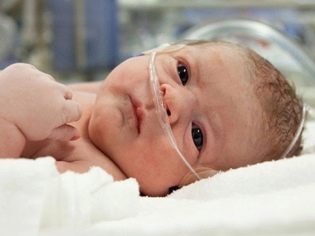
Ischemia of the brain in the newborn
Parents of the newborn most often learn about cerebral ischemia while still in the hospital. If this is not reported there, then a neurologist and a pediatrician may later mention ischemia, trying to explain what is happening with their child, why he spits up, slowly gaining weight or does not sleep well. In this article we will tell you about why ischemia develops, how it can be treated and what consequences it may have.
What it is?
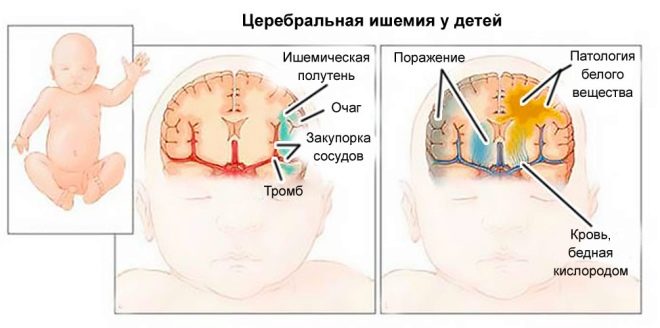
Under this concept in official medicine describes the state of oxygen starvation of the brain. In a newborn baby, cerebral ischemic disease is essentially a response to the state of hypoxia.
With a lack of oxygen, neurons begin to change and die, which causes hypoxic-ischemic changes in the cerebral cortex. The longer the starvation was, the wider the affected areas, and hence the harder the consequences.
Most often ischemia is found in premature babies. It may also be in infants who experienced a lack of oxygen, which is so important for him during pregnancy, or experienced acute hypoxia during childbirth.
It should be noted that this diagnosis has recently become very widespread. And not because the children have become worse born or more often suffocate in the womb. Some experts, including Dr. Komarovsky, believe that neurologists quite often make such a diagnosis for babies, because with mild ischemia it is very easy to explain to parents the most complicated processes and peculiarities of the development of a newborn. Another reason - the lack of understanding of what is happening in the doctor himself. If it is not clear that with a child, the easiest way to say is that "it is because of ischemic metamorphosis in the brain."
Light degrees suggest violations did not cause irreversible consequences. These include 1 and 2 degrees of cerebral ischemia. The third degree is much more difficult. Until now, medicine is not known for certain how to treat it, and therefore forecasts are considered unfavorable.
The reasons
Ischemic brain damage is always closely associated with only one root cause - the lack of oxygen to power the cells of the organ. There are a lot of reasons that lead to a lack of oxygen, and they are divided into perinatal and postnatal.
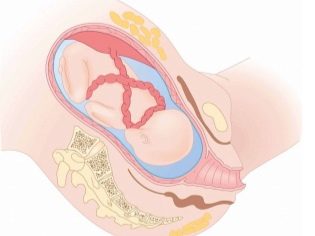
If during the period of pregnancy chronic hypoxia was observed, the brain lesions are somewhat compensated. With acute hypoxia, which the baby could have experienced at the time of childbirth, ischemia develops more severe.
Common causes of intrauterine hypoxia:
- chronic diseases of a pregnant woman, especially if there are illnesses of the lungs, kidneys, liver, heart and blood vessels;
- acute infectious diseases in the first trimester (influenza, chickenpox, rubella, acute respiratory viral infections, herpes infections);
- wrong way of life of the expectant mother: smoking while carrying a baby, taking drugs and alcoholic beverages, medicines for which the doctor did not give permission;
- the age of the future mother at the time of pregnancy: the risk of fetal hypoxia is higher for very young pregnant women who have not yet turned 19 years old, and also for future pregnant mothers over 36 years old;
- problems that arose directly during pregnancy: violations of the placenta and uteroplacental blood flow, the threat of miscarriage, which persisted for a long time, lack of water and plenty of water, as well as entanglement of the umbilical cord or nodes on the umbilical cord, Rh-conflict);
- inadequate nutrition of the mother during pregnancy, violation of her doctor's recommendations
Acute oxygen deficiency can also occur during childbirth. At risk include premature birth and late (after 42 weeks of pregnancy).Dangerous childbirth, as well as protracted, long delivery with weak labor.
A large fetus, multiple pregnancy, entanglement with umbilical cord, early discharge of water or premature detachment of the placenta quite often lead to the development of acute hypoxia followed by cerebral ischemia of the newborn baby to one degree or another.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms depend on how large-scale the damage to the central neurons of the baby’s brain has become. The more severe the starvation was, the longer it lasted, the more nerve cells died. The earliest symptoms occur immediately after birth: the child does not scream in the time allotted for this in obstetrics or his cry is too weak. Children with ischemia most often have an Apgar score lower than 7/7.
