Metronidazole for children
Metronidazole is one of the most popular drugs against protozoa and bacteria. It is prescribed for adults with trichomoniasis, stomatitis, arthritis, pneumonia, and many other diseases. But can children be treated with such a remedy, under what pathologies is it in demand and at what dose is it administered?
Release form and composition
The drug is manufactured by many Russian and foreign companies, among which Darchharm, Synthesis, Pharmaprim other. Often the drug is called Metronidazole, but sometimes there is a prefix in its name indicating the manufacturer (for example, Metronidazole-Eskom, Metronidazole Nycomed, or Metronidazole-TEVA).
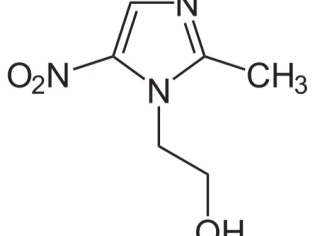
The main component of the drug is a substance with the same name - metronidazole.
The medication is made in several forms:
- Pills. They usually have a white, white-green or white-yellow shade, round shape and small size. One pack can contain 10, 20 or more tablets. The dosage of metronidazole in one tablet is 250 or 500 mg. Additionally, this medicine contains talc, stearic acid, potato starch, or other substances.
- Injections. This form is represented by a light yellow, yellow-greenish or colorless solution, containing 5 mg of metronidazole in each milliliter. It is packaged in plastic or glass bottles of 100 ml, as well as in bottles of 20 and 50 ml. Additionally, the solution contains sodium chloride, sodium phosphate, sterile water, citric acid or other substances.
In addition, the drug is released in the form of vaginal suppositories and 1% vaginal gel. These types of metronidazole are not used in childhood, because they are in demand in women for the treatment of infections of the genital organs.
Operating principle
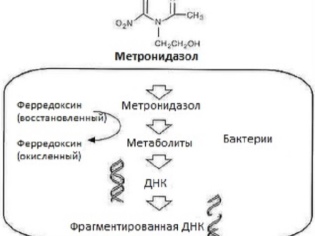
In metronidazole, antimicrobial and antiprotozoal effects are noted associated with the inhibition of the formation of nucleic acids in the DNA of bacteria and protozoa, resulting in their death. The drug effectively destroys:
- Trichomonas.
- Gardnerella
- Lamblia
- Bacteroids.
- Fuzobakterii.
- Dysenteric amoebas.
- Peptococci and many other microorganisms.
When administered together with amoxicillin, the drug acts on Helicobacter pylori.
Indications
Metronidazole is used:
- With intestinal amebiasis, liver or other organs.
- With trichomoniasis.
- With balantidiasis.
- With giardiasis.
- With infections of the joints, heart, lungs, bones, central nervous system, skin and other organs caused by bacteroids.
- With pseudomembranous colitis, which has arisen due to antibiotic therapy.
- With the defeat of the gastrointestinal tract, the cause of which is H. pylori (only in adults).
From what age is prescribed?
The use of metronidazole in children is possible at any age (even in infants), if there is reason for such treatment.
Contraindications
The drug is not prescribed:
- With a reduced number of leukocytes in the blood test.
- With organic diseases of the central nervous system, including epilepsy.
- When liver failure.
- With hypersensitivity.
If the child has a kidney disease, treatment should be carried out with caution.
Side effects
- The drug can provoke a negative gastrointestinal reaction. in the form of diarrhea, poor appetite, constipation, metallic taste, stomatitis, intestinal colic, nausea and other symptoms.
- In some children, metronidazole causes an allergic reaction.For example, in the form of skin hyperemia or nasal congestion.
- The nervous system of young patients may respond to the treatment of vertigo., weakness, irritability, poor coordination, irritability and other disorders.
- In rare cases, the use of medication affects the urogenital system. (causes polyuria, cystitis, urine discoloration or incontinence), blood counts and ECG.
Instructions for use
Tablets are taken either with a meal or immediately after it. The smallest medicaments are given in powdered form during feeding. Older children are recommended to swallow the tablet without chewing and drink water or milk.
The dosage depends on the infection at which Metronidazole is prescribed. For example, if a child has giardiasis, the medicine is given for 5 days in the following daily dose:
- Children under the age of 125 mg (half tablets 250 mg).
- Children aged 2-4 years - 250 mg (250 mg whole tablet).
- A child of 5-8 years old - 375 mg (1.5 tablets of 250 mg).
- The patient is older than 8 years - 500 mg (2 tablets of 250 mg).
This dose is divided into two doses, that is, one-fourth pills should be given to a baby up to a year at a time, and half a pill should be given to a child at 3 years of age. The injection form of Metronidazole is injected into a vein drip for 30-40 minutes, and if the patient tolerates the drug well, then go on a jet injection. The daily dose of this medicine for children under the age of 12 is 7.5 mg per 1 kg of weight of a small patient. It is divided into 3 doses.
A child over 12 years old during the first injection is given 500-1000 mg, and then every 8 hours, 500 mg are injected. The duration of use of this form of metronidazole is usually 7 days.
Drug interaction
Treatment with Metronidazole is not recommended to be combined with the use of anticoagulants, cimetidine, phenobarbital, lithium preparations and some other drugs indicated in the instructions for tablets / ampoules. The antimicrobial effect of the drug will increase if prescribed with sulfonamides.
Terms of sale and storage
Purchasing any form of metronidazole at a pharmacy requires a prescription from a doctor. The average price of 20 tablets of 250 mg is 20 rubles, and one bottle of solution for pricking costs about 30 rubles. Both the pill and inject form of the house should be stored in a place hidden from sunlight and small children at a temperature of up to +25 degrees. The shelf life of a drug is often 2 or 3 years.
Reviews
There are various reviews on the treatment of children with Metronidazole. In many, the drug is praised as an effective remedy against bacteria and protozoa. Also advantages of the medication is its low cost and availability in most pharmacies. However, complaints about side effects, such as nausea, rash, or diarrhea, can often be seen.
The disadvantage of the drug is called the uncomfortable dosage form, since Metronidazole is not produced in suspension or syrup (forms that are more convenient for children).
Analogs
Instead of metronidazole, you can use other drugs with the same active compound, for example, Metrogil (it is often used in children for inhalation and rinsing), Flagil or Klion. In addition, the doctor may prescribe drugs with a similar therapeutic effect, for example, if a child has amebiasis, Metronidazole may be replaced by drugs. Tinidazole, Tiberal or Dazolik.
For how to use Metronidazole, see this video.