Dr. Komarovsky on valgus foot deformity and flatfoot
The parents perceive the first steps of the child as a very joyful family event. But it can be overshadowed by the identification of such orthopedic pathology as the valgus deformity of the feet. This violation usually becomes apparent just in time for the start of walking and after a while. Evgeny Komarovsky, a well-known children's doctor and author of books on children's health, tells about the causes of the problem and what to do in this situation.
About the disease
In medicine, valgus is called such a deformation of the feet, in which they are cruciform in relation to each other, resemble Latin X. Most often, the pathology becomes noticeable when the child tries to step on the legs and take the first steps - pathology is expressed in the fact that while walking, the crumb rely on the inside of the foot.
Steps for such a kid are extremely difficult - he gets tired quickly, sometimes he experiences pain, the steps themselves are shaky and insecure. Orthopedists describe this condition in terms of the processes occurring in the feet - the fingers and heels are turned out, the middle part of the foot is somewhat omitted. If the legs are straightened and pressed against each other in the knee area, the distance between the bones of the ankles will be more than 3-4 centimeters. If at the same time the height of the arch of the foot is significantly reduced, then the orthopedists will already speak about the fact that the child has flat-foot oralgus feet. Valgus flatfoot is considered the most common diagnosis in pediatric orthopedics.
Such curvature of the feet, there are two types: congenital and physiological (acquired). In the first case, the legs are bent even in the period of prenatal development of the fetus under the influence of certain factors, about which the medicine knows not so much. Congenital abnormalities of the foot are usually quite heavy, and you can see them in the first 2-3 months of independent life of the child.
Acquired deformity is often associated with errors in the development and functioning of the musculoskeletal system, ligaments, tendons. Such violations become apparent closer to one year old. At risk - crumbs with weakened muscles, premature babies suffering ricketswho have suffered frequent and severe viral infections in the first year of life. The legs risk bending in obese children, since the load on the lower limbs with excess weight is very significant.
Sometimes parents themselves are to blame for the occurrence of pathology. So, putting the baby on his feet too early may well “start” the foot deformation mechanism, and an inadequate load on the foot, walking solely on an even floor can cause acquired flat-footedness or a flat -alus foot.
Flatfoot scares parents no less. However, Komarovsky advises not to panic, since from birth absolutely all children have flat feet, this is a feature of babies. The arch of the foot will be formed gradually, as it grows, the loads on the legs, and then everything is in the hands of parents, with the exception of congenital flat feet, which can only be corrected surgically.
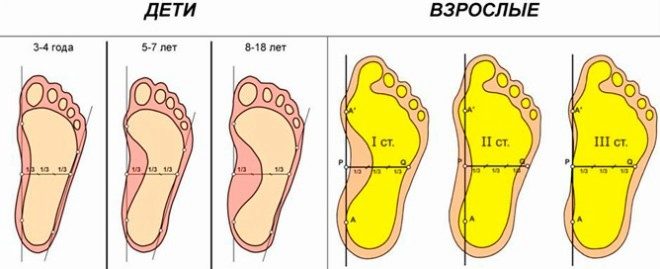
Degrees of pathology
There are four main degrees of valgus disease according to the severity of the defect and the severity of the course:
- First degree The angle of deviation from the norm does not exceed 15 degrees. Pathology is well amenable to correction by conservative methods.
- Second degree The deflection angle is not more than 20 degrees. This condition is also successfully treated with exercises, massage and physiotherapy.
- Third degree The deflection angle is no more than 30 degrees. Pathology is difficult to correct, treatment is long, but with proper patience and perseverance on the part of parents and doctors, the prognosis is very favorable.
- Fourth degree The angle of deviation from normal values - more than 30 degrees. With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment prescribed surgery.
Flatfoot also has several degrees, which are similarly classified according to the degree of deviation of the arch of the foot from the norm. As in the case of valgus deformity, the first and second degrees of ordinary flatfoot are treated fairly simply and fairly quickly. The third and fourth will be more difficult.
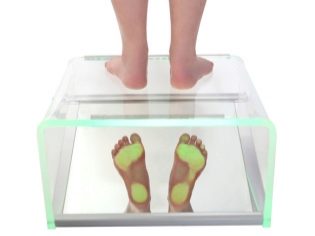
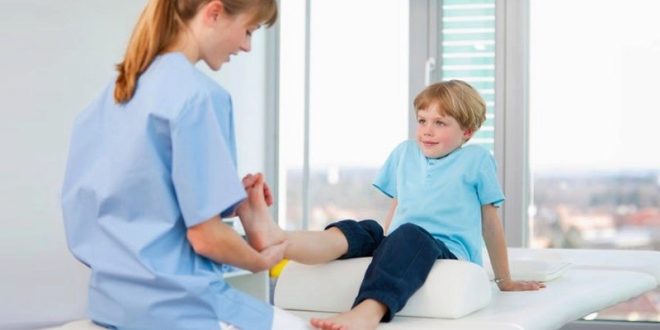
Diagnostics
The diagnosis puts the child orthopedic surgeon. This is done on the basis of visual inspection and designated additional studies, which include foot radiography, computer plantography, podometry. If such tests are not prescribed, and the doctor puts you on an appropriate diagnosis, you should contact another doctor. Quite often, young patients with confirmed valgus pathology are advised to visit a neurologist to rule out problems with the peripheral and central nervous systems.
As soon as the causes that underlie the modification of the feet are identified, the doctor will determine the type of lesion according to etiology:
- Static deformation. Such a problem is found if incorrect posture is involved in the curvature.