On the very first day, doctors may suspect cerebral ischemia due to increased hypertonicity of large muscle groups of the baby, convulsions, tremors, and a long, weeping newborn, even if there are no objective reasons for crying. Too dull apathetic newborns who do not suck well, sleep a lot, will also cause reasonable suspicion.
Symptoms of ischemia depend on the degree. Grade 1 is characterized by minor deviations in the child’s behavior and condition. In the first days of life, it is manifested either by excessive inhibition of the nervous system, or by its increased excitement. Usually such mild ischemia disappears within a week.
If pathological abnormalities are noticeable even after the first seven days of the baby’s life, they are talking about grade 2 ischemia. When it is to the small neurological manifestations (crying, sleep disturbance, abundant regurgitation) are added seizures, strabismus. With timely medical care it can cope.
The third degree of ischemia is usually manifested by comatosis. The kid is unconscious, he has no swallowing and sucking reflexes, muscle tone. Many children cannot breathe on their own - without the use of a ventilator. If a baby can be saved in resuscitation, brain lesions are most often large-scale in nature and can manifest themselves in violations of certain functions (hearing or vision) and systemic lesions - paralysis, paresis, cerebral palsy, and dementia.
Infant stroke — a cerebral hemorrhage during acute cerebral ischemia — mostly develops in premature babies. In babies who have appeared on time, the probability of such a complication is only 10%, whereas in children weighing less than 2 kilograms a stroke or microstroke (transient ischemic attack) develops in 35% of cases, and in deep premature babies weighing less than a kilogram, stroke occurs in 95% cases.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke are also based on neurological manifestations and are very similar to the symptoms described above.
Treatment
Unfortunately, medicine cannot give an exact and definite answer to the question of how to treat cerebral ischemia in newborns. Pharmacology has not created any drugs for oxygen starvation, and there are no effective methods to restore the dead central neurons.
With mild to moderate ischemia, all hope is for the compensatory abilities of the child’s body. At the third degree, by the way, too. Healthy neurons can take on the responsibilities of the dead "mates". With a slight ischemic brain damage, this works fine. The harder the defeat, the harder it is to compensate.
This does not mean that the child does not receive treatment. The task of the doctors after the detection of ischemia in the newborn is to quickly establish the extent of the lesion and begin to contribute in every way to the natural compensatory mechanisms. To do this, prescribe symptomatic treatment. If the baby is excited, they give him sedatives, if he has convulsions - anticonvulsants.
Conventional treatment regimens include drugs to improve blood circulation in the brain. For this, they recommend vascular and nootropic drugs. The effectiveness of these groups of funds today is a big question, but they are approved by the Ministry of Health.
With the third degree of ischemia, the child is provided with a full range of resuscitation measures. These include artificial lung ventilation, probe feeding, and heating of the incubator. Medicines basically use the same. The task at the stage of resuscitation is to stop the death of neurons, to prevent the death of neighboring areas of the cortex of the brain. After the child is transferred to the general department, he is shown a long course of treatment and rehabilitation, depending on the severity of the consequences of ischemia.
After discharge home, a child with a history of ischemia is given a massage. Recommended walks in the fresh air, adherence to the day, water treatments, swimming in the bathroom with a cervical orthopedic circle (from 1 month).
If on examination at 1 month with the passage of neurosonography, pathologies of the brain are detected, a new course of drug treatment is prescribed.
Forecasts
The possible negative effects of severe ischemia include epilepsy, mental retardation, paralysis, a decrease in the adaptive ability of the child and his or her ability to learn. Mild cerebral ischemia usually does not have serious long-term effects.
Doctors do not like to predict anything when it comes to brain damage, because the consequences are in fact unpredictable and can appear in five, and ten, and twenty years later.
After severe ischemia and prolonged stay of the child in intensive care, the consequences are inevitable. Quite often they lead to disability.
Reviews
According to parents, in the case of severe third-degree ischemia, newborn girls usually show more “fighting qualities” than newborn boys, so they survive more often and the effect on their health most often is not so significant.
Whatever the degree and cause of cerebral brain damage, mothers emphasize that much depends on whether parents can find a good neurologist to plan the treatment. According to reviews, in case of mild ischemia and with promptly initiated treatment, neurological symptoms disappear by half a year. Some mothers claim that in the year a child after grade 2 ischemia was already completely healthy.
The treatment is long. The most difficult are usually the first six months, and experienced mothers who have gone through this test warn that they need patience. A young mother will have to master nursing, massage, and learn to understand medicines, and become a rehabilitologist for her baby. It will require strength. But the main thing is to love your baby and support him. Newborn crumbs perfectly feel maternal support, even if they are in intensive care. Without it, you can not.
The video details the symptoms of cerebral ischemia in newborns.