On which week it is better to do a cesarean section and why sometimes the operation is carried out until the 37th week of pregnancy?
Caesarean section is one of the most popular operative obstetric practices. Over the past 30 years, the proportion of surgeries in the total number of births has increased worldwide. Back in the 1980s, in Russia, no more than 3% of children appeared surgically into the world. Today it is about 15%, and in some large perinatal centers the number of operative births exceeds the average values, and this number goes up to 20%.
Expectant mothers who have to give birth to their baby on the operating table are concerned about the timing issue: which week of pregnancy should be considered optimal for the appearance of a child? In this material, we will explain how terms for surgical deliveries are determined and why they may change.
Who needs surgery?
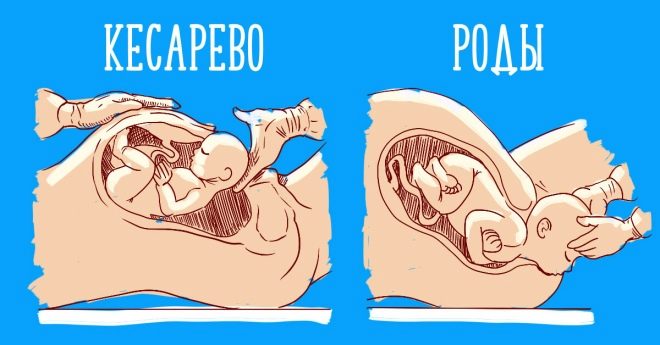
Surgical births, named after the Roman emperor Gaius Julius Caesar, do not imply the passage of the baby through the birth canal of the mother. The child is born as a result of laparotomy and hysterotomy - incisions in the abdominal wall and the wall of the uterus.
This method of delivery is sometimes salutary. It is carried out urgently in order to save the lives of the woman and her baby, if in the process of physiological labor or as a result of the injury something went wrong. Emergency cesarean section takes no more than 7-9% in the proportion of all surgical deliveries. The remaining share is allocated to planned operations.
A planned caesarean section is always a thorough preparation, as a result of which the risks of complications are significantly reduced.
Indications for elective surgery may appear from the very beginning of pregnancy, and may become apparent only at the end of the gestation period. Therefore, the decision on the timing of the operation is taken at different times.
For emergency cesarean section, the timing question is irrelevant. It is carried out when there is an urgent need for it. A planned operation is carried out according to indications provided by the list in the clinical guidelines of the Ministry of Health of Russia. This list is regularly reviewed, it is amended.
Today it provides the following situations:
- Pathological location of the placenta - low placentation with incomplete overlap of the internal pharynx or placenta previa.
- Postoperative cicatrices on the reproductive organ from cesarean or other surgical procedures on the uterus. Also, cesarean is recommended as the only delivery option if there is two or more cesarean sections in the history.
- Clinical narrowness of the pelvis, pathology of the bones and joints of the pelvis, trauma and deformity, tumors of the pelvic organs, polyps.
- Pathological discrepancy of the bones of the pubic joint - symphysitis.
- Pathological position of the fetus. By the 36th week of pregnancy - pelvic, oblique, transverse. Also pathological include some types of presentation, for example, buttock-foot.
- The estimated weight of the child is more than 3.6 kg if it is incorrectly located in the uterus.
- Plural fetus, in which the nearest to the exit of the fetus is located in the breech presentation.
- Monozygous twins (twins are inside one sac of sacs).
- IVF pregnancy is twins, triplets, and often singleton.
- Insolvent cervix, with scars, deformity, scars in the vagina, remaining after the previous difficult labor, which took place with gaps above the third degree of severity.
- A significant delay in the development of the baby.
- The lack of effect of conservative stimulation of labor during retreatment after 41-42 weeks.
- Preeclampsia severe form and degree, preeclampsia.
- The inability to push because of the ban on such action in myopia, retinal detachment of the woman's eyes, some heart diseases, as well as in the presence of a kidney-transplant.
- Prolonged compensated hypoxia.
- Violation of blood clotting in the mother or baby.
- Genital herpes, HIV infection of the mother.
- Anomalies of fetal development (hydrocephalus, gastroschisis, etc.).
On an individual basis, a decision can be made about a planned operation for some other reason.
Optimal time
If circumstances that are indications for surgery arise already in the process of carrying a baby, for example, a pelvic presentation occurs with a large fetus or placenta previa, then doctors wait until 34-36 weeks of gestation. This term is considered “control”. If by the 35th week the baby does not turn over to the correct position, if the placenta does not rise, then the indication for the operation becomes absolute. An appropriate decision is made, and the date of operative labor is appointed.
When circumstances that imply surgical delivery as the only possible or only rational occur from the very beginning after the onset of pregnancy, the question of caesarean section is not considered separately. Prompt delivery is meant a priori.
