Dr. Komarovsky on abnormal urine analysis in a child
Everybody, both healthy and sick, pass urine for analysis. According to her composition, the doctor will try to draw conclusions about the condition of the child. Parents for urine analysis does not cause questions.
Questions arise when it is necessary to collect material for research, and also later, when there is a piece of paper with a mass of incomprehensible symbols, letters and numbers. Dr. Komarovsky tells what analysis is considered normal, and what deviations from the norms can mean.
How to collect the analysis?
It depends on whether the material is collected for laboratory research, what will be the composition of urine. Komarovsky does not advise using empty jars, which used to be containers for food or drugs, for collection.
Use should be special cans, plastic or glass, which are sold in any pharmacy. The bottom of the tank should be flat, the lid should be tight. At the time of collection, check that the jar is dry and clean, so that there are no traces of detergents on it.
The child before collecting urine should be thoroughly washed with soapy water. It is necessary to collect all morning portion of urine entirely. Bring the jar to the laboratory should be no later than one and a half hours after collection.
Decoding analysis
In the form received at the hands of the result, if it is compiled by all the rules for conducting clinical analysis, there will be a lot of important and not very important information.
In the process of research the laboratory assistant will evaluate:
- urine color and transparency;
- smell;
- density;
- chemical reaction with respect to pH;
- presence or absence squirrel;
- glucose level;
- ketone bodies (acetone in urine);
- the presence or absence of bile pigments;
- composition of urinary sediment (red blood cells, white blood cells, cylinders, epithelial cells, salts).
Colour
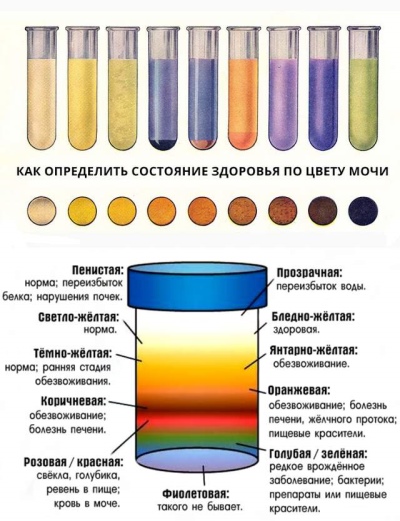
It depends on what the child ate, drank, or took medication. Some antibiotics stain urine in red, and fresh carrots eaten the day before - in orange. But color sometimes speaks of a possible illness. So, in children with diabetes, the urine is almost transparent, colorless, and in a child with jaundice, it is richly yellow. But based on the color alone, no one will diagnose diagnoses.
Transparency
Normal urine is clear. It begins to grow dim after a while, as a precipitate falls, sometimes in the form of flakes. If the newly collected urine is turbid, it “signals” the presence of leukocytes in it, a large amount of salt. In any case, it is necessary to understand further, the conclusions do early.
Urine smell
This indicator does not represent a special clinical value, and therefore it often does not fit into the research form at all. But parents should be aware that urine, which has the smell of fruit (vitamins) often appears after taking vitamins, as well as diabetes.
If the liquid smells strongly of ammonia, it can be a sign of a metabolic disorder.
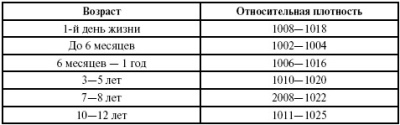
Density
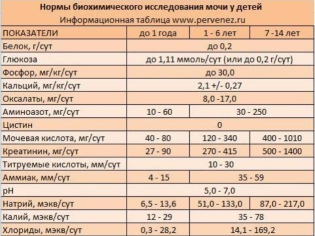
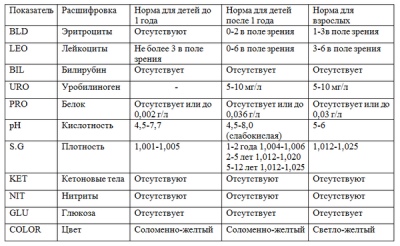
This indicator is presented in a numerical value, which will symbolize the relative density - the concentration of all other substances in the liquid. Normally, the child must have the values of 1,002-1,004 for up to half a year. A child under 1 year - 1,006-1,010. In the urine of a child from 3 to 5 years, the density is considered to be 1,010-1,020.At the age of 7, the rate will expand somewhat - 1.008 - 1.022, and for a child in adolescence - 1.011 -1.025.
Deviations from normal numbers may indicate impaired renal function. Often parents in the study form in the “Density” section see something completely unintelligible - “m. m "or" small. m "," little m ". This means that the presented sample was insufficient in volume to determine the density, since at least 50 ml of liquid must be poured into a special device.
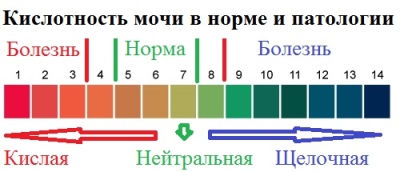
pH
Normal urine of a perfectly healthy baby gives a weak acid reaction. Any deviations of this parameter alarm the doctor. If the urine gave a more pronounced or high acid reaction, this may be a consequence of eating a large amount of protein, fasting, and postponed fever. If the urine gives an alkaline reaction, it is often a natural consequence of the meatless diet, the recent strong multiple vomiting, chronic diseases of the urinary tract. The norm - pH = 5,0-7,0.