- Structural deformation. Curvature of the foot, with congenital causes. As a rule, the talus under such a deformation is located incorrectly with a deviation in one direction or another.
- Compensatory deformation. If a child has a shortened Achilles tendon, oblique lower legs, the foot will be functionally deformed when walking.
- Corrective deformity. Such a curvature occurs if the child is completely incorrectly treated or not treated at all the usual clubfoot.
- Spastic nervous deformation. The reason for such a curvature is in the improper functioning of the cerebral cortex, as a result of which limb spasms often occur.
- Paralytic deformity. It is usually the result of encephalitis at the early age or complicated poliomyelitis.
- Rickety deformation. Occurs with rickets.
- The consequences of injury. Rupture of ligaments, fractures of the bones of the foot, ankle, hip and hip injuries can lead to pathology.
When diagnosing flatfoot the same techniques and methods of research are used.
Treatment
The child’s foot is finally formed only by the age of 12, therefore many problems found by experts and parents themselves at a more tender age can and should be corrected precisely up to this point, says Dr. Komarovsky.
Usually, treatment of both flatfoot and valgus curvature is aimed at strengthening the ligamentous apparatus, the muscles of the foot, and forming the arch. To do this, prescribe foot baths, therapeutic massage, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, swimming, physical therapy. In case of congenital abnormalities, lower limbs are immobilized with gypsum. In the absence of the desired effect of all these measures, surgery may be recommended to the child.
If the defect is not treated and not corrected, in the case of severe deformity, the child faces a subsequent disability., as the increased load on the knee and hip joints causes deformation and destruction of them, which leads to irreversible changes in the functions of the musculoskeletal system.
Forecasts
The earlier the pathology is revealed, the easier it will be to correct it. Medical statistics shows that the valgus curvature of the feet and legs, detected at the age of one year and a little older with appropriate therapy, has very favorable prognoses - the probability of eliminating the problem completely and forever approaching one hundred percent.
If the disease is detected late or the child has not been provided with the necessary medical care for a number of reasons and the disease is neglected, there is a very high probability of developing problems with the spine in adolescence. The more time since the beginning of the curvature has passed before the start of treatment, the less chances for a complete successful recovery.
Footwear
Quite often, parents tend to blame themselves for problems with the foot of the child. Moms feel guilty for the fact that they may have chosen the wrong shoes for the child, which caused the violation of the anatomy of the foot.. Yevgeny Komarovsky reassures parents - the deformation of the legs is in no way dependent on the shoes. Since the man originally appeared on the world without shoes, it is not so necessary for him from a biological and physiological point of view.
However, with the help of special, orthopedic shoes, you can correct some pathological changes in the feet.e. Although Komarovsky does not recommend fully relying on the healing properties of expensive orthopedic shoes. They can have an auxiliary effect, but they need to be treated in other ways, and prevented through an active lifestyle, walking barefoot on uneven surfaces, running and jumping. The more active a child is, the less likely it is acquired foot distortion or flatfoot.
Most parents are interested in when you can begin to wear shoes to a child. Komarovsky says that doing this right after the first steps makes no sense. Let the baby walk barefoot for as long as possible - around the house, on the street, if the opportunity allows. Naturally, in kindergarten or for a walk in the park you need to put on your child.
In case of severe valgus symptoms, it is often recommended to buy insoles with instep supports, which do not allow the foot to “collapse” inside. Such shoes usually have stiff sides, which fix the foot in the correct position, a solid heel retainer. Most often, you have to make such shoes to order, taking into account the degree of deviation from the norm, which measures and describes the orthopedist.
You should not buy orthopedic shoes for a child just for prevention, just because it seemed to her mother that the crumbs of the feet are not located that way.
In the selection of ordinary casual shoes Komarovsky advises to adhere to the basic rules:
- Shoes should be in size, not small and not large, the child should be comfortable and comfortable.
- Buying shoes “for growth” does not make sense, since the geometry of the foot changes as the leg grows.
- It is desirable that the shoes were not sewn of synthetic materials, the foot should "breathe".
- Pointed noses and heels in models of children's shoes are unacceptable.
Practical advice
The best prevention of foot problems is the ability to give the child more often to walk barefoot, not only on a flat surface, which is our floor in the apartment, but also on “broken” terrain. If you do not have your own courtyard, where you can let your barefoot child run on the ground, grass, and various hummocks, then the Swedish wall, which parents can buy and mount in the child’s children's room, will be an ideal option. When climbing and walking on it, the foot muscles will “work” in the child, and there will be no flat-footedness and valgus curvature.
A great way to prevent functional (acquired) flatfoot or curvature of the feet - children's floor mats with convex elements ("shells", "stones", etc.). They are sold in any large children's store, as well as in orthopedic salons.
Early legging is not allowed. Despite the fact that the average medical standards indicate an approximate age of starting to walk 9-15 months, do not rush the child, said Komarovsky. It is not necessary to force him to stand on his legs, if he himself does not make attempts to stand and walk, do not “shove” the child into the walkers, since early verticalization can cause problems not only with the anatomy of the foot, but also with the spine, which is much worse and more serious.
If, on the occasion of the detected valgus foot pathology or flatfoot, the doctor prescribed a therapeutic massage, get ready for the procedure to be quite lengthy.
In order not to spend extra money, ask the massage therapist to teach you how to perform all the effects. Typically, a massage for this ailment includes a massage of the sacro-lumbar area, legs, legs, feet. Do the techniques should be in a strictly defined sequence.
A few sessions with the involvement of a specialist will be quite enough to master the massage yourself.
What is flatfoot, what factors lead to it and how to prevent it - Dr. Komarovsky will tell in the video below.