All about cesarean section
Back in the 1980s, cesarean section was a measure of medical despair, and this operation was used in obstetrics only when there was no other way out. The share of operative labor was about 2% of the total number of deliveries. Today, caesarean make about 15-20% of pregnant women, that is, almost every fifth baby is born thanks to the efforts of the surgeon.
In this article we will tell you what this operative intervention is, when and to whom it is done, how the recovery process is going on, and answer the most common questions of expectant mothers and those who recently passed through a caesarean section on their own.
What it is?
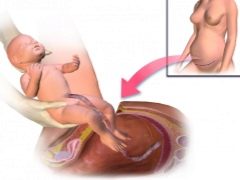
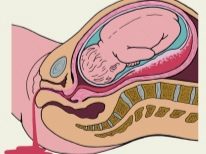
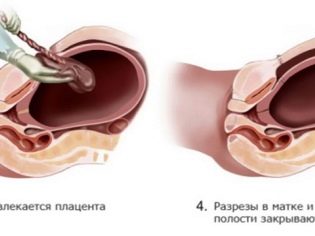
Physiological labor is the process of the birth of a child through the genital tract under the action of the pushing forces of the uterus. With a caesarean section, the baby appears through an incision in the uterus. Exactly the same, the so-called upper path, and removed the placenta.
The history of this operation is very interesting and long, which is easy to guess by analyzing its name: caesarea - “royal” and sectio - “cut” (from Latin). The royal section, the Caesar section, the imperial section - all these are the names of one operation that people have known since ancient times.
The name of this manipulation gave Guy Julius Caesar. He issued a decree, which ordered to dissect the womb of all pregnant Roman women who died or die, in order to save the still living babies. Everyone was on the bill - in conditions of constant conquests of the Great Roman Empire, boys and girls were needed. The first could be warriors, and the second - to give birth to warriors.
If you believe the ancient Greek myths, it was in this way that the famous healer Esculapus was born. His father Apollo extracted him from the womb of the deceased mother by a dissection method. There are ancient Japanese and Chinese legends, as well as myths of African peoples, in which there is a description of celiac section for the extraction of a child.
Until the XVI century, the operation was performed only to dead and dying women, which could not be saved. The French surgeon Ambroise Paré at the King’s court tried Caesar live women, but without success. The stitches on the uterus are not imposed, mistakenly believing that it can grow together, like a cut finger, itself. All his patients were dying. Only in the XIX century, the Italian Edouard Perrot suggested giving women a chance to survive, and for this purpose began to remove the uterus.
At the beginning of the 20th century, doctors began stitching the uterus, and this significantly reduced the female mortality rate. And with the advent of antibiotics, the operation has become quite ordinary.
In modern obstetrics there are two types of operations:
- elective caesarean section;
- emergency caesarean section.
The first is done according to indications revealed during the period of pregnancy, and the second is still a peculiar measure of medical despair, it is used when you need to save the life of a child and a woman during complicated labor.
There is also a small cesarean section, which is carried out for the period from 18 to 22 weeks of pregnancy in the presence of urgent medical indications for abortion, but the labor activity is not shown to a woman.At this time, it is no longer possible to clean the uterus with instruments or to perform a vacuum abortion. Artificial childbirth is a danger to the health of the woman.
Who is shown?
When carrying out operative labor, the risk of complications for the mother increases 12-14 times compared with physiological labor. That is why the Ministry of Health of Russia developed a provision that was included in the clinical guidelines for caesarean section regarding indications for surgery. The need for this has matured, since the number of such genera has grown.
Experts believe that there are a lot of reasons for the widespread use of surgical obstetric care: this is also an increase in the age of women in labor (there were more of those who come for the first child only after 37).40 years), a lot of IVF is performed, some couples even come for a second or third ECO child. Women who once had a cesarean, increasingly want to become mothers again, not wanting to be content with only one heir in the family. Ladies have become hypodynamic, so the list of reasons for giving birth in the operating room has increased in recent years.
Today, routine surgical delivery is performed under the following circumstances.
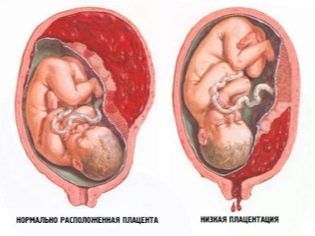
- Low location of the placenta, its presentation.
