Dr. Komarovsky about pharyngitis in children
The child has a sore throat. Grandmothers with a view of experts say that this is a cold because of the extra portion of ice cream eaten the day before. Moms suspect a sore throat. Last word for the doctor who is urgently taken to show the child or who is called to the house. However, the doctor does not share the points of view of parents and the older generation and confidently declares that the baby has pharyngitis. Authoritative children's doctor Evgeny Komarovsky will tell about pharyngitis in children.
About the disease
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous and lymphoid tissue of the pharynx. If the inflammatory process moves and captures the nasopharynx, this is rhinopharyngitis (its other name is nasopharyngitis). Throat inflammation occurs for a variety of reasons:
- viral infectioncaused by viruses fluadenoviruses;
- bacterial infection with streptococci, staphylococcus, pneumococci, fungi of the Candida family;
- allergy that develops in the larynx - due to inhalation of toxic, toxic substances, dust.
Pharyngitis can be acute and chronic. Acute develops immediately after a negative impact or infection, and chronic - against the background of constant or sometimes unsuccessful factors that haunt the child for quite a long time. Sometimes chronic pharyngitis is generally an independent disease, non-viral and non-allergic, in no way associated with SARS, influenza or manifestations of an allergic reaction. At the same time, such an “independent” pharyngitis can have full-fledged periods of exacerbation and remission.
Evgeny Komarovsky argues that there is nothing unusual in pharyngitis - the disease occurs in children more often than parents are accustomed to thinking. There are babies who are given such a diagnosis 3-4 times a year, but this cannot be considered the norm. Quite often, inflammation of the pharynx and nasopharynx can be triggered by too dry air, inhaled by a child, whose parents love to close all the vents and maintain a hot microclimate in the apartment.
Symptoms
Viral pharyngitis is usually acute. It develops in the background ARVI or flu, which means that all the symptoms of these diseases are characteristic of him - a runny nose, current snot, headaches, fever up to 38.0 degrees. With this pharyngitis, the child will complain of pain or sore throat, it will be painful for him to swallow. A nursing baby who cannot complain about anything will begin to refuse to eat, cry and worry.
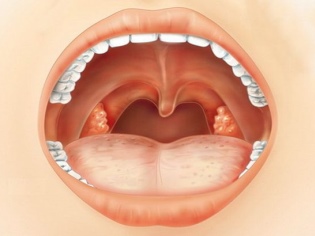
Another distinctive feature of pharyngitis is a dry cough that torments a child, especially at night. Often the lymph nodes in the neck become inflamed. Yevgeny Komarovsky claims that there is nothing surprising in this, because it is through these nodes that the lymph flows from the inflamed larynx. Sometimes on the tonsils or the walls of the larynx one can notice large red granular formations-granules. Then the pharyngitis will be called granular (with damage to the lymphoid tissue).
Allergic pharyngitis develops most often too acutely, a short time after inhalation of chemicals or allergens. When it does not have symptoms of SARS, but it may well be a cold. The temperature rises slightly - up to 37.0-37.5, above - extremely rare. Dry unproductive cough and pain when swallowing are also quite intense.
Bacterial pharyngitis is severe, with a rise in temperature above 38.5 degrees, with severe pain in the throat. On visual examination in the larynx and on the tonsils, purulent formations can be seen, which are often confused with angina.
The main difference between acute tonsillitis (sore throat) and acute pharyngitis (parents' information) is that the tonsils are affected in sore throat, and the inflammatory process is more blurred during pharyngitis and it extends to the laryngeal walls. When tonsillitis, the child complains of pain when swallowing, and pharyngitis will surely have a dry cough, as well as other symptoms associated with the disease.
Chronic pharyngitis occurs less clearly, and sometimes it is noticed only during periods of exacerbations. A child with a chronic form of the disease often has a sore throat, often there is a feeling of dry mouth and larynx, a dry cough often appears, but the temperature does not rise (at least until the next exacerbation). Exacerbation as two drops of water will resemble the usual acute pharyngitis.
Treatment
The choice of treatment tactics depends on what kind of illness the child developed - viral, bacterial or allergic. It should be noted that even a very experienced doctor will not be able to answer this crucial question only on the basis of a visual examination of the child and an assessment of all associated symptoms. The doctor, of course, will say that the baby has pharyngitis, but its origin will help to find out only two simple analyzes: a clinical analysis of blood and a pharyngeal smear for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics.
Without these studies, says Yevgeny Komarovsky, there can be no normal, responsible and conscious treatment of pharyngitis. After all, all three types of illness are treated in completely different ways and drugs.
Do not rush to comply with the recommendations of the doctor, who, looking into the throat and establishing the fact of the presence of the disease, immediately prescribes antibiotics or prescribes several types of antiviral drugs. Such a doctor should be asked to write a referral for tests, which should show how and what is better to treat.
Viral pharyngitis occurs more often than other species, because children suffer from viral infections more often than others. Approximately 85% of acute pharyngitis are viral in nature. Such pharyngitis cannot be treated with antibiotics, says Yevgeny Komarovsky. Antimicrobial agents against viruses do not show activity at all, but increase the risk of bacterial complication by a factor of 7–8.
Anti-virus drugs that are so effective are usually injected intravenously and are used in inpatient settings at infectious diseases hospitals. They have a large number of side effects and are rather difficult to tolerate. Neither homeopathic remedies, nor other tablets and syrups with the declared antiviral effect, which are freely sold in pharmacies in Russia, advertised on television and radio, do not affect viruses and immunity.
The only correct treatment of viral pharyngitis is an abundant warm drink., sufficiently moistened air in the apartment where the sick child is located, irrigation of the nasal mucosa and nasopharynx with saline (1 teaspoon of salt per liter of water). If the age of the child allows, it is possible to provide gargling with the same saline. Locally for the sore pharynx, an antiseptic is used (for example, "Miramistin"), As well as candy with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. Komarovsky warns that apply "Lugol"(And even more so to cauterize the tonsils and larynx with iodine) is not necessary, since it is much more harmful for the child than pharyngitis, which is not smeared, treated and not cauterized.
Allergic pharyngitis will require a more detailed approach. Antibiotics in the treatment of such a disease is absolutely contraindicated.The doctor may prescribe antihistamines - depending on the allergen (if its type can be quickly installed). Saline washings of the nose and larynx, as well as local antiseptics (except iodine) are relevant.
In addition, it will be necessary to remove from the premises all items that are able to accumulate dust - carpets, soft toys, books. Air is humidified to the level of 50-70%, airing and often doing wet cleaning in a child’s room.
When bacterial pharyngitis, according to Evgeny Komarovsky, the question of the need to use antibiotics is solved individually. Far from all cases antimicrobial agents are generally needed. If they need, then most often use drugs penicillin group.
The child is contagious until he was given antibiotics. Usually a day after this, the child may well attend school or kindergarten if he has no temperature. Bed rest is optional.
If a child's laboratory tests confirm streptococcal pharyngitis, then all family members must pass similar smears from the throat. If necessary, treatment with antibiotics must pass all households - in order to avoid re-infection of the baby.
Tips of Dr. Komarovsky
The best antiseptic for the throat, which even the most expensive pharmaceuticals cannot match, is saliva. If it is enough, it can well protect the child from pharyngitis. To saliva does not dry out, it is desirable to have in the house humidifier and use it for its intended purpose. In addition, the child should drink enough liquid (to preserve the consistency of saliva). Vaccination against pharyngitis does not exist. Home prevention - care for the quality of saliva and strengthen the immune system.
In the next video about the sore throat in children, Dr. Komarovsky will tell.