Contrary to the popular opinion among women, that a caesarean section is optimally performed when contractions begin, because it is “closer to nature” that doctors prefer to operate on the relaxed and calm muscles of the uterus, rather than straining during labor contractions.
So there will be fewer complications, and surgical deliveries will go more safely. Therefore, it is better to carry out the operation before the start of physiological labor.
The Ministry of Health of Russia in its protocol and clinical guidelines for caesarean section calls for quite specific terms at which the operation is considered the most desirable. It is recommended to do a caesarean routinely after 39 weeks gestation.
How long does a cesarean section do? Yes, on any, if required. But week 39 is considered the most favorable, because by this time the vast majority of children have lung tissue matured enough for independent breathing to be possible, the child is ready, he will not need resuscitation care, the risks of distress syndrome and the development of acute respiratory failure are minimal.
Viable children are considered from 36 weeks of pregnancyand, children born earlier also survive, but the risks of respiratory failure increase in proportion to the period of prematurity.
If there is no reason for an early delivery, then it is better to allow the child to gain weight, and his lungs to mature.
During pregnancy twins or triple the probability of the onset of physiological labor a couple of weeks before the expected date of birth is higher, and therefore, in case of multiple pregnancies, they are trying to prescribe a planned caesarean section at 37-38 weeks, and sometimes up to 37 weeks. Children may need resuscitation care in the first hours of life, and therefore not only surgeons, but also a team consisting of a neonatologist and pediatric resuscitator, always prepare in advance for such operations.
When the doctor decides on the date of the operation, he takes into account not only the wishes of the pregnant woman, her state of health and the totality of indications, if there are several, but also the interests of the child. If the baby according to the results of surveys revealed any signs of ill-being, then the period of surgery may be scheduled for an earlier time.
Does this mean that women are not given the right to participate in the discussion of the date of birth of their own child? By no means. The doctor may indicate the time frame - a few days in which he considers it appropriate to conduct the operation. A woman may, at her own discretion, choose one of these days. On weekends and holidays planned operations try not to carry out.
Reasons for changing the timing
If we talk more about the reasons that may lead to a change in the timing of operational delivery, then It should be borne in mind that there are two types of influence factors: evidence from the mother and evidence from the fetus.
- According to maternal indications the operation can be postponed earlier because the woman's body begins to actively prepare for childbirth. In a woman, the cervix begins to flatten and shorten, the amount of cervical mucus increases, the mucus plug moves away from the cervical canal, and the amniotic fluid begins to flow slowly and gradually. Also, the time will be reduced if there are signs of threatening uterine rupture along the old scar. The deterioration of the woman’s condition due to preeclampsia, increased pressure, and severe swelling are grounds for an earlier delivery if conservative therapy is inconclusive and it is not possible to stabilize the pregnant woman’s condition.
- Earlier delivery of the fetal factor carry out if the child shows signs of oxygen starvation, if there is entanglement with the umbilical cord around the neck with accompanying signs of trouble, with severe Rh-conflict. If a child has congenital abnormalities identified during screening prenatal diagnostic studies, the deterioration of his condition is also a reason to postpone the operative delivery.
Referral for hospitalization to the maternity hospital or perinatal center is given in the antenatal clinic where the woman is observed at 38-39 weeks during the first pregnancy, at 37-38 weeks if a re-caesarean section is required for single-pregnancy. When multiple, as already mentioned, above, hospitalized earlier on average for 2 weeks.
35-36 weeks of pregnancy for women becomes decisive, it is on it that ultrasounds are performed, control tests are done to help find out all the nuances of the fetus and mother.
COP up to 37 weeks
As already mentioned, a caesarean section can be medically prescribed before, but the risks to which the baby will be exposed increase with prematurity.
A child who is born by caesarean section at 30 weeks will have little chance of survival, but because the operation on this period is carried out only in case of mortal danger to the life of the mother.
At 32-33 and 33-34 week pregnancy baby's chances of survival increase, but still the risks of death after birth are high.
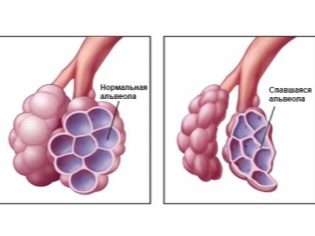
The main danger lies in the fact that the child at this time has not yet accumulated a sufficient amount of subcutaneous fatty tissue, in connection with which the crumb simply cannot keep the body heat in a stable state. Also, in the lungs, not enough surfactant has been developed - a special substance that ensures the ability of the lungs to inhale and exhale without sticking.
From week 36, the chances of survival increase substantially. From this point on, the child is formally considered viable.
But the individual characteristics of the development of each baby may differ, and therefore doctors weigh the pros and cons, comparing the risks to the mother and the fetus. The benefits of the proposed surgery should be many times greater than the possible harm from his absence at a specific current gestational age.
For details on the timing of the operation, see the following video.