- Thinned, insolvent scar on the genital organ from the previous operation, and not only obstetric, but also any other, if it included the suturing of the uterine wall.
- Signs of placental abruption, which occurred prematurely.
- More than two scars on the wall of the uterus in the personal medical history of the woman in labor.
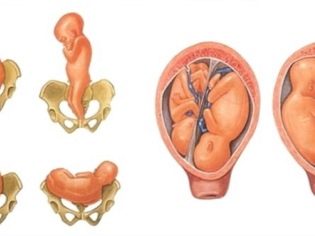
- The presence of obstacles to the movement of the child in the physiological birth canal (narrowness of the pelvis from 2 degrees, deformed bones of the pelvis, tumors of the uterus, cervix, vagina).
- Severe pronounced symphysitis.
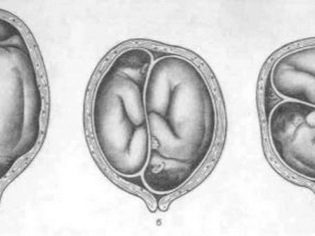
- The position of a child in the womb (transverse, pelvic, oblique, buttock-foot) that is unsuitable for birth in a natural way. In some cases, childbirth is possible and physiologically, but only if the weight of the child is not above 3600 g.
- Pregnancy is twins, if one fetus is located in the wrong position or in the pelvic presentation one of the babies is located closer to the exit of the uterus.
- Severe first birth, after which there were gaps from the third degree and above.
- Anatomical features - narrow vagina, two-horned or saddle-shaped uterus.
- Intergrown twins, as well as identical twins, who are in the same fetal bladder.
- Pregnancy after IVF (at the discretion of the doctor).
- Delayed fetal development from the third degree. Such children are very weak for childbirth.
- Renal - gestational age 42 weeks or more. Surgical intervention is carried out if the induction of labor has been ineffective.
- Severe preeclampsia (high blood pressure, edema, signs of pre-eclampsia).
- The impossibility of straining without risk to health - such an action is contraindicated for women with a transplanted kidney, with diseases of the heart, blood vessels and retinal detachment in history.
- Oxygen starvation of the child (according to ultrasound, CTG).
- Genital herpes is primary.
- HIV in the mother, if she did not receive anti-retrograde therapy.
- Violation of hemostasis in the mother and fetus.
- Malformations of the child.
For emergency surgical delivery, other indications are provided:
- discharge of water ahead of time and a long anhydrous period in the absence of a result from the stimulation of labor;
- developed bleeding;
- placental abruption before birth;
- threatening uterine rupture or the beginning of a rupture;
- primary or secondary generic weakness;
- embolism amniotic fluid;
- the development of acute sudden oxygen starvation of the fetus during childbirth;
- the death of the woman in labor or the state of agony to save the child.
When indications are found in the process of carrying a child, the appointment of a planned operation is considered reasonable, since in case of emergency the probability of complications is always higher.
Is it possible to do as desired?
A caesarean section of its own accord, if there are no valid reasons for the operation, is called elective. In world practice, this phenomenon is gaining momentum, and today doctors of many countries agree to such operations for a fee. But in Russia, this is more complicated.
In state maternity hospitals, clinics, and in any perinatal center that provides assistance free of charge under the policy of compulsory medical insurance, an elective caesarean section will not be conducted so as not to expose a healthy woman, who may well give birth to herself, to an unreasonable and unjustified risk only because she is afraid of birth pain.
But, in the opinion of women, the options still exist, however, costly. The one who invented private medical practice did not lose at all - it is profitable and profitable. Therefore, a woman who does not agree to endure pain and fear, and give birth herself for any price, can turn to private clinics. Thus, the networks of the “Mother and Child” clinics, for example, in August 2018, requested for an elective cesarean section from 340 to 560 thousand rubles (depending on the specific doctor who will perform the operation).
Before such births, a woman is offered an impressive package of documents for signing, setting an autograph in which, in essence, she refuses any claims related to possible risks, complications, consequences, the presence of a scar after surgery and the associated difficulties in bearing the next baby.
Advantages and disadvantages
Operational childbirth has its pros and cons, about which a woman should know if she is going to have a planned operation, and also if she decides on an elective COP.
