Gliatilin for children: instructions for use
The nervous system of a newly born toddler is not fully mature yet, and its development takes place in each infant according to an individual schedule. However, sometimes the development is hampered by certain factors, among which may be a birth trauma, prematurity or genetic pathology. In such cases, they often resort to drugs called nootropics.
One of these tools is Gliatilin. The drug is very popular among older people, because it helps to eliminate the effects of a stroke, improves the condition in case of dyscirculatory encephalopathy and dementia. But is it possible to give it to children when such a medicine is prescribed in childhood and how does it affect the nervous system of babies?
Release form
Gliatilin is available in two forms:
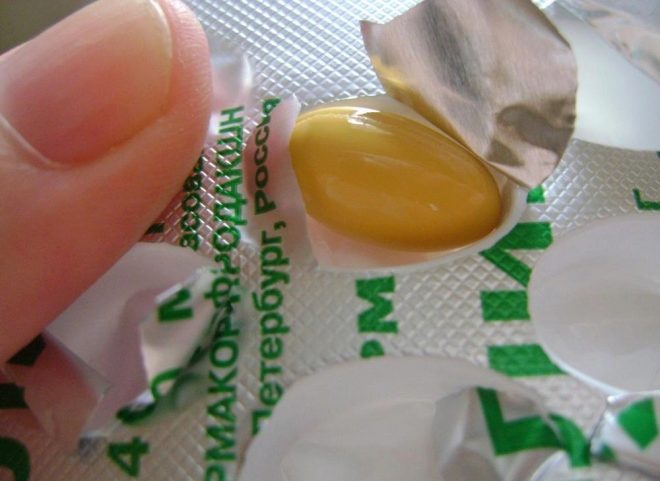
- Capsules They are made of gelatin, soft, yellow and oval in shape. Inside the capsules is a colorless viscous liquid. One pack contains 14 capsules.
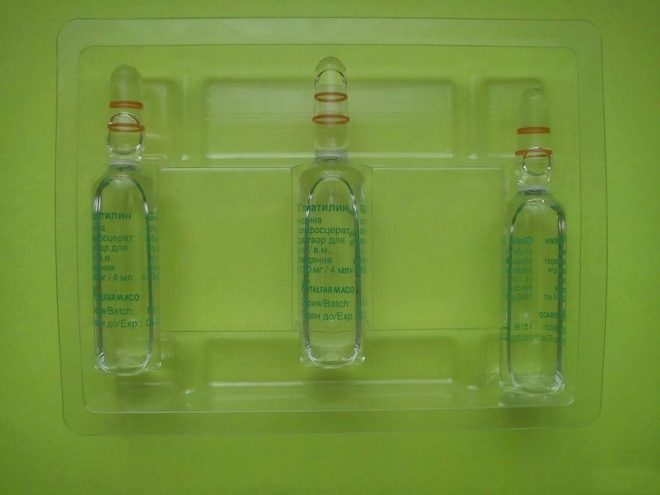
- Solution, which can be stabbed intramuscularly or in a vein. He has no smell and color. One ampoule contains 4 ml of this solution, and one package contains either one or three ampoules.
There are no other forms (drops, tablets, suspension, syrup, powder, etc.).
Composition
The active substance in any of the forms of Gliatilin is choline alfoscerate. Such a compound is presented in one capsule at a dosage of 400 mg, and in one ampoule it contains 1000 mg.
Additionally, the capsules include glycerin and purified water, and their shell is made of gelatin, propyl and ethyl parahydroxybenzoate sodium, esitol, iron metahydroxide, sorbitan and titanium dioxide. The only auxiliary ingredient of the injection solution is water for injection.
Operating principle
Gliatilin is a group of nootropic drugs, since this drug is able to influence the nerve cells in the brain, with the result that their condition improves and nerve impulses are better carried out. In addition, the use of such a drug has a positive effect on metabolic processes in the brain tissues and increases their blood saturation.
The result of Gliatilin will be:
- Memory improvement.
- Increase the ability to focus.
- Elimination of apathy.
- Improved mental performance.
- Optimization of cognitive abilities.
- Mood enhancement.
- The change in behavioral reactions in a positive way.
- Restoration of functions damaged during brain injuries.
- Regression of symptoms of neurological diseases.
In the patient's body, the drug is converted into two substances. One of them is choline, which is involved in the synthesis of such an important neurotransmitter as acetylcholine. It is important for the normal transmission of impulses through the nerve cells. The second compound is glycerophosphate, from which phospholipids are formed. They are necessary for neuronal membranes; therefore, a sufficient amount of glycerol phosphate protects nerve cells and speeds up their recovery if damaged.
Indications
Neurologists prescribe Gliatilin:
- With traumatic brain injury (in the acute period).
- With a stroke of a different type.
- With psychoorganic syndromes, in which memory is weakened and intelligence decreases.
- During the recovery period after small focal lesions of the brain associated with impaired blood circulation.
- With increased irritability and other emotional disorders.
In pediatric practice, medicine is also used:
- With autism.
- With ADHD.
- With nervous tics and other neurosis.
- In children who have suffered hypoxia during childbirth.
