at 36-37 a week are already quite viable. This is so, but the risk of slow maturation of the lung tissue in a particular child exists, and this may cause the development of respiratory failure after birth. Therefore, in order to avoid unnecessary risks, the Ministry of Health recommends carrying out a planned operation on the period after the 39th week of pregnancy. By this time, the lung tissue matures completely in almost all children.
In addition, delivery is considered more favorable, as close as possible to the expected date of birth - for a woman's body, stress will be reduced, and lactation will begin, albeit with a slight delay compared with physiological birth, but still almost on time.
If there are no indications for an earlier operation, the referral to the maternity hospital at the antenatal clinic is issued at 38 weeks. Within a few days, a woman should go to the hospital and begin preparations for the upcoming surgical labor.Preparation is an important stage, which largely depends on how successfully and without surgery the operation and the postoperative period will pass.
On the day of hospitalization, the woman takes the necessary tests. These include a complete blood count, an analysis to determine and confirm a blood group and Rh factor, a biochemical blood test, and in some cases a coagulogram to determine the rate of blood clotting and other hemostasis factors. Do a general analysis of urine, conduct laboratory research smear from the vagina.
While the laboratory technicians do these tests, the attending physician collects a complete and detailed obstetric history of his patient - the number of births, abortions, miscarriages, history of missed abortion, and other surgeries on the reproductive organs.
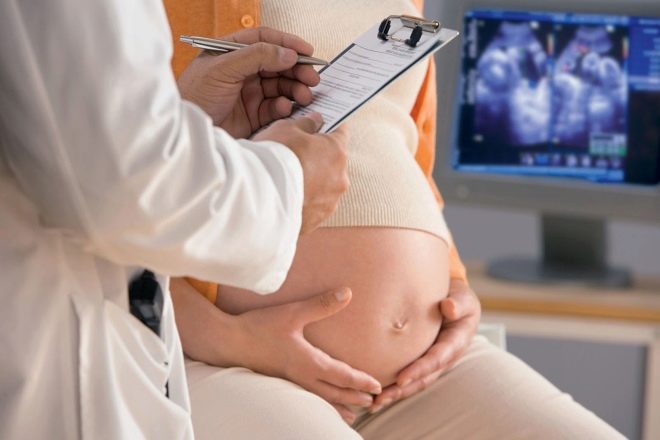
Also examine the condition of the baby. Do ultrasound to determine its location in the uterus, the size, the main one being the diameter of the head, calculate the estimated weight of the baby, determine the location of the placenta relative to the front wall of the uterus, on which it is planned to make the incision. Conduct CTG to determine the baby’s heart rate, motor activity and general condition.
About a day a woman meets with an anesthesiologist. The doctor reveals the presence of indications and contraindications to certain types of anesthesia, together with the woman plans her anesthesia, not forgetting to tell how she will act, how much time and what are its side effects. After the patient signs an informed consent for an epidural, spinal or general anesthesia, she is prescribed a means of sedation.
Since the evening of the previous day it is forbidden to eat. It is forbidden to eat and drink on the morning of the operation. A woman is given an enema to cleanse the bowels, shave the pubis, and dress in a sterile shirt.
It is recommended to bandage the legs with an elastic bandage or to wear compression stockings to eliminate the unpleasant, but quite likely complication of the operation - the development of a thromboembolism.
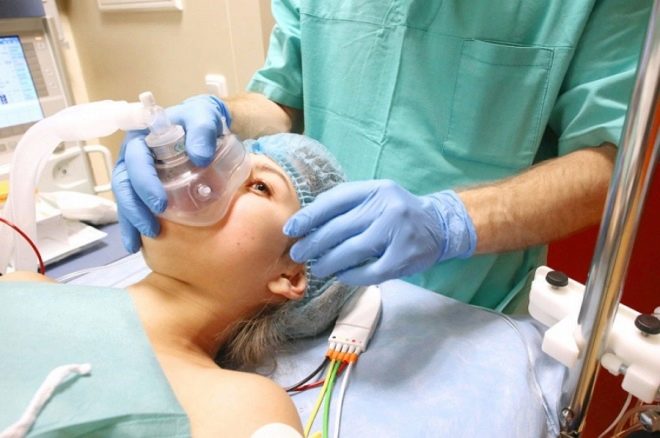
After the preparatory activities, the woman is taken to the operating room. There, everything is ready for the assigned operation. It is already awaited by the surgical team and the anesthesiologist, who, in fact, begins the first stage of the operation - anesthesia.