The advantages are:
- no generic pain, the operation takes place with the use of general or spinal (sometimes epidural) anesthesia;
- the probability of a birth injury being tenfold reduced;
- childbirth is fast (25-45 minutes compared with the many hours of birth of a child with physiological labor);
- there is an opportunity to organize a partnership childbirth and at the same time not cause a shock from what he saw, and the rejection of the whole feminine nature of the newly-made father;
- the operation makes it possible to be born to a child who, in another way, simply could not have been born alive and healthy.
Now consider the disadvantages of cesarean compared with physiological childbirth.
- Longer and painful recovery postoperative period. Life after a cesarean will have many limitations.
- Surgical completion of pregnancy is unnatural, and therefore is a great stress for both the child and the mother.
- The child does not pass through the genital tract, does not receive from the mother the necessary and beneficial bacteria that facilitate the process of its adaptation to the new environment.
- Anesthetics, which are used by the anesthesiologist, also affect the child.
- The presence of a scar on the uterus, which may complicate subsequent pregnancies.
- High probability of infection, mechanical injury during surgery, medical error, complications in the early and late period after surgery.
Training
The timing of an emergency operation is difficult to account for and predict. In any maternity hospital there is an opportunity to carry out surgical childbirth according to vital indications as soon as these indications arise. Preparation of the operating room will take no more than 10-15 minutes. About planned surgery, the final decision is usually taken at 34-36 weeks of pregnancy. By this time, the baby’s parameters, the ratio of its size to the size of the pelvis, its position in the uterus, and some other features of pregnancy become apparent.
If the testimony was absolute from the very beginning of pregnancy (more than two scars on the uterus, anatomical features of the structure of the uterus, insolvent scar, etc.), then a separate decision on the planning of the operation is not made. It is implied from the very beginning.
In the clinical guidelines, the Russian Ministry of Health advises to conduct a planned delivery operation after 39 weeks gestation. The child is viable, according to statistics, from 36-37 weeks, but the likelihood of developing respiratory failure in the newborn remains and persists until almost 39-40 weeks.
The third, fourth and subsequent cesarean can be carried out a week earlier, because the condition of the scar with each subsequent child worsens, and therefore there is a probability of divergence of uterine tissue along the scar.
Earlier, 39–40 weeks, a cesarean may be prescribed if the fetus’s interests urgently require it - it is in a state of hypoxia, experiencing a different disadvantage. Also, the previously defined terms of the operation can be changed due to the beginning of generic harbingers of a woman, with a deterioration of her condition.
At 38 weeks, the woman receives a referral, usually hospitalized 3-5 days before the operation. Preparation begins:
- determine the condition of the fetus, its size by ultrasound, weight, location in the uterus, the location of the placenta;
- make analyzes to the future mother;
- A conversation is held with the anesthesiologist, who must identify possible contraindications to any particular type of anesthesia, and as a result of the conversation, the woman signs consent to a particular type of anesthesia.
On the day of surgery, the woman is given a cleansing enema, and the pubic area is shaved. It is recommended to wear compression stockings or bandage the legs with elastic bandages before surgery. This will help avoid varicose veins and thromboembolism after it.
Technique of
There are quite a few methods for caesarean section. The surgeon is free to choose the one that considers most acceptable and safe in a given situation.
The operation begins with anesthesia. A woman gets into the operating room, where everything is ready. The anesthesiologist injects drugs either intravenously followed by the introduction of the tracheal tube (with general anesthesia), or makes an injection of painkillers into the epidural or subarachnoid space of the lumbar spine. In the first case, the woman instantly falls asleep. In the second, it remains conscious throughout the entire operation, just the lower part of the body loses sensitivity.
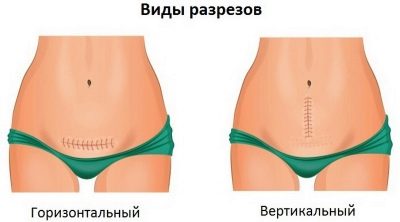
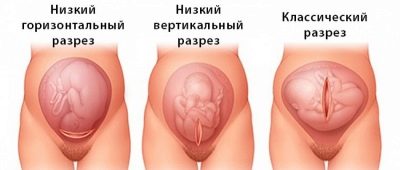
As soon as the anesthesiologist makes sure that the patient does not feel pain, he allows the surgeons to begin work. Cuts are of two types - horizontal and vertical. Planned cesarean is usually performed with a horizontal dissection of the anterior abdominal wall in the lower uterine segment, just above the pubic line. This cut is called the Pfannenstiel section.
