Why use bacteriophages in the treatment of children and what is the instruction on their use?
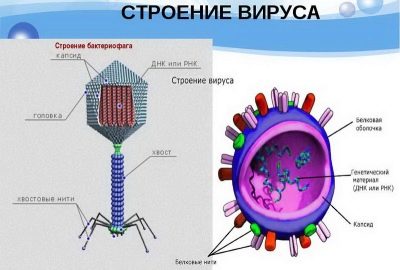
In the treatment of diseases provoked by bacteria, antibacterial drugs are most often used, especially with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial action. However, there are more specialized drugs that selectively destroy disease-causing agents of a certain type. They are made with the help of bacteriophages, special viruses that destroy microbial cells.
Special features
Bacteriophages in our country are produced by the large pharmaceutical company Microgen, in the assortment of which there are also serums, test systems, interferons, toxoids, vaccines and other drugs. All bacteriophages are represented by liquid, poured into vials of 20 or 100 ml (sometimes 10 ml). Such a solution must be transparent, and when clouding is considered spoiled.
The basis of such drugs are destroyed microorganisms that are in a nutrient medium along with the bacteriophages that caused their lysis. Because of the method of obtaining such a basis is called a lysate or phagolysate. In addition to it, there is only one auxiliary ingredient in the solution, which is a preservative and is called 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate.
The list of drugs from "Microgen" includes such bacteriophages:
- streptococcal - includes lysates of different strains of streptococci, therefore, it has a specific effect on such microbes;
- if - contains destroyed pathogenic E. coli;
- coliprotein - unlike the previous version, it acts on different serogroups of Escherichia, and on the protea of the genera Mirabilis and Vulgaris;
- Klebsiella polyvalent - affects Klebsiella ozena, pneumonia and rhinoscleromatis;
- salmonella - contains lysed salmonella of different groups;
- staphylococcal - made from a variety of staphylococcal strains;
- pyobacteriophage complex - in the composition of such a means there are destroyed entero-, strepto-and staphylococci, as well as pseudomonads, pathogenic Escherichia, Klebsiella and Protea;
- sextaphagus - shows activity against six types of microbes, including E. coli, staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumonia, Proteus and Streptococcus;
- dysenteric polyvalent - acts on dysentery pathogens, in particular, on Shigella Sonne and several Shigella Flexner serovars;
- intest bacteriophage - contains destroyed Salmonella, Proteus, Escherichia coli, Shigella, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas and Enterococci.
How to act?
Phagolysates, which are contained in a particular medicine, help to destroy precisely those strains and types of microorganisms from which they are derived. For example, streptococcal bacteriophage acts specifically on Streptococcus microbes, and "Enteri bacteriophage»Kills various bacteria that provoke intestinal infections. At the same time, such drugs do not affect the beneficial microflora, but, on the contrary, due to the effect on pathogenic microbes, they allow the natural intestinal flora to develop normally.
Indications
Doctors prescribe bacteriophages in such cases:
- with dysbacteriosis;
- if the bacteria are damaged by the digestive tract, for example, if the child has dysentery or Salmonella enteritis;
- in rhinitis, sinusitis, otitis, sore throat, adenoids and other diseases that fall under the competence of ENT doctors;
- inflammation of the bronchi, trachea, pleura and other parts of the respiratory system;
- for boils, cellulitis and other bacterial infections of the skin;
- with cystitis and other diseases of the urinary organs, triggered by bacteria;
- with suppuration of the umbilical wound or purulent conjunctivitis in newborns;
- with sepsis.
The solution can be used prophylactically, for example, for treating wounds or postoperative stitches to prevent adherence of infection, or in the form of enemas for newborns with a high risk of nosocomial infections.
Contraindications
Bacteriophage therapy is prohibited in case of hypersensitivity to any ingredient of the solution used. There is no age limit for such drugs, therefore bacteriophages can be prescribed from birth, including newborn babies and babies up to one year old. Before use, a sensitivity test is required to ensure that the bacteriophage is effective.