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is necessary because the operation is abdominal and lasts from 25 to 45 minutes, and sometimes longer. The first stage is adequate pain relief. It depends on him how comfortable the patient will feel and how easy it will be for the surgeon to work.
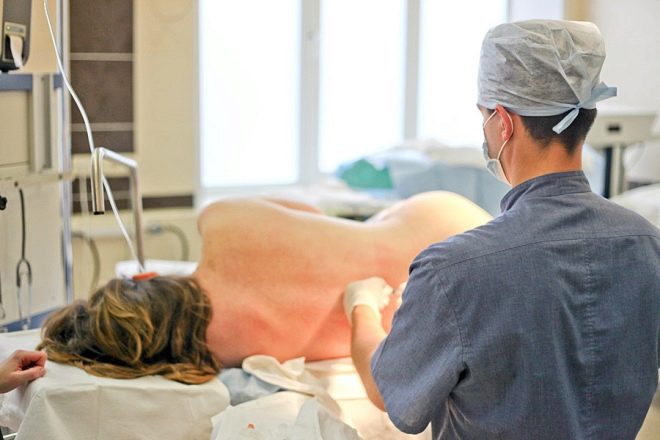
If it was determined that epidural anesthesia will be used, the operation itself will start somewhat later, since approximately 15–20 minutes pass from the moment of anesthesia to the achievement of the corresponding effect. A woman is laid on her side with her legs tucked in (fetal position) or she sits on the operating table, with her head and shoulders bent low, her back rounded.
The lumbar spine is treated with an antiseptic, the anesthesiologist conducts lumbar puncture - a puncture is made between the vertebrae with a thin special needle, a catheter is inserted and a test dose of anesthetic is injected into the epidural space of the spine. After three minutes, if nothing happens, take a basic dose of anesthesia. After 15 minutes, the woman begins to feel numbness and tingling in the lower body, no longer feel the legs, lower abdomen.
The anesthesiologist constantly monitors the pressure, heartbeat and condition of the patient, communicates with her. He conducts a sensory and motor sensitivity test, and then gives a command to the surgical team that the patient is ready for surgery. In the face of the woman in labor, a screen is set (to contemplate what is happening to the woman is completely unnecessary), and the doctors proceed directly to the operation. The woman is conscious but does not feel pain, because the drugs inside the epidural space block the transmission of nerve impulses from the nerve endings to the brain.
General anesthesia requires less time. The woman is placed on the operating table, the arms are fixed, a catheter is inserted into the vein and anesthetics are injected through it. When the patient falls asleep, and this happens in a matter of seconds, the anesthesiologist inserts an intubation tube into the trachea and connects the patient to the ventilator. During the operation, the doctor may add or reduce dosages of drugs. Doctors can start an operation in which a woman in labor is fast asleep and does not feel anything.
The course of operational childbirth in stages
It should be noted that there are many methods of operation. Specific surgeon selects depending on the situation, circumstances, history, indications and personal preferences. There are techniques in which each layer is cut and sutured, then there are methods in which the dissection of tissues is minimized, and muscle tissue is simply manually removed to the side. The incision can be both vertical and horizontal.
A low horizontal incision in the lower uterine segment is considered to be the best option, since such stitches heal better, make it possible to endure subsequent pregnancies without problems and even give birth to a second child in a natural way if the woman wants it and there are no medical contraindications.
Whatever the method of delivery chosen by the doctor, the operation will include the main steps, which we will discuss in more detail.