The vertical section from the navel to the center of the pubic line is called corporal and is used quite rarely, mainly during emergency operations, when there is an urgent need to remove the baby as quickly as possible.
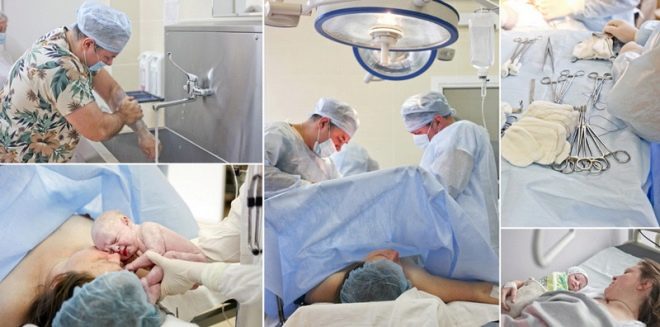
The stages of the operation as a whole look like this:
- anesthesia;
- dissection of the anterior abdominal wall and expansion or incision of muscle tissue and subcutaneous tissue (depending on the method preferred by the surgeon);
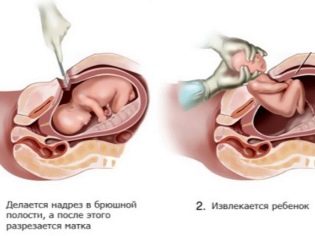
- incision in uterine tissue;
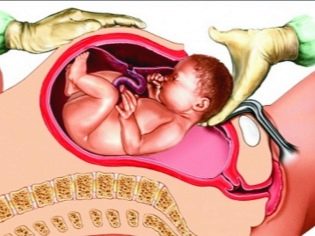
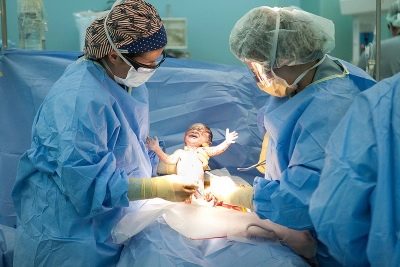
- child retrieval;
- umbilical cord cutting;
- the seizure of "child seats";
- suturing all incisions.
On average, the operation lasts 25 to 45 minutes. The second or subsequent cesarean can last a little longer, as the doctors need to excise the old scar and form a new one.
Classic
Classic caesarean section is performed by one of two dissection methods.For the most part, it implies making a Pfannenstiel incision, a Diannar semi-lunar incision, or external dissection and manual abduction of muscle tissue followed by dissection of the peritoneum and uterine wall according to Gusakov. In addition to the above methods, at the personal choice of the doctor can be carried out:
- corporal low;
- T-shaped or J-shaped cuts;
- bottom transverse.
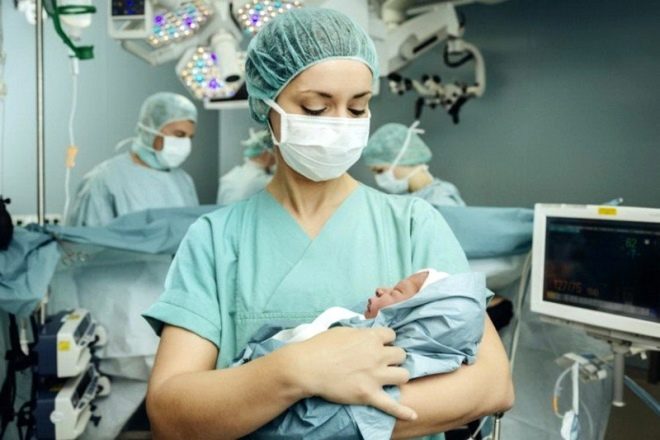
Having gained access to the uterine cavity, the doctor perforates the fetal bladder, drains the amniotic fluid, inserts 4 fingers of the right hand into the uterus through the incision and leads them to the back of the head. Gradually, he helps the head to go into the cut. Then the front and rear shoulders are gently withdrawn, they take the baby out completely, seizing under the arms.
