Galactosemia in newborns and children
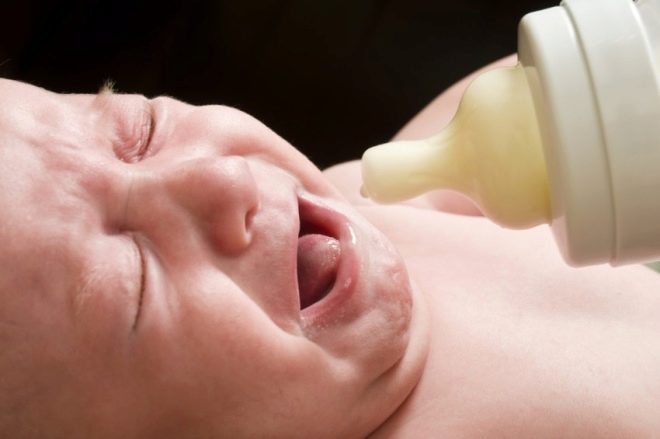
Contrary to popular belief about the benefits of milk for children, this product is not useful and necessary for all. So, babies born with galactosemia cannot eat milk and dairy products due to their illness. But galactosemia is not a verdict at all, and mom and dad should just be clearly aware of how to act if such a diagnosis is made to the baby.
What it is?
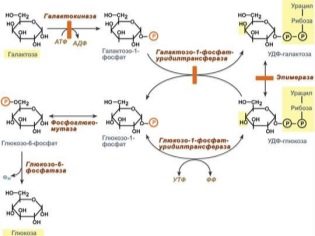
Galactosemia is hereditary disease, occurring with metabolic disorders in the conversion of galactose into glucose. Genetically, the birth of a special enzyme substance with a complex name, galactose-1-phosphate-iridyltransferase, is disturbed from birth.
Galactose in the composition of milk, more precisely, with milk sugar (lactose) enters the children's body. Further, in a healthy baby, lactose under the influence of this enzyme with a long name and two more enzymes is converted into glucose and absorbed. In children with a genetic impaired enzyme synthesis, this metabolism is disturbed, which is why lactose is not converted or is not fully converted to glucose.
Gradually, in sick children lactose accumulates in the blood, in the tissues of the internal organs, begins to have a toxic effect on the nervous system, liver and lens of the organs of vision.
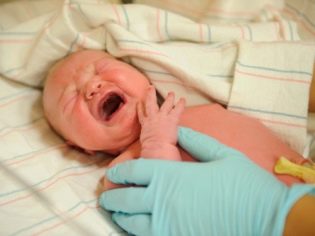
Typically, the disease is detected already in newborns, and the people call it simply - intolerance to milk and milk formulas.
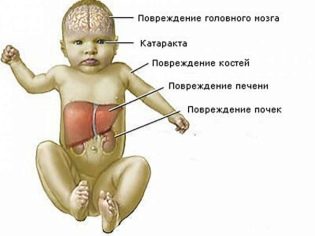
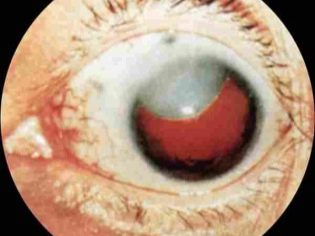
The baby reacts to standard feeding with vomiting, he loses weight, suffers from extensive jaundice, he gradually develops cirrhosis, edema and cataracts. If this metabolic disturbance is ignored, mental and motor developmental delays gradually develop.
Galactosemia is a rare genetic disease, it occurs in one case for 30 thousand births, and, according to WHO, and in one case for 50 thousand births.
The first case was described as early as the beginning of the 20th century; then the doctors noticed that the symptoms of the disease receded when the child was stopped giving milk. The true cause of milk intolerance and its connection with genetics was described and substantiated in 1956 by Hermann Kelker.
The reasons
The cause of the disease lies in the gene inherited by the child. Inheritance occurs in an autosomal recessive manner, in other words, only that child will suffer from galactosemia, which inherited two copies of the defective gene from both mom and dad. Parents themselves may not even realize that they are carriers of a gene with a defect, and sometimes they also show milk intolerance, but to a very small extent.
Since three enzyme substances take part in the breakdown of galactose, three types of diseases are distinguished - it all depends on which enzyme is produced little. In the blood of a child with a violation of this metabolic process, the accumulation of individual metabolites begins, which negatively affect the state and functioning of the internal organs: the liver, kidneys, spleen, digestive organs, central nervous system suffer.
