Dr. Komarovsky about scarlet fever
In childhood, a person can have such illnesses that are peculiar only to children, but for adults they are not dangerous. One of these diseases is scarlet fever. Yevgeny Komarovsky, authoritative children's doctor, author of books, articles and television programs about children's health, tells how to recognize her, how to distinguish her from other infections and how to properly organize the treatment of a baby.
What it is
Scarlet fever is an infectious disease that causes Streptococcus group A.
A child can become infected with these hemolytic microbes in one single way - from a person:
- if the baby has been in contact with someonewho get sore throat or streptococcal pharyngitisespecially at the initial stage of the disease,
- if he communicated with a man who recovered from scarlet fever not so long ago - three weeks had not passed since the cure.
In addition, there are perfectly healthy people, including adults, who are carriers of Streptococcus A. They may not even guess about this, because they themselves do not get sick, but regularly release microbes into the environment. Such people are not as few as they seem. According to estimates of infectious disease specialists, carriers of Streptococcus A on the planet, about 15% of the total adult population.
Children's immunity is weaker than an adult, which is why adults do not suffer from scarlet fever, because they have acquired immunity to streptococci. The child does not have such protection. The only exceptions are babies up to a year - they have inborn, received from the mother, anti-toxic immunity. Therefore, scarlet fever in infants in the first year of life is an extremely rare phenomenon.
The rest of the children, up to the age of 16, are at risk. When communicating with someone from the above groups (who have been ill, sick or carriers), when sharing toys, household items, airborne droplets or contact paths, infection occurs.
It is this insidious microbe (not to be confused with all streptococci, because there are a lot of them), getting into the children's body begins to release a strong poison, which is called erytotoxin. The body reacts violently to it, which causes the symptoms of the disease. The incubation period lasts from days to 12 days. For habitat and reproduction, Streptococcus A chooses the mucous membranes of the tonsils.
Due to erythrotoxin, which paints the tonsils in bright red, the disease has a second name - purple fever.
Symptoms
Scarlet fever always begins acutely:
- body temperature rises sharply;
- severe sore throat;
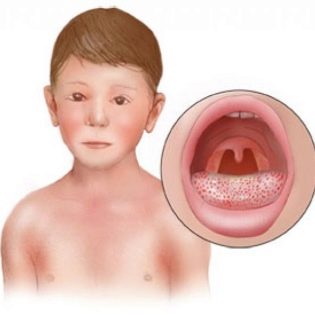
- tonsils, larynx and tongue at the same time have a scarlet, very bright color. On the tonsils may be observed fragments of purulent plaque. On the tongue for 3-4 days granular formations become noticeable;
- the body reacts to a strong toxin produced by streptococcus A, rash. It appears almost immediately after the onset of the disease.
This last feature is considered the most characteristic. About him should learn more. On the already reddened skin, small red dots appear, which, by the degree of color, are brighter, they are not difficult to see in all details. The rash spreads quickly until it covers the entire body of the child. Most red specks - on the sides, on the folds of the arms and legs. The skin becomes dry and rough to the touch, like textured cardboard.
Scarlet fever is not difficult to suspect even at one glance at the face of the baby: bright red cheeks with a rash, the same forehead. At the same time - completely clean and pale nasolabial triangle.After 7-10 days, the skin affected by the rash begins to peel off. After the first week of illness, the rash usually begins to disappear, it does not leave marks on the skin, age spots and scars. 14 days after the onset of the disease, desquamation usually stops.
Treatment
Despite the fact that scarlet fever is known to doctors for a long time, in ancient times, doctors often confused it with measles and rubella. But if viral rubella and measles do not require any specific medical treatment, then antibiotics are indicated for scarlet fever. Therefore, before the advent of antibacterial agents, scarlet fever was often fatal.
Today, doctors are divided into two "camps": some believe that successful predictions in the treatment of scarlet fever were made possible by the invention of antibiotics, others claim that a general improvement in the quality of life and nutrition of children played a role. Yevgeny Komarovsky is confident that deaths from scarlet fever have declined due to both reasons.
Streptococcus A is very sensitive to antibiotics, so it’s quite simple to handle. Treatment is usually prescribed at home. Only very young patients who are not 2-3 years old and children with a complicated form of scarlet fever can be sent to an infectious diseases hospital when there is a risk of damage to hemolytic streptococcus internal organs.
General treatment rules are as follows:
- bed rest until temperature decreases and signs of intoxication disappear;
- Plentiful warm drink (juices, tea, fruit drinks, compotes). Milk giving is not recommended;
- diet (according to the method of Pevsner, the so-called table number 2). Food should be given in a shabby, mushy state; soups, semi-liquid mashed potatoes are welcome;
- antibiotic therapy.
Most often, children are prescribed antibacterial agents of the penicillin group. These antibiotics do an excellent job with the causative agent of scarlet fever, and after 12 hours (maximum a day) after starting the medication, the child becomes much better. If a baby has intolerance to penicillin, other antibiotics may be prescribed for it - almost all existing groups of these drugs are quite effective against streptococcus A.
It’s not at all necessary to inject a child with shots, it is quite enough to drink a course of antibiotics in pills, Komarovsky says. The most commonly prescribed drugs - «Amoxicillin» and Retarpen. With a severe course of the disease in the hospital, the child will additionally be placed dropper with hemodezom to reduce toxicity.
Yevgeny Komarovsky argues that with the timely use of antibiotics, scarlet fever is almost always possible to win without serious complications. In the absence of adequate treatment or attempts by parents to treat a child with folk remedies, severe complications almost always occur, such as rheumatism of the heart, kidney damage (glomerulonephritis).
Prevention
Scarlet fever is normal can not get sick two or three times in my life. After infection, the body produces lifelong immunity to a particular type of streptococcus. But this does not mean that the child can not then get sick with any other streptococcal infection.
Repeated scarlet fever is a rare phenomenon. Usually this becomes possible, if antibiotics in the treatment of the first malady acted too quickly, the microbe was destroyed before the immunity formed specific antibodies to it. Also, the recurrence of the disease can happen in children with severely weakened immune systems. To treat a secondary infection should be the same way as the primary one, although the doctor will have to choose another antibiotic for this.
Scarlet fever vaccinations do not exist. After identifying a sick child, the children's team is quarantined for 7 days.
Tips of Dr. Komarovsky
Several important recommendations that, according to Komarovsky, will help to quickly cure scarlet fever and avoid complications:
- Do not stop treatment at the first sign of improvement.. The course of treatment must be strictly followed and must pass to the end;
- scarlet fever is contagious, but with the timely use of antibiotics, the child ceases to be dangerous to others already for 2-3 days of antibiotic therapy. Usually, the patient is isolated for at least 10 days. After that, you can walk, but for this it is better to choose places where the child can not contact with other children. This restriction must be sustained for at least 3 weeks after the onset of the disease. In the garden - after 22 days;
- if there are several children in the family, and one of them is sick with scarlet fever, the rest should be taken to the clinic and donated from the pharynx for the presence of a microbe. If it is not identified, children can attend their kindergartens and schools. If they do, treatment and quarantine will be assigned to them. In any case, the sick child should be isolated from the brothers and sisters.
In the video below, Dr. Komarovsky reveals some of the details of this disease.