The umbilical cord is cut and the child is passed to the pediatrician, neonatologist or nurse of the children's department. The placenta is separated manually after intravenous administration of oxytocin. The uterus is sutured either in the abdominal cavity or outside. This question completely remains at the discretion of the doctor.
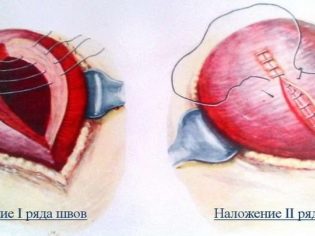
A double-row or single-row suture is applied to the uterus using self-absorbable material, all incisions are sutured separately, and the operation is completed by imposing external sutures or metal staples from a special medical alloy.
According to Stark
More than 20 years ago, the Israeli surgeon Michael Stark introduced his method, which looks less traumatic than the classical caesarean. In a number of countries, including Russia, the Stark section has its supporters and opponents. During the operation, the surgeon will have to make only two incisions - the skin of the abdomen and the uterus. Everything else is not subject to surgical incisions, the muscles and the subcutaneous layer are shifted by the doctor to the side, until they reach the child. Then there is no need to suture these layers, and the recovery is less complicated.
A more benign method has its own contraindications, these include: the presence of fibroids, large blood vessels, veins. Even if the surgeon began to lapse across Stark, he can end it traditionally if at least one of the contraindications is revealed.
Slow COP
Slow caesarean is a fundamentally new method of performing a delivery operation. It is a kind of compromise between surgical and natural childbirth. Doctors make a very small incision in the uterus and inject oxytocin, causing contractions. The child gets the opportunity to be born almost naturally, but not through the genital tract, but through an incision in the abdomen.
The method is already practiced by Russian doctors, but so far the doctors who undertake such an operation are not in every perinatal center and maternity hospital.
Recovery features
The first woman who has passed from the category of pregnant women, into the category of women in labor, spends in the intensive care unit or in intensive care, if there are any complications. She is closely watched, blood pressure, temperature are measured, painkillers and reducing agents are injected, and antibiotics if necessary. After 5 hours, a woman, if there are no negative consequences, is transferred to a regular ward.
There, after a couple of hours, she should start to turn sideways, then you can sit. It is important to behave calmly, without sudden movements, so as not to injure the seams. Headaches after anesthesia are quite natural, especially after epidural anesthesia. Pain in the abdomen relieves painkillers, which are administered in the first 2-3 days.
The postoperative period is very important for further recovery. There is nothing superfluous in it. All recommendations are important and aimed at minimizing the likelihood of complications.
Nutrition
On the first day after surgery, you can not eat, you can only drink, but not more than one and a half liters of fluid per day. Perfect clean drinking water without gas with a little lemon juice.On the second day, a woman can eat secondary chicken or beef broth, white croutons, cooked at home without sugar, salt, flavors and spices. You can eat mashed potatoes without butter, drink apple juice in moderation. On the third day, a woman can eat porridge (an exception is barley and rice porridge), drink compote, kefir. A common table is allowed from the fourth day after the operation.
Further, the diet is not much different from the diet for nursing mothers after natural childbirth. It is important to avoid constipation. Therefore, for 3-4 days a woman in labor, in the absence of a bowel movement, is given an enema or a glycerin suppository or microclyster is prescribed.
Can I lie on my stomach?
Women after physiological delivery, as well as women after cesarean section, doctors not only do not prohibit it, but also welcome it, because this posture contributes to a more rapid recovery of elasticity of the abdominal muscles and has a positive effect on uterine contractions.
As soon as a woman stops experiencing severe pain, she can roll over and lie boldly on her stomach. This position contributes to the prevention of fistula and adhesions, allows you to quickly get in shape, removing a saggy belly, and more quickly cope with the divergence of the abdominal muscles (diastasis). Among other things, this posture improves the functioning of the stomach and intestines, is the prevention of constipation and swelling.
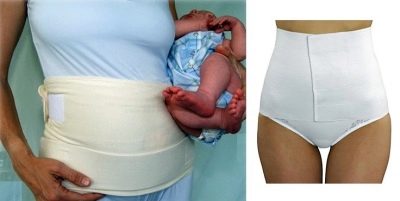
Bandage
According to mummies and doctors, the postoperative bandage significantly speeds up recovery, contributes to faster healing of scars, since it relieves part of the load from the abdominal and lower back muscles injured during the operation.
