When does a newborn begin to see and focus?
Vision is one of the main functions of knowing the world. Thanks to the visual images, the child receives up to 90% of the information about what is happening around him. There are a lot of conjectures about the sight of newborns: someone claims that the baby sees everything upside down, upside down, someone is sure that the little ones are not able to distinguish colors.
In this article we will look at how our world is seen. newbornand find out when the baby begins to focus his eyes and how to help the baby develop visual functions.
Organs of sight before birth
Visual analyzers in the fetus originate in the second week of pregnancy. Mom still does not suspect her “interesting position”, and the embryo already has eye bubbles, which then become his eyes. The lenses are born by the end of the first month of pregnancy. By the end of the third month, the child had blood vessels formed and blood supply to the eyes was adjusted.
The formation of sclera occurs in 4-5 months of pregnancy, by the same time the baby has fully formed eyelids.
In the full understanding of this word, the fetus in the space of the uterus cannot see until the formation of the center of vision in the brain is complete. In the third trimester of pregnancy, the baby, through tightly closed eyelids, begins to define and differentiate light and darkness outside the maternal abdomen.
At birth, the child’s eyes have a structure identical to that of an adult, but all departments are not physiologically mature, are smaller, functionally lag behind the analyzers of adults.
Stages of development after birth
Vision continues to develop after birth, eyes and nerves ripen. This process goes along with the development and formation of brain functions.
After birth, babies have poor eyesight, they cannot boast of sharpness. Large and bright (compared to the womb of the mother) the world is a great stress for the baby, who is also unable to properly consider what is happening around. What we see for a baby of the first month of life is a “patchwork quilt” - a cluster of multi-colored spots that have no clear boundaries.
But the process of formation of the organs of vision and neural connections in the brain occurs continuously, and also very intensively, and therefore, already a month a baby can distinguish certain forms in general terms by bringing an object close to his eyes.
However, it is still very difficult to pinpoint the gaze to an infant of this age, the muscles responsible for the movement of the eyeballs and the fixation of the gaze are still very weak.
Do babies see everything in the black and white spectrum? The answer to this question is rather negative, but the newly born child does not perceive the special variety of colors. Rather, it is a set of halftone spots. The allegations that babies perceive everything upside down are generally far from reality. Your newborn sees everything in the correct projection, only very vaguely.
Since the eyeballs are significantly inferior in size to adults (16 mm in newborns versus 24 mm in adults), the image is formed not on the retina of the eye, but immediately behind it, therefore some physiological long-sightedness is characteristic of all newborns without exception.
As the eyeballs grow, the image begins to form correctly and precisely where it should appear - directly on the retina.
Let's look at the main stages of the formation of visual ability in infants.
Newborn
In the first days after birth, the child distinguishes only light and darkness. Neither mom nor dad, nor even his grandmother, he can not consider, no matter how relatives tried to prove the opposite.
If you send too bright a light to a child, he may cry, a sudden change of lighting (from darkness to light) causes tearing and quite understandable indignation of the little man. These abilities belong to the category of visual reflex reactions, they are evaluated in the parent house after the baby is born. If there are reactions, it is believed that the child is sighted.
3 weeks after birth
The period of primary adaptation passes, the baby adapts to the new conditions of his habitat. After 21 days, color vision begins to form, the baby will begin to discern some spots as more or less bright.
At a distance of about 40 centimeters from the face, he can see them best. But neither understand nor analyze what they saw the baby is not able to. He does not distinguish between faces, can not see his mother, but can feel her - by smell, by voice, by his usual touch.
1 month
After the first month, the infant begins to hold its gaze briefly on an object that is no more than 50-60 centimeters removed from it. But it turns out this is still bad, but because parents start beating all the bells - “the baby is squinting,” “his eyes are looking in different directions,” “one pupil is trembling.”
All these are not signs of pathology, but signs of immaturity of the muscles of the eyes, it will take a little more time, and an infant will learn to treat objects longer.
2 months
By the end of the second month, the child may focus a little longer on a large toy. But it’s still very difficult to watch her with a look.
The kid begins to recognize the mother, and this is an undisputed breakthrough. The beginnings of color differentiation appear - the baby perceives a red color.
3 months
By this age, the child’s organs of vision “have stepped” far ahead. Now he can not only follow the static object, but also try to keep his gaze on the subject moving, however, provided that the subject moves smoothly and smoothly.
The eyes of the baby can already move to the right and left, up and down. The ability to distinguish colors is improved - the baby begins to see the yellow color.
4-5 months
By the end of the fifth month, the baby distinguishes between blue and green, as well as all the basic colors of the spectrum, but half tones are not yet available to him.
He will learn to see them by 7-8 months. A child recognizes relatives, distinguishes faces, can quite clearly see objects that are a meter away from him.
6 months
In six months, the expression on the face of the child begins to acquire a “lively” look, quite conscious and reasonable. Eyes no longer look in different directions, do not run back and forth, the baby can clearly see the faces, toys at a distance of up to three meters, fix the eyes on them.
Vision becomes stereoscopic. This means that the baby begins to see the world not flat, as before, but three-dimensional, three-dimensional, as we adults see it. Without labor, the child can see the toy, reach it, take it in his hands.
7 months and older
At the age of 7 months and after this, vision is formed in its base. But this does not mean that the processes of improvement in the organs of vision and the brain stop. Visual analyzers will develop up to 3 years inclusively, but the base has already been laid.
The child begins to fix his gaze on distant objects, quickly “switch” the gaze from distant objects to neighbors, and vice versa. At 8-9 months, the child can estimate the distance between objects.
