Spinal anesthesia for caesarean section
Spinal anesthesia is one of the methods of anesthesia of surgical operations and manipulations. The method is widely used when performing cesarean section. In this material we will talk about what this anesthesia is, how it is made and what its advantages and disadvantages are.
What it is?
Nerve endings are concentrated inside the human spinal column, which constantly send certain impulses to the brain, on which the work of the central nervous system is based. If you block the sending of these "messages", the brain will not perceive signals of pain or cold, touch. This is the basis of spinal anesthesia for caesarean section.
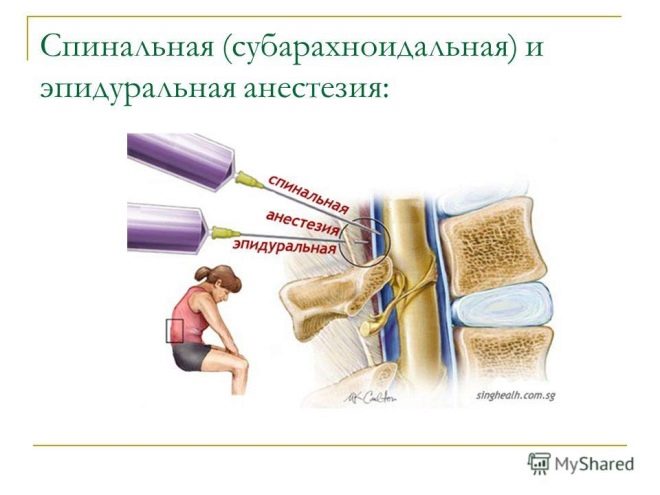
The operation is associated with incision and penetration into the abdominal cavity, and therefore must be carried out with the use of anesthesia on a mandatory basis. But the choice of anesthesia is a rather complicated question, because there are several types of anesthesia for this operation. Epidural and spinal anesthesia are classified as regional anesthesia.
The only difference between them is that with epidural anesthesia, drugs that block the sensitivity of nerve endings are injected into the epidural space, and with spinal medication - into the subarachnoid space of the spine, that is, somewhat deeper than in the first case.
Such penetration makes it possible to block nerve impulses at the level of the roots of the spinal nerves. Drugs that are administered at caesarean section, have a high degree of purification and do not contain preservatives. This is usually one of the anesthetics, for example, lidocaine, with the addition of opiates, for example, promedol. Recently, ketamine has often been used.
It is believed that spinal anesthesia is superior to epidural in quality of pain relief, and also better than general anesthesia, simply because getting out of it is easier, not associated with nausea and severe dizziness.
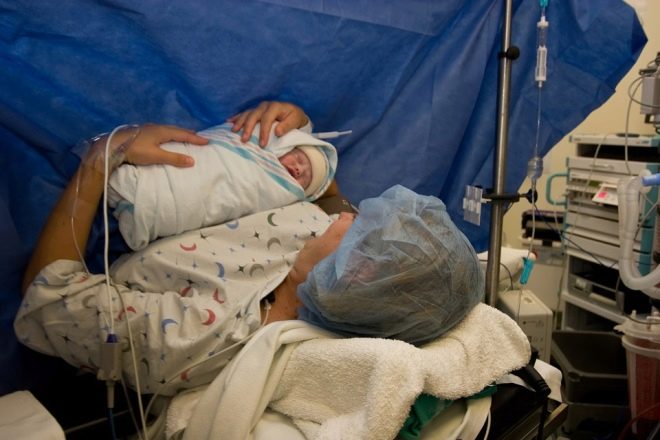
During the whole operation, the patient is conscious, understands everything, can communicate with doctors, but does not feel the lower part of the body from the waist to the tips of the toes. At the same time, the upper part of the body retains its sensitivity, a woman can move her arms and head, which gives her a unique opportunity to hug her baby immediately after his birth. For this, in fact, many mothers and insist on spinal anesthesia.
How is it done?
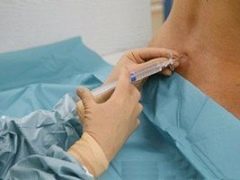
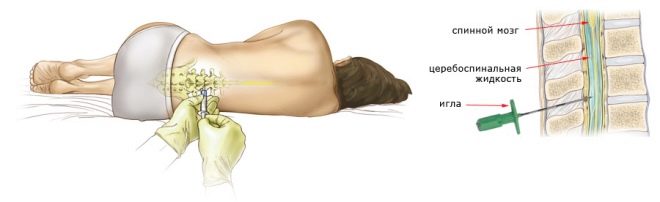
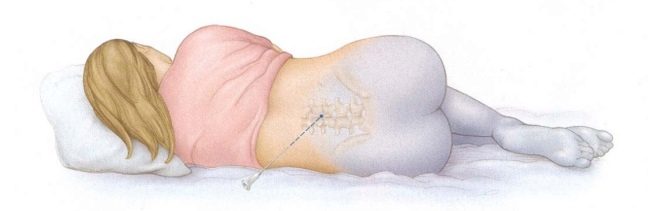
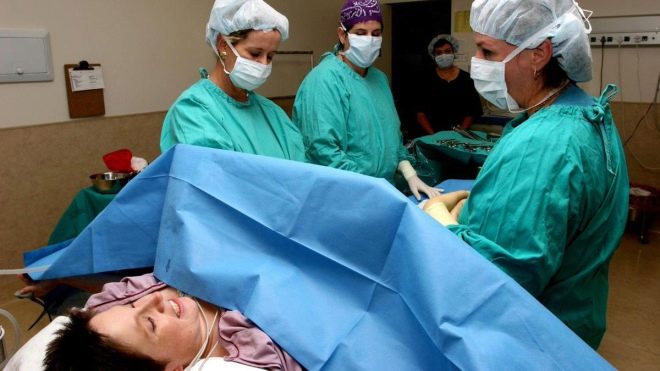
Drugs are inserted into the spine via lumbar puncture. At the same time, the woman either sits, leaning as far forward as possible, or lies on her side, with her head bent toward the chest. In order to numb the lower body, the anesthetist inserts a puncture needle into the lumbar spine. The injection point is located between the vertebrae. The needle itself is thinner than with epidural anesthesia. The needle must pass through the space of the yellow ligament between the vertebrae, without hitting them, bypassing the epidural space and penetrating into the subarachnoid space filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
It should be noted that for spinal anesthesia drugs require less than for epidural, and the effect occurs much faster. In most cases, anesthesia for epidural anesthesia takes about 15 minutes, and numbness in the lower body and the subsequent loss of sensitivity during spinal anesthesia occurs in a few seconds after administration.
