Dr. Komarovsky about intestinal infection in children
Intestinal infections are very common among children. And this is not surprising, because kids love to explore the world in taste, and as soon as they acquire the ability to grab various objects with their hands, the first thing they do is to drag these objects into their mouths. On how to prevent unpleasant consequences, how to treat a child with an intestinal infection and what you should know about it, says the well-known pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky.
What it is
Intestinal infections are not a separate ailment, but a whole large group of diseases that combine similar symptoms - diarrhea, vomiting, fever. Bacteria and viruses can cause diseases. The disease does not develop immediately, but only 10-45 hours after the pathogen has entered the body.. The most dangerous are salmonellosis, dysentery, staphylococcuscholera Among viral infections - the leaders in the frequency of occurrence enterovirus and rotavirus infections.
Sometimes a disease caused by a particular pathogen from the outside is complicated by the fact that opportunistic bacteria that live in the intestines, for example, hemolyzing E. coli, start to "rebel". While the child is healthy, she does not manifest itself, but the body, weakened by infection, becomes for her not a home, but a battlefield, and the microorganism begins to parasitize, worsening the child’s condition.
Dr. Komarovsky about the problem
There is nothing to be ashamed of, says Yevgeny Komarovsky. Even the cleanest mother, even if she chooses only the best products for her child, the baby may well get an intestinal infection. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, every day on the planet a lot of children suffer from these ailments. More than 2 million babies under the age of 5 die each year precisely from such infections. But there is a consoling figure among official statistics - 90% of all cases of intestinal infections among babies can be quickly and effectively treated without using any medication on their own at home.
The symptoms most parents are well aware of: diarrhea (loose stools), nausea, emetic attacks, complaints of pain in the abdomen. This is precisely the localization of pain. Evgeny Olegovich recommends paying attention first of all.
If bacteria or viruses hit the stomach, then the child has gastritis. If inflammation develops in the small intestine, it is enteritis, and if the large intestine is affected, then we can talk about colitis. But here, too, not everything is simple, and often the children have mixed diagnoses - enterocolitis, gastroenteritis.
Despite the fact that intestinal infections in the people are considered to be “the disease of dirty hands,” Yevgeny Komarovsky argues that this would be too simple. After all, children can play in the same sandbox, eat the same apples bought in the same store, but one child will fall ill, and nothing like this will happen to the other. The main risk is not even dirty hands, the doctor says, but a combination of the three most important factors for the development of an intestinal infection: the child’s environment, the food he eats, and the liquid he eats.
If there is a person in his environment who is a source of infection, it is enough to have common toys, household items, the slightest physical contact for an infection to occur. With regard to food, it is easiest for large families - food is not stored there for a long time, which means that the risks of bacteria multiplying directly in food are reduced tenfold. Quality water is a common problem in many regions of Russia. Therefore, parents should carefully monitor the fact that the baby is drinking, and if the tap water is not very good, it is better to boil it even before brushing your teeth.
The younger the child, the greater his chances of getting an intestinal infection. Komarovsky recalls that gastric juice has an important function - it destroys most of the bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth. However, in young children, the juice has less acidity than in adults, and therefore bacteria and harmful agents of viral origin have a much higher chance of surviving in the children's stomach.
The antibodies produced by the child’s body in response to the penetration of the pathogen do not remain for life, as is the case with chickenpox. Bacterial infections (staphylococcal or salmonellosis) cannot be defeated by antibodies alone to the corresponding pathogens, and drug treatment is required. But viral intestinal infections (the most common among which is rotavirus) can stimulate the emergence of specific antibodies that will protect the child from similar pathogens for quite a long time. Long, but not always.
Treatment
In acute treatment intestinal infectionaccording to Komarovsky, the main thing is not even the medicines that parents want to deal with pathogens as soon as possible. Much more important - to create favorable conditions for the work of the immunity of the baby. There are very few infections that require treatment with serious antibiotics. In most cases, no special treatment is required, the doctor stresses. The child just needs to be helped “to hold out” for 3-5 days, until his immune defense can cope with the pathogen.
How to treat intestinal infections will tell Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.
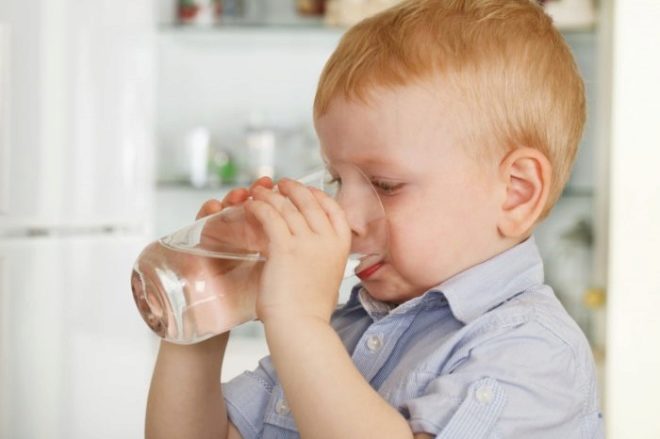
The main danger these days is the risk of dehydration. In severe cases, they die not from infection, but from dehydration, Komarovsky emphasizes. Therefore, abundant drinking should be the main means of treatment.