Wearing a bandage is not considered mandatory, a woman can decide for herself whether to use it or not. Waistpants, corsets and other orthopedic appliances will help choose a doctor.
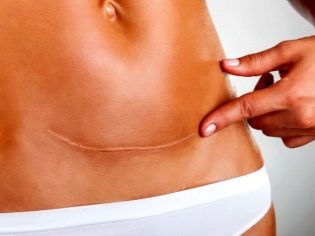
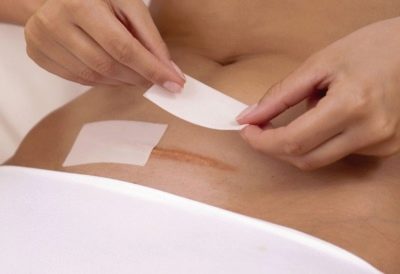
When do stitches heal?
The outer scar heals in about three weeks after surgery. The stitches are removed for 8-9 days. At home, the woman should continue to treat the stitches, dry the postoperative wound with hydrogen peroxide, and also lubricate around it with green paint to avoid bacterial contamination.
Internal seams complete their primary formation two months after surgery, the final formation of the internal scar on the reproductive organ is completed 2 years after surgery.
Possible complications
Caesarean can not be considered natural, it was not intended by nature as a method of alternative delivery, and therefore such an operation is always a great stress for the body of a woman and her newborn baby. It is considered preferable to abdominal delivery before the onset of contractions, and this means that the baby is not too ready for birth, the hormonal background of the woman has not changed into the mode of labor.
Means that are used by anaesthesiologists to achieve the effect of anesthesia, act not only on the mother, but also on the baby. That is why in the first days the crumb can sluggishly suck, refuse from the breast, sleep a lot, demonstrate some inhibition. But it is reversible.
Complications can be much more alarming during the operation, as well as in the early period after it, and even some time later. During the operation, the doctor may inadvertently injure the vascular bundles, damage the bladder, ureters, and sometimes even the perforation of the intestinal wall. The probability of such complications is not higher than 0.01%.
Postoperative bleeding, which is usually associated not only with vascular injury, but also with abnormal processes of uterine regression, can be dangerous. If the cuts are absent or they are insufficient in strength and intensity, it is possible that the lochia (postpartum discharge) is difficult to separate.
The most severe complications include various infectious inflammatory processes. They can be lethal for a woman if they are not noticed on time.They are manifested by fever, more severe abdominal pain, the appearance of atypical discharge, suppuration of the postoperative wound. The frequency of such complications is about 1%.
Subject to the recommendations of the postpartum period will proceed more easily, and it will be possible to reduce the likelihood of late complications, which include: divergence of the scar, the formation of an insolvent scar, the appearance of fistulas and hernia in the scar area.
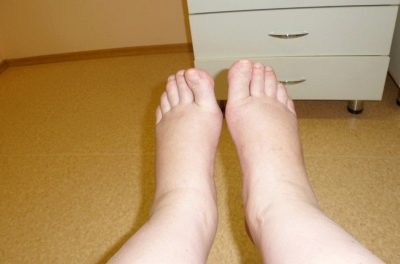
Swelling of the legs after cesarean is quite common, usually it goes away on its own within a few weeks after surgery. Foot baths help, as well as lying with raised legs (a roller is placed under the ankles), foot massage.
After cesarean, chronic diseases, such as gastritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, are often exacerbated by a woman, since in 100% of cases, surgical birth leads to a temporary decrease in the mother's immunity.
Lactation after COP
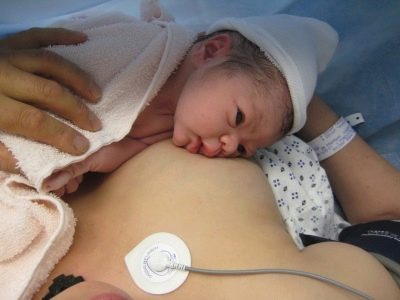
After cesarean section, breastfeeding slows down somewhat, because breast milk comes later than after physiological delivery. If the operation was done under epidural anesthesia, the child can immediately, right in the operating room, be applied to the chest, which will contribute to the earlier development of lactation. If operated on under general anesthesia, they bring the child when the woman learns to sit, walk, that is, after 8-10 hours.
