Dr. Komarovsky on the symptoms and treatment of mononucleosis in children
When a child is born, his immunity begins to "explore" all the surrounding hazards. So, gradually, encountering certain viruses, of which there are several hundred on the planet, protection in the form of antibodies to viruses is developed.
Infection with some agents is hard to miss, and some diseases disappear unnoticed or almost imperceptible to the parents of the crumbs. Quite often, many mothers and fathers do not even suspect that the child has had infectious mononucleosis. Authoritative doctor Evgeny Komarovsky tells whether it is possible to determine the symptoms of this disease in children, and what to do if the diagnosis is confirmed.
About the disease
Infectious mononucleosis is a viral illness. It is caused by Epstein-Barr virus, which is a common agent and is, in fact, herpesvirus type IV. This "elusive" virus is more often in contact with the population of the planet than people might think, as a result, more than 90% of adults have ever been infected with it. This is indicated by the presence of antibodies in the blood.
Similar antibodies, indicating that the infection was, the immunity has developed, are approximately 45-50% of children aged 5-7 years.
The virus feels great in certain cells of the human body - lymphocytes. There, it replicates rapidly under appropriate conducive circumstances, including weakened immunity. Most often, the virus is transmitted with physiological fluids - saliva, for example, for this its infectious mononucleosis is often called the "disease from kisses." Less commonly, the virus is transmitted by airborne droplets.
The pathogen is transmitted through blood transfusion, organ and bone marrow transplantation operations, as well as from a pregnant mother to the fetus through the general bloodstream.
Infectious mononucleosis refers to acute viral diseases, it does not have a chronic form. From the affected lymph nodes, the virus spreads rapidly throughout the body, affecting the internal organs that have lymphoid tissue in their structure.
Symptoms
In 90% of cases, infectious mononucleosis children have a mild form, says Yevgeny Komarovsky, and therefore it is rarely possible to diagnose it. Children under 2 years of age suffer from this disease infrequently, and in most cases the disease is mild. Children from 3 years and older take the disease much harder, and boys are sick more often than girls. Why this is so, medicine can not answer, but the fact is obvious.
After a mononucleosis virus enters the child’s body, the foreign agent can behave peacefully for quite a long time. It is all about the baby’s immunity. If natural protection is strong, then one and a half or two months may pass. If the body is weakened, then the symptoms of the beginning of the disease may appear after 5-6 days.
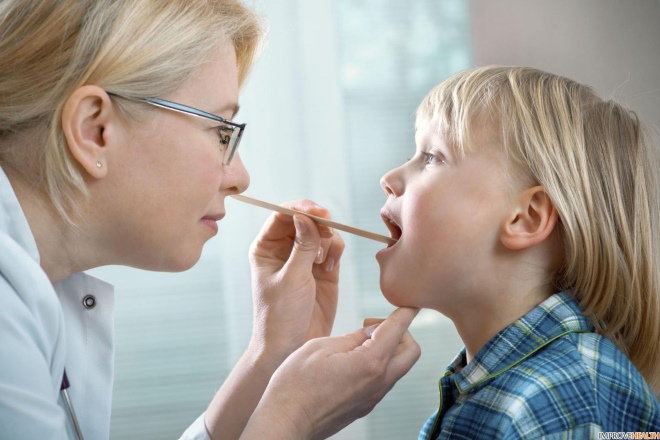
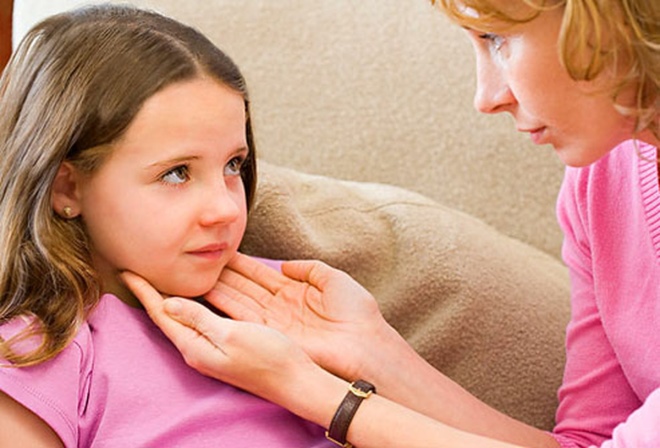
According to Yevgeny Komarovsky, the very first sign is an increase in lymph nodes. All groups of nodes increase to varying degrees, but most strongly - cervical, submandibular, occipital. An ultrasound at this time can reveal an increase in the size of the spleen and liver (these organs consist of lymphoid tissue). And in clinical blood tests, an altered lymphocytic formula will be revealed.
Immediately after this, the lymphoid tissue in the nose begins to inflame and grow in size (swelling), the tonsils become inflamed. The child's nasal breathing is disturbed, it breathes mainly only through the mouth, there is a strong night snoring. A child may complain of sore throat.
Common symptoms, which are misleading by both parents and doctors, are not specific:
- Lack or reduction of appetite.
- Weeping, capricious, lethargic.
- Increased body temperature.
- Pain when swallowing.