The gene responsible for producing the necessary enzymes is located on the site of the second chromosome. Inheriting a defect from mom and dad causes a defective gene in a child, and this is the only reason for the lack of enzymes necessary for normal digestion of milk.
Symptoms and signs
Usually, the diagnosis becomes obvious in the first few days of the baby’s life after birth. To guard mom and doctors should systematic vomiting, which appears every time after the crumb tastes breast milk or formula. The child suffers from diarrhea, fecal masses are fluid, watery in nature, and symptoms of general intoxication gradually increase.
Newborn becomes sluggish, begins to refuse the proposed breast or bottle with the mixture. He quickly loses weight, literally in a few days the tot can reach exhaustion. The tummy is swollen due to the accumulation of intestinal gas. The reflexes with which all healthy children are born gradually begin to fade, persistent jaundice appears, the liver increases and can be edematous.
If nothing is done, then cirrhosis of the liver can develop in 6-8 weeks.
The processes of blood clotting are broken, the baby has bruises and small hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes. Delay of mental and motor development becomes apparent very early. Already by the month a cataract can be detected on both sides, urine tests show impaired kidney function, the hemoglobin rate in the blood is reduced. The baby suffers from a lack of body weight or severe exhaustion, liver failure. His immunity is very weak, due to this various infections usually join.
The liver suffers with any degree of severity of galactosemia - and with mild and severe. Complicated condition may sepsis, ovarian exhaustion in girls. Half of preschoolers with such a diagnosis have problems with speech, coordination of movements, while the understanding of the speech of others is usually not disturbed.
What to do?
The main thing - do not panic. The clinical guidelines of WHO and the Ministry of Health of Russia state that Early detection of metabolic problems will help to quickly take action and reduce potential complications. Sometimes a geneticist may even suspect galactosemia in a child during her mother's pregnancy, and then answering the question whether the child has a hereditary illness or not will help chorionic villi biopsy, cordocentesis and other invasive prenatal diagnostic methods.
But even if nothing was known about galactosemia during pregnancy, after birth, all newborns undergo, according to clinical guidelines, screening, which includes tests for such hereditary diseases as phenylketonuria, hypothyroidism, galactosemia, cystic fibrosis and adrenogenital syndrome.
Analyzes are usually done on day 3, if the baby is full-term, and on day 7, if the baby is born prematurely. This first medical examination allows to find out at an early stage whether the infant has one of the above genetic diseases.
If galactosemia becomes apparent, the geneticist and pediatrician are talking to the parents. The main thing that they should learn is the information on how to properly feed the child. In addition, general and biochemical analyzes of blood, urine, feces are prescribed, ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed in order to reveal how much the organs are already affected. A neurologist and an ophthalmologist are involved in therapeutic interventions.
Treatment
A baby with galactosemia is given a special diet - It is based on the lack of whole milk in the diet. This applies to any product from this line: breast, cow's milk, goats, dairy mixes, all dairy products, bakery products, yeast pastries, sausages and sausages, chocolate and other sweets, margarine. Under the ban is soybeans, legumes, chicken and other eggs, liver and other offal. So food will be almost for life.
To feed the child will have special therapeutic lactose-free mixtures. They can be received in the direction from the doctor.From the age of four months, the child will be able to receive supplements in the form of juices from fruits and berries, from five months - fruit, vegetable purees, and then - dairy-free cereals, which should be diluted with special lactose-free mixtures. For half a year tots can get meat supplements, while the preference should be given to rabbit, turkey, beef. From the age of eight months, it is permissible to add fish to the child’s diet.
Medicines that would help cure galactosemia do not exist. But in order to improve the metabolic processes in the children's body, vitamins, cocarboxylase, potassium orotate can be recommended.
Important! Children with diagnosed and confirmed galactosemia are prohibited homeopathic medicines. All without exception. The fact is that homeopathic medicines contain lactose.
A child will not become blind, oligophrenic or a patient with cirrhosis of the liver, if therapy begins literally from the first days of life. In this case, the forecasts are relatively favorable. If you start feeding the baby properly and treat it at a later age, when damage to the liver and nervous system already takes place, it is unlikely that you will be able to completely eliminate unpleasant consequences. Unfortunately, in severe galactosemia, it is often all fatal.
It should be understood that the establishment of the child's diagnosis of "galactosemia", regardless of the severity and timing of the establishment, gives parents the right to design the baby status of a disabled child. There is scientific evidence that with age, the manifestations of galactosemia gradually weaken, but it is not possible to recover from this hereditary disease until the end.
How not to confuse rare diseases with conventional digestive disorders, as well as whether children have lactose deficiency, says Dr. Komarovsky in the video below.