It should be noted that the most dramatic changes in the organs of sight of the child occur throughout the first year of life, but because parents must do everything possible so that the baby’s vision develops harmoniously, correctly. This will help avoid problems in the future.
Premature babies are somewhat behind in the stages of vision formation. It all depends on how sooner the baby is born. To ripen the eyes of babies born prematurely will be a little longer, and this is quite natural.
How to develop visual functions?
To ensure that the baby’s vision is normal, parents should from the first days. The room in which there is to be a baby should not be very dark. In the twilight, all stages of vision development will be delayed. But the room should not be too brightly lit either: in the first months, the bright light will annoy the child, cause him noticeable inconvenience.
Eliminate the source of light near the bed. It is also undesirable to have large mirrors in the room.
Do not push the crib to the wall - you need to approach the baby from different sides so that he can learn to perceive objects both on the right and on his left.
Mobile, rattles, and other “graces and charms” that mothers prepare for crumbs during pregnancy, it is better to start using when the baby reaches one month of age. Previously, he just did not see them and did not appreciate. After a month, the toys are hung at a distance of at least 50 centimeters from the face of the baby.
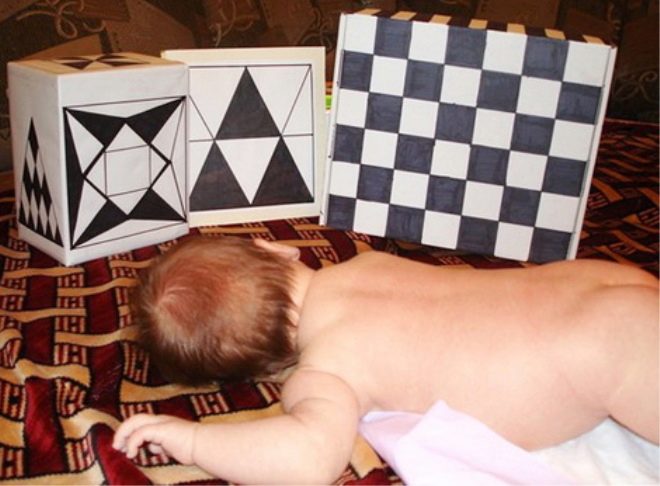
Classes on the development of vision will be useful for your karapuzika with one and a half months. To begin with, show your baby black and white geometric images.
From the age of three months, begin to study with your child using colored objects and toys. At the same time, remember that you first need to offer objects of red and yellow color, and only for half a year - blue and green.
As soon as the baby learns to crawl, give it free rein. Manege is an excellent device that makes life much easier for mom and saves nerves and strength, but in it stereoscopic vision will develop much more slowly.
While exploring the space with your own pens and knees, the baby also comprehends the laws of distance and volume, do not forget about it.
Be sure to walk with the child. The sun's rays contribute to the development of the retina, and besides, the child receives an excellent training for tracking moving objects that are not yet fed up with him, unlike home animals — a dog runs, a car rides, a flower sways in the wind, etc.
Self vision test
Looking at the mowing and muddy eyes of the baby (and they are almost all babies up to a certain age), the parents no-no, and begin to wonder whether everything is fine with the sight of the child. Of course, only an ophthalmologist can give a definitive answer to this question, but the parents of a baby may well determine some signs and disturbing symptoms of their own vision in order to immediately visit the same ophthalmologist. So, problems most often occur in children who:
- were born prematurely, ahead of time;
- were born in a family where close relatives have vision problems (ophthalmic problems are often inherited);
- per month do not demonstrate the reaction of the pupil to light (the pupil does not become smaller in response to bright lighting);
- at three months they do not focus their attention on large objects that do not make sounds, show interest only in toys that can produce sounds;
- at four months do not follow moving objects;
- in half a year they do not recognize the faces of relatives, they do not differentiate them from strangers;
- in half a year they demonstrate involuntary nystagmus (trembling and spontaneous movement of pupils from side to side or from top to bottom);
- half a year demonstrate pronounced unilateral strabismus;
- at the age of one year do not pay attention to dogs, birds or cats on the street, they are not interested in moving objects.
Medical examinations of the child
Not only parents, whose task is to prevent injury to their eyes, chemical burns, but also specialists, should monitor the eyesight of babies.
The first physical examination on the subject of the baby’s view is conducted at the children's maternity ward. Already at this stage, doctors are able to identify severe malformations and diseases, for example, retinopathy of newborns, glaucoma and cataracts.
But having heard from neonatologists the conclusion that no defects were found, parents should not relax and calm down: many eye pathologies, including genetic ones, appear only with the passage of time. That is why it is important not to “skip” visits to a pediatric ophthalmologist.
The first such visit should be made to the oculist when the child is 1 month old. Premature babies need to visit the doctor again at three months, and then at 6 months. If the child was born on time, then after an examination at 1 month he should repeat the diagnosis at half a year.
A visit to an ophthalmologist at 1 year is also required. Then you should show the child to the appropriate medical specialist every six months.
Useful tips
- Toys for visual inspection should be safe, because sooner or later the baby will begin to reach out to them with his hands and drag in his mouth. All these actions are quite normal for babies.
- Do not move away from the child at the time of the game with soap bubbles or in the sandbox: very often eye injuries occur from contact with the chemical composition of the soap solution, as well as grains of sand.
- A newborn should not scratch his face as a minimum because he can injure his eyes with sharp, like blades, nails. Use special undershirts with sewn hands, mittens on pens, envelopes from which the baby will not arbitrarily take out his hands.
How the baby sees in the first year of his life can be found in the following video.