- In babies with birth injuries of the brain.
- With hydrocephalic syndrome.
- With cerebral palsy.
- In children with mental or speech developmental delay (with FRA).
At what age is it allowed to take?
There are no age restrictions in the annotation to Gliatilin, so the drug is allowed even for newborns and children up to a year. However, only a doctor should prescribe medication for young children, determining the desired dosage and method of administration.
As a rule, babies under 2 years of age are given injections, and capsules are recommended for children of school age and older. This tactic is due to the ability to divide the solution in the ampoule, getting a smaller dosage that suits a particular child by age.
Contraindications
The drug is not used if the child has an intolerance to any of its components.
Side effects
Treatment with Gliatilin may cause an allergic reaction. In addition, this medicine sometimes provokes nausea, which disappears after reducing the dosage.
Instructions for use
Gliatilin capsule should not be cracked or opened. This form of the drug is swallowed whole, washed down with non-carbonated water in a small amount. In the abstract there is a recommendation to take this drug before eating (best of all - before breakfast).
Gliatilin injections can be administered either intramuscularly (in the shoulder or thigh muscle) or in the form of intravenous drip infusions, for which the ampoule is diluted with saline. Injection is advised to do before a meal in the morning. Unused solution should be poured out.
Dosage
If a child has a traumatic brain injury, then Gliatilin is prescribed 1 ampoule per day for 1 week. The drug can be administered both in the vein and intramuscularly. After 7 days from the start of treatment, you should switch to capsules. They need to be taken within 2 months on 1 capsule twice a day.
When hypoxic encephalopathy or birth trauma, a child under one year old (for example, at 6 months) is prescribed injections of 1-2 ml of Gliatilin. The drug is administered daily 1 time per day for 10-12 days. If the child is 1-3 years old, then the daily dosage is increased to 2-3 ml, and at the age of 3 years the medication is administered in the whole ampoule (4 ml once a day).
Children who can ingest capsules are prescribed one capsule twice a day with a course of one to three months. There is also an opportunity to collect the solution from the capsule with a syringe and give it to the child to drink, removing the needle, after which the contents of the capsule can be washed down with water. However, this use of the medication is rarely used, since the injections are considered more effective and are prescribed by shorter courses (from 5 to 14 days).
Overdose
Excess doses of Gliatilin cause nausea. If a small patient has such a symptom, it is a reason to reduce the dosage of the medicine. In addition, the drug may provoke other manifestations of dyspepsia, such as belching, thinning of the stool, or flatulence. In such cases, the use of sorbents is recommended.
Drug interaction
On the incompatibility of Gliatilin with other drugs, the manufacturer does not have any information. It can be taken together with any other medications, for example, with antipyretic, if the child has had an ARVI during the course of treatment.
Terms of sale
To buy Gliatilin capsules or injections at a pharmacy, you need to show a prescription from a doctor. The average price of a package with 14 capsules is 750 rubles, and for 3 ampoules of the drug you need to pay from 600 to 700 rubles.
Storage conditions and shelf life
It is necessary to keep both ampoules and capsules of Gliatilin at home in a place inaccessible to a small child where the temperature does not rise above +25 degrees Celsius.The shelf life of the capsules is 3 years, and the injection form is 5 years.
Reviews
About the use of Gliatilin in children there are a lot of good reviews. Parents and doctors note the high efficacy of this drug in various lesions of the central nervous system and delayed speech development. According to mothers, despite a fairly long course of treatment, children tolerate the drug mostly well, and side effects in the form of nausea or allergies are very rare.
The disadvantages of the drug are the relatively high price and the need for long-term therapy (often from several courses), since the effect of the use of Gliatilin does not occur immediately. Also, sometimes there are negative reviews, which mention the lack of therapeutic effect of the drug in a particular child. In this case, the lack of effect is more often noted when taking capsules, while after a course of injections in most cases, the state of the nervous system improved.
Dr. Komarovsky treats Gliatilin, as well as other nootropics, as drugs, whose effectiveness has not been proven. He does not prescribe such drugs to his little patients and recommends that they deal with the child patiently with FRA, and not resort to injections or tablets. However, the famous pediatrician does not consider this medication harmful and allows its use in children, if there are indications for this and the drug is prescribed by a doctor.
Analogs
Any other medicine with the same active substance can be a replacement for Gliatilin. These drugs include drugs Cereton, Cerepro, Nookholin Rompharm, Gleatser, Deletsit, Cholithilin and others. Most of them come in injectable form, but there are also capsules and oral solution.
In addition, the doctor may recommend other nootropic drugs instead of Gliatilin, for example:
- Pills Aminaloncontaining GABA. They are allowed from 1 year.
- Capsules Anvifen. Such an aminophenylbutyric acid based drug has been used since 3 years of age.
- A drug Nootropilcontaining piracetam. It is produced in syrup, injections, tablets and capsules. The form of syrup is used in children older than 1 year.
- Syrup Pantogam, which is composed of hopantenic acid. This medication is prescribed at any age.
- Injections Cortexin for children allowed even for premature babies.
You can find out about the need for using nootropic drugs from the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.