The closer the term of cesarean section to the expected date of birth, the faster the milk will come. The role is played by what food will be for a nursing mother, how the early postoperative period will proceed.
In order for milk to begin to be produced, the level of a particular hormone, prolactin, must increase in the body. It rises gradually as the level of progesterone drops. But even a few drops of colostrum are very important for the baby, do not neglect them. Colostrum is very nutritious, it provides all the needs of the crumbs for the first 1-2 days. A woman just needs to calm down and wait patiently in the wings. Usually, after cesarean milk comes in 3-4 days.
Regular expressions, breast massage, plenty of warm drinks, regular attachment of the baby to the chest will help. The application, in addition to the obvious benefits for the infant, is also of tremendous benefit for the woman - under the effect of the oxytocin produced at the moment of nipple stimulation, the uterus begins to contract more actively and is cleared of lohia more quickly.
Limitations and recommendations after surgery
After surgery, it is important for a woman to follow medical advice. Here are the main ones.
- Exercise should be moderate and proportionate to well-being. A woman can not lift weights more than 4 kilograms, squat. It will be possible to return to sports only after the internal scars have grown well. You can run after a cesarean only after 7-8 months, lift the barbell and work out with dumbbells - after a year, swing the press - in six months. Yoga and Pilates, like swimming, can be available already 3 months after surgery.
- Hard monodiets are contraindicatedBecause the diet for a nursing woman should be high-calorie and balanced.
- After discharge, the woman should closely monitor the nature, profusion and duration of discharge, and the condition of her scar on her stomach. Postnatal pads in the maternity hospital use only sterile, hospital, and change every 3 hours, at home you can use the pads purchased, change them every 2-3 hours. Tampons are prohibited. Lochia should complete 6-8 weeks after surgery.
- Take a bath after surgery is not necessary for 2-3 months. The same ban applies to visiting the bath and sauna. Hygiene procedures should be carried out under the shower. When flushing, tap water should be avoided in the vagina.
- Do not allow constipation and abdominal distention. Nutrition must meet these goals completely.
- 3-4 weeks after the external suture is healed, “Contractubex» to reduce the seam and its more aesthetic appearance. If you find discharge from the seam or seal in its individual sections, swelling, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Sex is contraindicated for at least two months after surgery.until the lochia ceases and the uterus is completely cleared. Violation of the ban can lead to injury of internal sutures and infection to the uterus through the genital tract during intercourse.
Common Myths
You can often hear that children born by caesarean section are weaker and have less strong immunity. Child psychologists say that they have less stress tolerance compared with children who have overcome the first difficulties in life, having passed through narrow birth canals on their own.
These statements fall into the category of numerous myths, which are widely known about cesarean. Pediatricians, including Dr. Komarovsky, categorically refute the information that children born by surgery, for health reasons, differ from children born naturally.
Also, young mothers can be frightened by “horror stories” that babies born through cesarean section are lagging behind in physical development, later they learn to sit and stomp, that they all suffer from hyperactivity syndrome and have whole bouquets of neurological problems.
Caesarean can not affect the type of personality of the child, his temperament, activity and character. Therefore, it is not worthwhile to fear that a baby born operatively will grow up “zatyukannymi” and passive. It is a myth.
Planning next pregnancy
Bearing a subsequent pregnancy can be complicated due to the presence of a scar on the uterus, and especially the scar of the insolvent. Therefore, for women who would like to have 2, 3, 4 or more children, it is important to follow the recommendations for rehabilitation. In a second pregnancy, a natural childbirth can be allowed, but only on condition that she got pregnant not too early, and the scar is consistent.
Menstruation after cesarean section comes at different times. In the presence of breastfeeding - after 6-9 months after childbirth, for women who do not breastfeed - in 2-3 months. Up to this point, it is important to protect yourself with condoms, and then, when the female cycle is normalizing, consult a doctor to discuss the possibility of taking pills, putting a spiral or choosing another method. It is recommended to get pregnant not earlier than in 2 years, but not later than in 7-8 years, because with age, the scar does not become more elastic, it loses its properties to stretch.
Even if independent labor will not be allowed, a second cesarean section is prescribed. Today, medicine has sufficient capacity to give a woman to carry out and 6 children, if necessary. But with the mind. Before conceiving you need to be examined, check the consistency of the scar.
All about caesarean section, see the following video.