At what time do the second cesarean section and what is important to know?
Repeated cesarean section is recommended for women who cannot or do not want to give birth to their second child on their own, since the mere presence of the first operation does not exclude the possibility of giving birth on their own during the second pregnancy. If there are coming second surgical deliveries, it is important for a woman to know some of their characteristic features. In this article, we will describe at what time the second operation is performed, how it differs from the first one.
The need for re-operation
Second births after cesarean section need not be performed surgically. Under certain conditions, a woman may well be allowed to give birth on her own. But no more than a third of pregnant women go to this with a single caesarean section in history. The patient’s categorical disagreement on physiological labor with a scar on the uterus is the first and most weighty reason for carrying out repeated operative labor.
But even when a pregnant woman wants to give birth on her own, she may not be allowed to do this if there are absolute indications for the second operation.
- Small or large period of time after the first birth. If less than 2 years have passed or more than 7–8 years, then the “reliability” of the connective tissue of the uterine scar will cause well-founded fears among doctors. Only 2 years after the birth of the firstborn, the place of scar healing becomes quite strong, and after a long break it loses its elasticity. In both cases, the danger is a possible rupture of the reproductive organ at the site of the scar at the time of severe contractions or attempts.
- Complications after previous delivery. If the rehabilitation period after surgical delivery is difficult: with fever, inflammation, joined infections, hypotonia of the uterus, then the second child is also likely to have to give birth on the operating table.
- Insolvent scar. If at the time of pregnancy planning, its thickness is less than 2.5 mm, and by week 35 it is less than 4–5 mm, then there is a possibility of uterine rupture during independent delivery.
- Large baby (regardless of his presentation). Repeated after a cesarean section can give birth to a baby through natural physiological pathways only with the expected weight of the child less than 3.7 kg.
- The wrong location of the baby. Options for manual reversal of the baby for a woman with a scar is not even considered.
- Low location of the placenta, placenta previa on the scar area. Even if the “children's place” by the edge affects the area of the scar, it is impossible to give birth - just be operated.
- Vertical scar. If an incision was made vertically during the first delivery, then independent labor activity is subsequently excluded. Only women with a well-established horizontal scar in the lower uterine segment can theoretically be admitted to independent childbirth.
In addition, the irreducible causes that led to the first operation are considered to be absolute indications for repeated surgical deliveries: narrow pelvis, uterine and birth canal abnormalities, etc.
There are also relative indications for the second operation.This means that a caesarean section will be offered to the woman during the second pregnancy, but in case of her refusal, a natural mode of delivery can be chosen. These indications include:
- myopia (moderate);
- oncological tumors;
- uterine fibroids;
- diabetes.
The decision to repeat the operation, if the woman does not object to such a mode of delivery and there are contraindications from the category of absolute, is taken when registering the pregnant woman. If there are no contraindications, the woman wants to give birth herself, then the way of childbirth will be chosen after 35 weeks of pregnancy at a medical consultation.
Dates
The Ministry of Health of Russia strongly advises maternity hospitals and clinics to adhere to clinical guidelines when performing a cesarean section. This document (Letter of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2014 No. 15-4 / 10 / 2–3190) prescribes the operation after 39 weeks gestation. This applies to the first, and re-cesarean section. The rationale indicates the risk of possible immaturity of the lung tissue of the fetus up to 39 weeks.
In practice, the second cesarean section is attempted to be carried out a little earlier than the first, since an independent onset of labor, the contractions that have occurred can pose a mortal danger to the baby and the mother associated with uterine rupture. Most often, the second surgical childbirth is done at the 38-39 week of pregnancy.
If the doctor finds a precursor of the woman on a scheduled examination in the later stages: the discharge of the plug, the readiness and maturity of the cervix, its smoothing, the timing of the operation can be postponed to an earlier time.