Presence of protein
Normal protein in the urine should not be. More precisely, there it is so small that the reagents are not able to catch traces of protein. If so, then the laboratory assistant in the corresponding column of the form puts "-". If protein is found, its quantity is found. The presence of protein is called proteinuria. A functional disorder (not requiring treatment) has completely harmless reasons - the child eats a lot of protein, has recently had or has a fever, has experienced stress.
Pathological proteinuria can talk about serious kidney disease, circulatory failure.
Glucose in the urine
If everything is normal with the child, then there is no sugar in the urine. The exception is when the baby ate something sweet before a lot of analysis. In this column in the paper received from the laboratory there will be numbers. Normal values range from 8.8 mmol / liter to 9.9 mmol / liter. Your number in this range indicates that everything is in order. An increase in this threshold is usually observed in children with diabetes mellitus, and a decrease in children with an inflammatory process in the tissues of the kidneys.
Ketone bodies
In normal condition they are not. But if ketone bodies are found, and in the graph it is worth a “+”, you should not be afraid. This “find” is evidence that the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats is disturbed, and this happens quite often in children. Due to certain metabolic peculiarities, ketonuria (the presence of ketone bodies) in children occurs during stress, fatigue, and an elevated temperature.
If a child has recently vomited badly, if there are not enough carbohydrates in his diet, if he is starving, then with high probability in this section of the form, parents will see a “+”.
Bile Coloring Pigments
If the saturated yellow or orange color of the urine has alerted the laboratory technician, he will definitely study more carefully whether there is no bile pigment in the fluid — bilirubin, urobilin, etc. They appear in the urine only when the child develops hepatitis or jaundice.
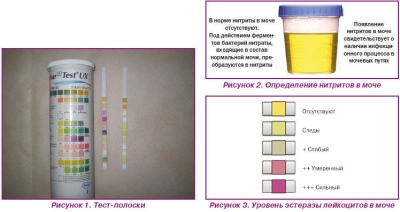
White blood cells
They are found in urine sediment after it is passed through a centrifuge. In this case, the laboratory assistant will study the material obtained through a microscope. A round picture before his eyes is the very “field of view”, which will be indicated in the form. If the leukocytes are rare, “2-6 in sight” will be written (or 2-6 pzr). The range is indicated so that the picture is the most complete - in one part of the field of view of the cells, two were counted, and in the other, by moving the microscope to the side - six.
If the leukocytes in the urine to the child are greatly increased, the analysis often looks like this - “leukocytes in the entire field of view” or “by ½ pzr.” This may mean the presence of a serious inflammatory process in the body, as well as elementary errors in the collection of urine (you forgot to wash the baby).
Normal values of leukocytes in the urine - 5-7 pzr (for boys), 7-10 pzr (for girls).
Red blood cells
These blood cells, like hemoglobin, in the urine should not be, except in single quantities.If more blood is found, the laboratory technician will not only put a “+”, but also write how many red blood cells in the field of view he counted, and what type they have - whether they are modified or not. A negligible amount suggests that the urinary tract is “scratched” by salts when urine passes through it. With a positive analysis, the doctor will call it “hematuria” and suspect the child. cystitis, nephritis or urolithiasis.
If there are so many red blood cells that the urine has a pronounced red blood color, it often speaks of kidney tumors, glomerulonephritis, hemorrhagic fever and other very serious and unpleasant ailments. The norms of blood cells in the urine are single cells from 0 to 2 not in every field of view (in the form it looks like “not 0-2 units not in every pzr).
Cylinders in the urine
This is not a separate type of cells or salts, but an accumulation of various substances, including fat and renal epithelium in the tubules of the kidneys. When such clusters come out, they are shaped like cylinders. The laboratory assistant will calculate how many of them and what is their origin. Hyaline cylinders - from the accumulation of protein, leukocyte - leukocytes, granular - the renal epithelium, and blood - red blood cells.
Normally, their content is estimated as a single, with a pathological increase in the doctor will suspect various renal ailments.
The salt
Their lab technician will look for urinary sediment. Urates are more likely to be present in acid pH analyzes. In the urine, which gives an alkaline reaction, phosphates will be found, and sometimes even amorphous phosphates. Oxalates can be found both there and there, and it does not mean anything alarming. The child just ate something sour, such as apples, grapes, oranges, or beets. But calcium oxalates in large numbers will induce a doctor to think about urolithiasis, that the child is likely to have “sand” in the kidneys or urinary tract.
Nitrites
Nitrites are found in the sediment if a child has inflammatory processes in the urinary system or kidneys caused by bacteria, intestinal sticks and Klebsiella. Therefore, if the laboratory technician writes that she has found Escherichia in the urine, the doctor will be entitled to prescribe strong antibiotics.
Calcium
Urinalysis according to Sulkovich allows to determine the quantity and quality of calcium in the urine of a child. This parameter is not determined by everyone, but only if there is reason to believe that a child does not absorb calcium or is rapidly losing it.
Dr. Komarovsky also talks about urine analysis in the next video.