Side effects
If the bacteriophage is used in the first months of life, it can cause regurgitation in the infant or cause a skin rash. Some babies may have diarrhea after taking the solution.
Instructions for use
To bacteriophage had the desired therapeutic effect, it must be used correctly.
- It is unacceptable to give children a cloudy or expired solution. In order not to accidentally bring other bacteria inside the bottle, the drug is advised to wipe with a sterile needle, and wipe the hands and cork with alcohol.
- Since bacteriophages are stored in a refrigerator, it is worth warming up a cold solution before use. To do this, rather briefly hold the syringe with the medicine in a clenched palm or elbow. You can also take the medication for some time before taking and leave at room temperature, but not longer than an hour.
- The most popular way to use a bacteriophage is to give it to children to drink. Taking the solution is recommended an hour before meals 3-4 times a day. The duration of oral use can range from 7 to 20 days.
- If the bacteriophage is given to the infant to drink in the first months after birth, it is additionally twice diluted with boiled water and monitored the reaction. In the absence of side effects, then the agent is used undiluted. In addition, for an infant, the solution can be mixed with mother's milk.
- The second common way to use bacteriophages is rectal administration. It is often used in children with regurgitation or vomiting, as well as with sepsis, enterocolitis, and in other cases. In order to enter the solution into the rectum, not microclyster is used, but the so-called high enema, which needs to be done through the venting tube or catheter. The course of enemas, as well as oral administration, usually lasts 7-10 days.
- Sexttaphagous, coli-protective, streptococcal, coli, staphylococcal, Klebsiella bacteriophage and pyobacteriophage may be prescribed for external treatment, for example, for irrigating wounds when they are infected, or for lotions for inflammation of the umbilical wound. If the drug is applied after treatment with any antiseptic, thorough washing with saline is required. In the surgical department, drugs can also be injected into the cavities, for example, into the pleural or into the inside of the joint.
- ENT doctors prescribe bacteriophages for gargling, washing the ears or nasal cavity. For such procedures, the amount of medication recommended by the doctor is used, since the dose depends on the disease. To irrigate the throat or drip the drug into the nose is permissible only after examination by a specialist.
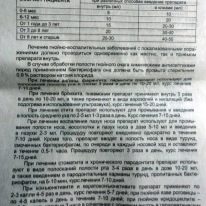
- A single dose of bacteriophage is determined by age. You can check with your doctor or look at the table, which is in the paper instructions for the drug. For example, babies under 6 months at one time are given to drink 5 ml of the solution, and to make such a small patient an enema, usually 10 ml of the drug is necessary.
- If a bacteriophage is prescribed as a prophylactic, it is often used once a day at a dosage appropriate for age. The duration of such prevention is determined by the doctor for each child separately.
Where can one buy?
All bacteriophages are OTC drugs and are sold in most pharmacies. The price of the drug depends on the name of the drug, and on the volume of the solution in one bottle. For example, for 4 flakonchika "Enteri-bacteriophage“20 ml each, you need to pay about 750 rubles, and one bottle of 100 ml of Salmonella bacteriophage costs about 650 rubles.
Storage features
It is important to store bacteriophages at temperatures below +8 degrees, so at home such a solution should be placed in a refrigerator. During the transportation of the drug, exposure to a higher temperature is acceptable, but it should be non-durable. In the refrigerator, the tool should stand there, where little children can not reach. Shelf life of drugs - 2 years.
Reviews
About the treatment of bacteriophages found a lot of positive feedback. Moms tell how such drugs helped in the fight against E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus and other harmful bacteria. Their advantages include the ability to use at any age, the liquid form and good tolerance, and the main disadvantage is the high price.
Sometimes there are also negative reviews, in which they complain about the bacteriophage's inefficiency or doubt their action, since such drugs are common only in our country and are not used abroad. In addition, many mothers have difficulties with the enema of the baby, and the minus of oral administration often include the unpleasant taste of the solution.
About what bacteriophages, see the following video.