According to emergency indications, a second pregnancy is performed at any time to save the life of the fetus and mother. Emergency situations include loss of the umbilical cord, signs of the beginning of uterine rupture during gestation, placental abruption before the prescribed period, signs of acute hypoxia and other fetal distress, in which it is mortally dangerous to remain in the womb.
If a woman is a supporter of the opinion that the CS should be done as close as possible to the expected date of birth, then theoretically they can carry out the operation (in the absence of contraindications for waiting tactics) at any time from 39 to 40 a week.
Training
Preparation for the second planned operation begins in the period of pregnancy. A woman with a scar on the uterus should visit her obstetrician-gynecologist more often than other pregnant women. In the third trimester, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the scar, in time to notice possible signs of its thinning. To do this, it is recommended to do an ultrasound scan with doppler every 10 days.
In the hospital a woman is hospitalized in advance. If at the first planned operation it is necessary to go to the hospital about a week before the operation, then for re-CU to go to the hospital under the supervision of doctors at 37-38 weeks to prepare for the upcoming birth.
Doctors prepare in their own way: they must again examine the pregnant woman, establish the exact location of the scar, its features, take tests, and agree on the method of anesthesia with the patient.
The day before the surgery, the anesthesiologist talks to the woman. From the evening before the operation, the premedication begins: the expectant mother is given a strong sedative (usually barbiturates) so that she can sleep and relax as much as possible at night. This will protect her under anesthesia from drops in blood pressure.
On the morning of the operation, a woman is shaving her pubis, putting an enema to cleanse the intestines, and can recommend foot bandaging with elastic medical bandages to prevent thrombosis.
Features of the operation
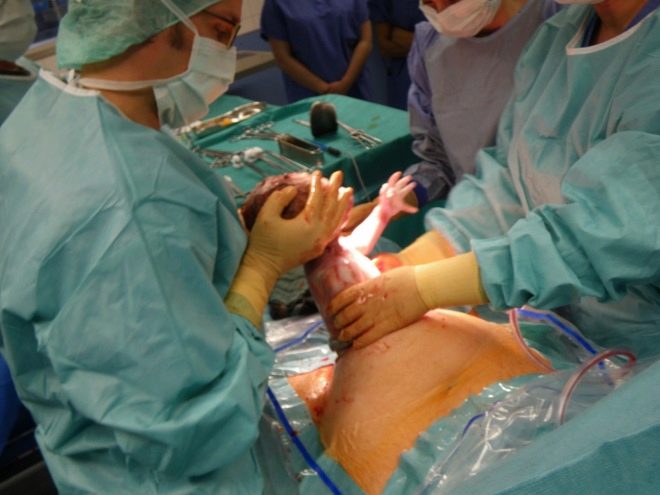
The main feature of re-cesarean section is that the operation lasts a little longer than the first.About this woman should warn relatives, so that they do not worry about wasting. Additional time is necessary for surgeons to remove the first scar. Each subsequent surgical delivery is carried out on the previous scar. Therefore, situations in which a woman had a vertical suture after the first operation, and after the second one will be horizontal, are completely excluded.
If the operation was with a longitudinal incision, then the second time, an incision will be made in the same place, cutting out the old connective tissue so that the new scar can be formed unhindered. Needless to say, with each cesarean section, the scar becomes thinner and thinner, and the risks for carrying increase!
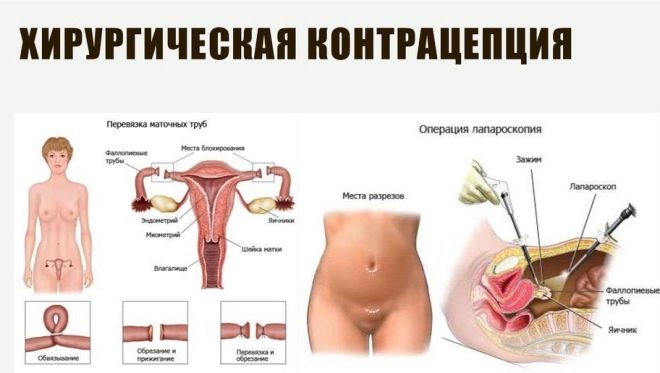
If a woman no longer plans to give birth, then she can sign consent to surgical sterilization in advance. After removing the baby, doctors begin to dress the fallopian tubes - the onset of a subsequent pregnancy becomes impossible. This simple manipulation can extend the total time that the patient spends in the operating room, another 10–15 minutes.