And in order not to replenish the sad statistics figures mentioned above, parents should remember the alarming symptoms like two and two and know the possible situations when self-treatment should be completely excluded. To the doctor, to the hospital of the infectious diseases hospital, and as soon as possible, should be sent if:
- The baby is too small or has very intense vomiting, as a result of which the child cannot drink water.
- In feces or vomiting, you notice blood, even the most insignificant.
- If diarrhea and emetic attacks are accompanied by very high fever. Severe intoxication, the appearance of excessive pallor, rash on the skin.
- If there are signs of dehydration. These include dry skin and mucous membranes, the absence or small amount of urine, which is distinguished by the baby, dry tongue. If a child does not pee for more than six hours at a time, this is a very alarming symptom; if he cries without tears, this is also a sign of dehydration. Outwardly noticeable sunken eyes, and in children under one year old, the spring on the head also falls.
High body temperature during intestinal infection performs an important task - stimulates the production of interferon, which is involved in immune protection. And if it is usually out of these considerations just not recommended to reduce without extreme need, then with intestinal infection attitude to the heat should be somewhat different.
Yevgeny Komarovsky stresses that at high temperatures the child sweats more, breathes through the mouth, and this causes the mucous membranes to dry out, he breathes more often, his heart beats faster in the heat. All this contributes to the additional loss of fluid. Heat becomes an extra burden on the already exhausted body of a child.Usually, Evgeny Olegovich advises to reduce the temperature after 38.5, but in the case of intestinal infections, a thermometer reading of 37.5 should be the reason for taking a febrifuge (such as Paracetamol).
In matters of the use of sorbents for intestinal ailments, doctors can not come to a common opinion. The World Health Organization does not advise to do this, but to prove that the sorbents are harmful to children's bodies so far no one has managed. Dr. Komarovsky recommends this issue to parents to decide on their own or consult with their physician, who knows the child better, but stresses that moderate use of sorbents, rather, will only benefit. Sorbents are Baktistatin, Polysorb, "Enterosgel"And the well-known activated carbon.
Otpaivat child with vomiting and diarrhea should be special preparations for oral rehydration. If during the flu it is enough to water the baby with sweet tea or fruit drink, then in the case of an intestinal infection, the child loses a large amount of not only the important fluid for him, but also the mineral salts during which he feels stool and vomiting.
That is why compotes are better left for later. And give the child large quantities of solutions "Rehydron"," Hydrovita ", suitable for replenishing the water-salt balance and" Humana Electrolyte ", and" Maratonik. " All of these drugs are bags of glucose and mineral salts, which simply dissolve in water and give the child a drink. Not very pleasant to the taste (solen!), But very useful and important.
To feed a child during the treatment of intestinal infections, according to Komarovsky, is far from useful.. Milk, meat food only worsens the condition of the baby, slowing recovery. However, if we are talking about skinny babes, with a lack of body weight, then such a child definitely should not starve, it can be deadly. To feed such a child it is necessary, just as before an intestinal infection, with products familiar to him, not to restrict him in food. If the peanut is not a goner, then it is better to temporarily limit the food, preferring liquid (broth, kissel). Children older than one year are best served with meals that do not contain meat and fatty ingredients. Milk, eggs, meat products are banned. Porridge is best cooked in water.
Tips
- If a child has an acute intestinal infection, it is important to ensure that no dehydration occurs. If with older children it is possible to control the amount of alcohol consumed and selected, then with infants everything is different. To determine how much crumb he peed, Komarovsky advises moms to use electronic scales. They need to weigh the used diaper. This will give more or less accurate data on the amount of liquid released.
- Do not panic, if the child suddenly became more liquid stool. If there are no associated symptoms, then it is most likely not an intestinal infection per se. It is characterized by several symptoms together. Komarovsky recommends not to sound the alarm and not to begin self-treatment of “I don’t know what” with folk remedies or medicines.
- Actively water baby with intestinal infections with high fever is also necessary because the most frequent complication of intestinal disorders is, however strange it may sound, pneumonia, says Komarovsky. If the moisture is enough, the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, bronchi, trachea and lungs will not dry out, and the risk pneumonia will be minimized.
- If financial opportunities do not allow buying enough sachets of oral rehydration mixture, Komarovsky advises to prepare the solution at home by yourself. The recipe is not an initiative of some home-grown folk healers, it is officially approved by the World Health Organization. For cooking you will need a liter of water, two tablespoons of sugar, and one teaspoon of soda and table salt.
- Drinking for a child should not be cold or hot. Ideally, it should fully comply with the body temperature, only then the rate of absorption of such a solution will be maximum, which is very important in the treatment of intestinal infections.
- During illness, intestinal upset in the face of decreased appetite, children often develop enzyme deficiency.. Therefore, as soon as the baby feels better, and he asks for food, you should not give him too much food or fatty foods, because there are not enough enzymes in the body.
- The best prevention is hygiene. The child should wash the pens more often, and the mother should properly store food and feed the child with clean or boiled water.