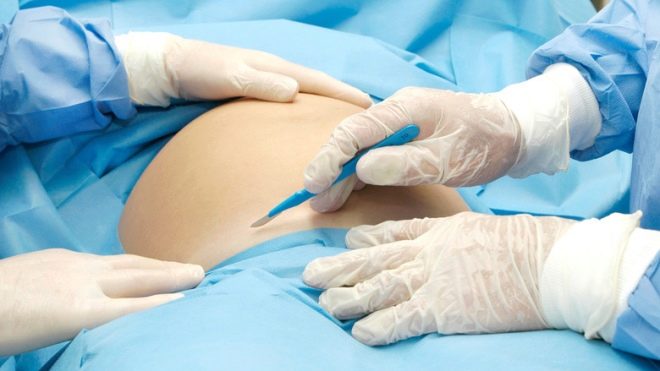
Laparotomy
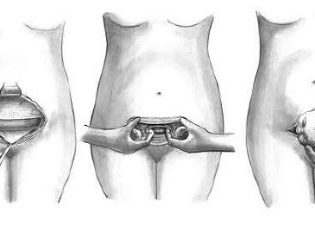
The abdomen is treated with an antiseptic, isolated from other parts of the body with sterile tissue and proceed to dissection of the anterior abdominal wall. With a vertical dissection, a lower median laparotomy is performed — a incision is made four centimeters below the navel and brought to a point four centimeters above the pubic joint. With a horizontal cross-section, which is called a Pfannenstiel laparotomy, an arcuate incision is made along the skin fold above the pubis with a length of 12 to 15 centimeters, if necessary, longer.
A Joel-Cohen laparotomy can also be performed, in which the incision runs horizontally below the navel, but well above the circumlobial fold. Such a cut, if necessary, can be extended with special scissors.
The muscles are gently pushed aside, the bladder is also removed to the side for a while, in order not to accidentally injure it. The doctor is separated from the child only by the wall of the uterus.
Uterine dissection
The reproductive organ can also be dissected in different ways. If the surgeon is a big fan of the traditional technique, he can make a cut through the body of the uterus horizontally, vertically along the midline using the Sanger method or a Fritch lunar incision that runs through the entire uterus - from one end to the other.
The most benign and recommended in the first place is the incision in the lower segment of the reproductive female organ. It can be transverse according to Rusakov, semi-lunar or vertical along Selheim.
The doctor opens the fetal bladder with a hand or surgical instrument. If the birth is premature, it is considered the best option not to open the membranes, in them the child will be more comfortable to be born, the adaptation will be easier.
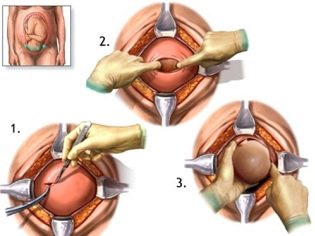
Fetal extraction
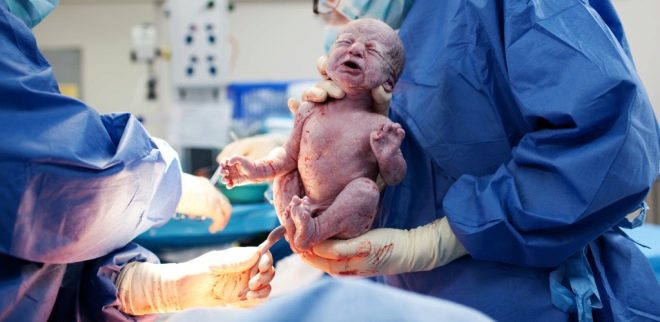
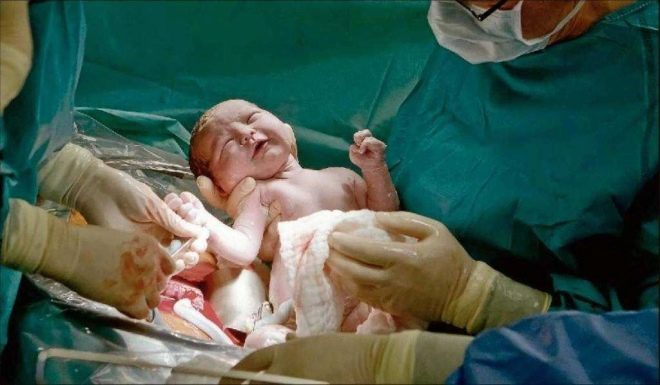
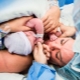
The most crucial moment is coming. When a child is born physiologically or during surgical procedures, doctors are equally worried, because the probability of injury to the fetus at the CS, although insignificant, still exists. To reduce such risks, the surgeon inserts four fingers of the right hand into the uterus. If the baby is head down, the doctor's palm goes to the back of the head. Carefully penetrate the head into the incision in the uterus and take out the hanger in turn. If the child is in pelvic presentation, it is removed by the leg or inguinal fold.If the crumb lies across, get it for a leg.