Opening the abdominal cavity, the doctor carefully, so as not to injure, removes the muscle tissue, as well as the bladder. Then an incision is made on the uterus wall itself, the fetal bladder with amniotic fluid and the baby is punctured. Water is drained, the child is taken out of the incision, the umbilical cord is cut and transferred to neonatologists. If a woman is not in a state of deep medication sleep (general anesthesia), then at this stage she can already look at her baby, touch it. Such an opportunity is provided by such types of anesthesia as epidural or spinal anesthesia.
While the mother admires the child or sleeps soundly under general anesthesia, the doctor separates the placenta, checks if there are any particles left in the uterine cavity and puts several rows of internal sutures on the reproductive organ. In the final part of the operation, restore the normal anatomical location of the muscles and bladder and impose external sutures or brackets. At this operation is considered complete. The puerperal for the next few hours is determined in the intensive care unit for close observation in the early postoperative period. The kid goes to the children's department, where he will be treated, redeemed, examined by doctors, and blood tests will be taken from the baby.
How is the recovery going?
The recovery period after re-cesarean section also has its own characteristics. A woman recovers longer than after the first operation, and this is quite natural, because the muscles of the uterus are more stretched, and the re-opening of this muscular organ makes it difficult to postpartum involution of the uterus. After surgery, the uterus remains quite large, but more like a blown ball or an empty sac. She needs to shrink to its former size. This process in involution is considered the most important.
To help the puerperal, from the first hours after the transfer from the operating room to the intensive care unit, doctors begin to introduce her contraction drugs. After a few hours, the woman is transferred to the general puerperal ward, where she is advised not to lie long. It is optimal to climb already 10–12 hours after surgery. Physical activity will contribute to the involution of the uterus. For the same purpose (and not only this!) It is recommended to put the baby to the breast as soon as possible. The crumb will receive nourishing and beneficial colostrum, and the production of its own oxytocin in the body of his mother will increase, which will certainly have a positive effect on the contractility of the uterus.
A woman is shown a diet up to 4 days after surgery, aimed at preventing constipation and pressure of the intestine on the injured uterus. The first day you can only drink, the second you can eat broth, jelly, white croutons without salt and spices.Only by the fourth day a woman can eat everything, but avoid products that stimulate the production of intestinal gases.
Lochia (postpartum discharge) after the second surgery usually ends completely by 7–8 weeks after surgery. The stitches are removed after 8–10 days after the operation (in consultation at the place of residence), the woman is discharged from the maternity hospital in the absence of complications on the fifth day, as is the case with the first surgical birth.
Reviews
Repeated cesarean section, in the opinion of women, practically does not differ from the first in terms of the subjective sensations of the mother herself. The difference begins to be felt only after the operation, in the process of rehabilitation. But, despite its longer nature, women usually get out of bed faster, because they already know exactly how to do it. Also, giving birth to a second child surgically knows well what complications can be after surgery, and therefore more carefully listen to the changes in your body in the first days after the baby is born.
Lactation after the second operation is most often set earlier than after the first. This is due to the better preparation of the nipples, the milk ducts for the upcoming breastfeeding.
According to reviews, few agree on surgical sterilization during the second operative delivery, because women want to preserve fertility, because the third Cesarean section today is not a curiosity, and it is difficult to predict all life circumstances in advance.
About what you need to know about preparing for cesarean section, see the following video.