Usually, in order to achieve permanent anesthesia for caesarean section, the drug is introduced into the space between two vertebrae in the range of 2 and 5 lumbar vertebrae. Most often, doctors choose a point between the 2nd and 3rd vertebrae of the lumbar spine.
The question of how much it hurts, women are asked very often. In most cases, the woman does not experience a sharp pain. Depending on the individual sensitivity, there may be short-term discomfort, the same as with any injection. If a woman feels discomfort, she must report this to the anesthesiologist. The main thing is not to turn to a specialist, not to try to look at him. All communication woman should exercise without changing the position of the body.
After making sure that the puncture needle has gone where it is needed, the doctor injects a test dose of the medicine. After 3-5 minutes, in the absence of negative signs, the rest is administered in stages and in parts. During the operation, the doctor can adjust the degree of blockade by adding or reducing the dosages of the injected drugs.
At the signal of the surgeon to complete the operation, the catheter is removed from the back. The woman is transferred to the intensive care unit, where not only the obstetricians, but also the anesthesiologist himself, is watching her for several hours to make sure that the anesthesia is over without complications. It takes about 2 hours.
Possible consequences and complications
Spinal anesthesia is considered a fairly safe method of anesthesia. Statistics of the Ministry of Health of Russia shows that the probability of severe or lethal complications is 0.01%. This means that for 10 thousand operations with the use of such anesthesia there was only one case of patient death, the cause of which was acute heart failure.
Many women complain of backache and headache after surgery. Postfunctional pain is a fairly common phenomenon and occurs in about 7-10% of parturient women. They are temporary and usually complete within 2-3 months without any special treatment.
Another likely complication of spinal anesthesia is a drop in blood pressure in the early postoperative period. This occurs in about 2-3% of cases. The situation is under control and is solved by the introduction of drugs that increase the pressure.
Much depends on the level of training, experience and qualifications of the anesthesiologist. An inexperienced and inept doctor can injure the spinal cord, the vertebral hard membranes, in this case various disruptions of the central nervous system are possible, from a feeling of prolonged numbness in the limbs to paralysis. The probability of such complications, according to statistics, is low, but it exists.
In 15% of cases, a persistent analgesic effect is not achieved; the sensitivity of the parturient can be preserved to a certain extent, which is highly undesirable for the patient or the doctor who performs the operation.
If there is a violation of blood clotting, coagulopathy, a small hemorrhage may appear at the puncture point - hematoma. The subarachnoid space where the drugs are injected requires precision, its injury is fraught with the development of seizures and paralysis.
Since the doses of drugs are reduced compared with other types of anesthesia, drugs affect the baby to a lesser extent than with epidural and general anesthesia.Still, there remains a slight likelihood of disturbances in the heart rate of the child, weak breathing, hypoxia, and muscular hypotension in the neonatal period.
Some women note the extremely difficult psychological background of the operation under spinal anesthesia - to be conscious and understand that it is you who are being cut on the table, and it is not so easy for the psyche to hear the doctors talking during the operation as it seems. Especially impressionable women already at the very beginning of the operation begin to require general anesthesia from doctors to sleep and wake up only when everything is complete.
Contraindications
There are two types of contraindications for such anesthesia. Some are relative, while others are absolute. Always absolutely spinal anesthesia is contraindicated in women with:
- severe bleeding disorders;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the skin in the region of 2-5 lumbar vertebrae, that is, where it is intended to introduce a puncture needle;
- high intracranial pressure;
- spinal injuries, spinal deformity;
- severe heart disease.
Relative contraindications to spinal anesthesia are:
- severe psychological and emotional disorders of a pregnant woman, mental illness;
- the indefinite duration of the operation (if, for example, doctors suggest that uterus amputation may be necessary due to the growth of the placenta or the woman has agreed to surgical sterilization after cesarean section);
- fetal death;
- bleeding in women or suspected bleeding.
Also, the patient will not be allowed to carry out spinal anesthesia if a cesarean section is performed not in a planned manner, but for emergency indications. In this case, the child must be removed from the mother's womb as soon as possible, for this purpose the general (endotracheal) anesthesia is considered optimal.
Reviews
Many women who have gone through such anesthesia for Cesarean section, argue that the postoperative period was fairly gentle and well. Only a few point out that it is painful to do the puncture itself, and few indicate that the discomfort (as if you were gutting) persisted throughout the operation.
Women also include post-puncture pains in the head and back as serious disadvantages. Especially they interfere in the first weeks, because it is extremely unpleasant to sit and walk.
Some young mothers, according to reviews on thematic forums, and for 3-4 months after cesarean section continue to experience numbness and tingling in the legs from time to time, as well as increased leg swelling. In this case, there are usually complaints of memory impairment and confusion.
Women who have not had enough spinal anesthesia claim that it was painful and scary, and therefore they will never give consent to such anesthesia for the future.
For details on spinal anesthesia for caesarean section, see the following video.