Cord cord is cut. The baby is given to a pediatrician, neonatologist or nurse in the pediatric ward for weighing, installing a pin on the umbilical cord and other procedures. If a woman is not sleeping, then she is shown a child, they are called sex, weight, height, they can attach it to her breast immediately after birth. During surgical births under general anesthesia, the meeting between the mother and the baby is transferred to a later time, when the woman recovers and recovers from the anesthesia.
Extraction of the placenta
The placenta is detached by hand. If it has grown, it may be necessary to excise part of the endometrium and myometrium. With total ingrowth, the uterus is completely removed. Also, the surgeon conducts a revision of the uterus, checks that nothing is left in it, checks the cervical cervical patency, if it is impassable, it is expanded manually. This is necessary so that lochia (postpartum discharge) in the postpartum period can freely leave the uterine cavity without causing stagnation and inflammation.
Uterus suturing
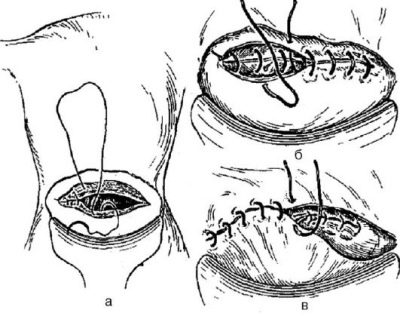
On the cut edges of the uterus impose single-row or double-row suture. The preferred is a two-row. It is more durable, although it takes a little more time to apply it. Each surgeon has his own technique of suturing.
The main thing is that the edges of the wound be joined as precisely as possible. Then a scar on the uterus will form an even, homogeneous, wealthy, which does not hurt to endure the next pregnancy.
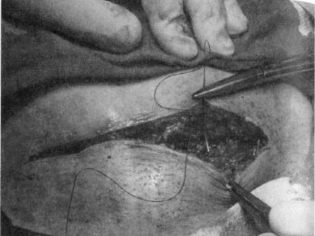
Closure of the abdominal wall
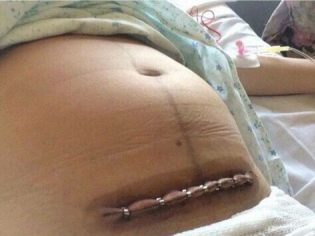
The aponeurosis is usually sutured with individual silk or vicryl threads or a continuous suture. On the skin impose staples or seams separate. Sometimes the skin is sutured with a continuous cosmetic suture, which is very neat.
Early postoperative period
A woman is transferred to the intensive care unit, where she is observed for 5-6 hours. Everything is important - how the anesthesia comes out, how the sensitivity returns, how the uterus contracts. Pain after the return of sensitivity for 2-3 days is blocked with painkillers. Measure the pressure and temperature, enter reducing drugs.
In the absence of complications, after 6 hours, the woman is transferred to the general ward, where she may soon begin to sit down, stand up. She brings a child.
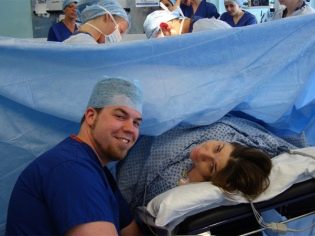
With partner
Caesarean section is a great way to conduct a joint birth without the risk of unpleasantly shocking a man as seen. In the operating room, the husband may not be a passive observer, but an active participant. His task will be to help the anesthesiologist - to talk with his wife, hold her hand, support. If the operation is performed under general anesthesia, there is no sense in joint labor, since the woman in labor is sleeping soundly. But at the request of the spouses and such partnership childbirth is quite possible.
In order for a man to be admitted to the operating room, he first needs to undergo a medical examination, provide the maternity hospital with certificates of the absence of infectious diseases, venereal ailments, recent fluorographic examination data describing the conclusion of the therapist and dermatologist.
It should be noted that not all maternity homes go to the presence of a stranger in the operating room. Then the joint labor looks like this: the doctors operate on the patient, and the husband is in the next room and watches the events through a small glass window. The baby after birth is brought to him and given to hold. Thus, it is the husband who becomes the first to take the crumbs into his arms and press them to his chest.
The question of the possibility of a partner caesarean section should be discussed in advance with the medical staff of the chosen maternity hospital.
You will learn more about the features of cesarean section, looking at the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.