- Sensation of "aches" in the body.
All of these symptoms, together with some of them individually, can cause suspicion in attentive parents and in the called pediatrician. Be sure to do a blood test. Lymphocytes, which are affected by the virus, cease to be so, and turn into new cells, which a healthy child does not have in the blood and cannot be. These altered cells are called atypical mononuclear cells. If the technician finds them in the baby’s blood, the diagnosis will be confirmed completely. In addition, the number of leukocytes and monocytes will be increased in the blood.
The danger of illness lies not even in the illness itself, but in possible co-infections. When lymphoid tissue is affected, which plays a crucial role in the functioning of a child’s immunity, the body becomes more vulnerable than usual to various viruses and bacteria. It can be dangerous from the point of view that a secondary disease can easily begin, either, depending on the microbe or viral agent that has "joined." Often the complications are bacterial: angina, otitis, pneumonia.
Komarovsky about treatment
The disease can not be called fleeting. The acute phase lasts from 2 to 3 weeks, some - a little longer. The state of health of the child, of course, at this time will not be the best, and sometimes quite heavy. We need to be patient, because infectious mononucleosis passes in all children, without exception.
Uncomplicated mononucleosis does not require any special treatment. If the child feels rather well, then nothing should be given except for abundant drinking. If the condition of the baby is disappointing, then the doctor may prescribe hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. There is no cure for mononucleosis, as such, treatment should be exclusively symptomatic: sore throat - rinse, does not breathe nose - instill saline solution, moisten bronchial mucous membranes to avoid complications of the respiratory system.
Komarovsky does not see expediency in taking antiviral drugs, since they will not have any effect on the herpes simplex virus of the 4th type, but they will significantly “hit” the money of their parents. In addition, with clinically proven efficacy in antiviral drugs, everything is rather pitiable. For the same reason, it makes no sense to give the child homeopathic medicines with the stated antiviral effect. Of course, there will be no harm from them, but you should not expect any benefits either.
Treatment should be based on the creation of favorable conditions conducive to the speedy independent recovery of the child:
- In the acute stage of the disease, the baby needs rest, bed rest;
- The child must breathe humid air (relative humidity in the room - 50-70%);
- It is necessary to provide plenty of warm drinks throughout the acute period;
- It is more often to do wet cleaning in a child’s room without using household chemicals that contain chlorine;
- At high temperatures, the child can be given "Paracetamol" or "Ibuprofen."
When the temperature becomes normal, it is possible and necessary to walk more often in the open air, refraining from visiting children's playgrounds, crowded places, so that the child does not infect others and does not “catch” another infection with a weakened immune system.
During treatment, it is worth adhering to a therapeutic diet, eliminating from the child's diet all fatty, fried, smoked and salty foods, as well as spicy, sour and sweet.In the acute stage, with difficulty swallowing, it is best to give vegetable soups, mashed potatoes, milk porridge, cottage cheese. In the stage of recovery it is not necessary to turn all food into a puree, but the ban on the above products remains in force.
If bacterial complications have "joined" mononucleosis, they can and should be treated exclusively with antibiotics. Parents should be aware that if a doctor prescribes "Ampicillin"Or popular in pediatrics"Amoxicillin, Then the child will have a rash with a 97% chance. Why this reaction occurs, medicine today is unknown. It is safe to say only that this rash will not be an allergy to the antibiotic, a symptom of a separate disease, or a complication. It just appears and then passes by itself. It should not scare.
Recommendations of Dr. Komarovsky
Parents should report the fact of infectious mononucleosis to a preschool institution that attends a child, or to school. But the introduction of quarantine does not require this disease. Just in the rooms will require more frequent wet cleaning.
Recovery from infectious mononucleosis is a long process, the immunity is greatly weakened. For the next year (sometimes for half a year), the attending pediatrician cancels all calendar vaccinations for such a child. The child is not recommended to stay in close groups of children for a long time. The baby should not be taken to the sea to “correct” its immunity, since heavy acclimatization after a viral illness suffered is guaranteed. During the year it is not recommended to walk in the sun, go to sections where there is a strong physical exertion.
To support the body in the recovery process should be vitamin complexes permitted by age.
The child after the illness should be shown to the doctor more often. The virus has oncogenic activity, that is, it can contribute to the development of cancer tumors. If, after an illness for a long time, the very modified mononuclear cells continue to be found in the baby’s blood tests, the child will definitely need to be shown and registered with a hematologist.
To the virus that causes infectious mononucleosis, after a postponed disease, a persistent lifelong immunity is produced. It is impossible to get sick again. The exceptions are only HIV-infected, they can have any number of episodes of acute illness.
Patient Reviews
Most parents, whose children had this disease, claim that the diagnosis was the longest and most painful period, because doctors are in no hurry to make an accurate diagnosis. Many patients who are not sent for treatment to the infectious diseases hospital because of the mild stage of the disease, the doctors recommended taking antiviral drugs.
Patients who were treated at home by the method of Komarovsky, argue that there were no complications, the disease resolved rather quickly and was tolerated relatively easily by the child.
Below is a video with recommendations from Dr. Komarovsky himself.