The use of saline (sodium chloride) in the common cold in children
To effectively get rid of the cold in a child, it is not necessary to use expensive drops, which have many side effects. In the treatment of rhinitis in childhood, the well-known saline. This tool attracts attention for its safety and effective exposure.
What is it?
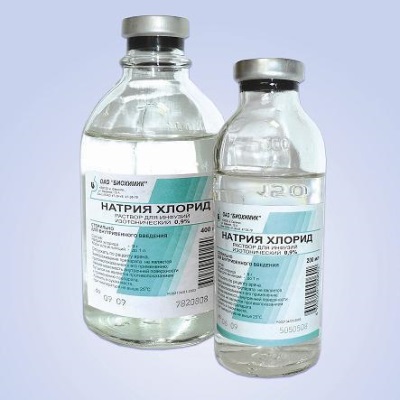
Physiological is a solution of sodium chloride in distilled water with a concentration of 0.9%. Most often it is used for intravenous fluids for dehydration, as well as for administering various medications. Saline is also in demand for inhalations and washes, so it is released in the form of nasal drops and sprays. As part of such preparations may be sea salt. These include drops No-salt, Otrivin Baby, Aquamaris, Aqualore, Salin and others.
Operating principle
The saline solution used for rhinitis moisturizes the nasal mucosa, and the sodium chloride that settles in the nasopharynx will be:
- To help the discharge of dried mucus.
- Remove inflammation.
- Destroy the bacteria.
Indications
Saline effectively copes with the common cold caused by:
- SARS.
- An increase in adenoids.
- Allergic reaction.
- Sinusitis.
- Exposure to dry air.
Contraindications
The use of saline in the common cold is not recommended if the child:
- There is pus in the discharge from the nose.
- Otitis developed.
- There is a tendency to nasal bleeding.
- Increased body temperature.
- Disrupted water-salt balance.
- There are heart diseases.
Cooking at home
To make saline with your own hands, you need to keep proportions - 9 g (one teaspoon) of salt per 1 liter of boiled or mineral non-carbonated water. Mix the ingredients in a glass container, which must be thoroughly washed.
Instead of the usual salt, you can use iodized or sea salt or add a drop of iodine to the solution prepared from common salt. Water is preferably slightly warmed, as this will accelerate the dissolution of salt and more pleasant to use.
This solution can be stored for no longer than a day in the refrigerator (it is heated before use). If the product has not been consumed, it is poured and a fresh solution is prepared for the child.
Another interesting and simple treatment of rhinitis with saline is described in the video below:
Application
Instillation into nose
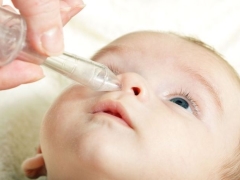
Such use of saline is acceptable at any age, even in the chest. 3-4 drops of solution are buried in each nostril. The optimal frequency of use is called 3-4 times a day, but if necessary it can be increased
Inhalation
Such procedures with saline are effective for the treatment of rhinitis and for the prevention such a disease. For their implementation, a nebulizer is used, which is best poured sterile pharmacy saline.
The amount of solution used depends on the age of the baby. For young children, 3-4 ml is enough, and dosage can be increased for schoolchildren. The procedure is carried out 1-3 times a day, and its duration is from one to five minutes. The baby should inhale the saline solution calmly, and for 1 hour after inhalation it is impossible to feed the child and walk with him.
The famous pediatrician E. Komarovsky expressed his opinion on inhalations:
Washing
For such washes, use a syringe or syringe. The head of the child is tilted to the side so that the saline poured into one nostril is poured from the second nasal passage. After the procedure, the child should be kept warm for at least half an hour.
It is permissible to wash the nose with a large volume of saline only over the age of 4 years, since in small children, with such washing, the liquid can get into the lower respiratory tract or cause otitis.
Features of use in newborns and infants
- Before using saline in infants up to a year, you should consult a pediatrician.
- In infancy it is forbidden to carry out inhalation and washing. The only permitted use of saline for babies with a cold is instillation into the nose.
- In each nasal passage enter no more than two drops of saline. The frequency of instillation is from 2 to 6 times per day.
- Do not dribble the baby with saline if a lot of liquid mucus is released from its nose. The procedure is justified only when the snot thickens and crusts appear.
- Because of the possible risk of the solution entering the auditory tube or into the lower respiratory tract, saline instillation is often advised to be replaced with more accessible and safer methods of moisturizing the mucous membrane. These include drink plenty of liquids, as well as normalization of humidity and temperature in the nursery.
- The use of saline is not recommended for physiological rhinitis, appearing in infants in the first months of life.
- If you purchased a pharmacy version of the saline in the form of a spray, you should remove the lid, Pipette the drug and then bury it in the nose.
Reviews
Saline like their parents safety, no side effects and addiction. Practically everyone who has buried the salt solution in a child with a cold, notes that the remedy improves the child’s condition, helps to quickly get rid of the symptoms of the common cold and makes breathing easier.