Brain hemorrhage in the newborn
Pregnancy and childbirth is not easy given to women. But in their own way they are not alone: the prenatal period and the subsequent birth of a baby are no less complex.
Unfortunately, not always everything goes smoothly, and certain dangerous complications are possible. One of these complications of pregnancy and childbirth is cerebral hemorrhage in a newborn. What it is and why it happens, we will tell in this material.
About pathology
Hemorrhage in the brain belongs to the category of the most severe birth injuries, which usually have an unfavorable course and prognosis. It occurs because of the violation of the integrity of the blood vessels, as a result of which, under the membranes of the brain, in the interhemispheric space, blood begins to accumulate, sometimes the entire brain tissue is impregnated with it.
Naturally, the brain functions are disturbed, the activity of the central nervous system undergoes changes, often lethal or irreversible. It is cerebral hemorrhage that is considered the most common cause of neonatal death of babies, as well as the development of cerebral palsy in survivors.
Of course, much depends on which vessel, in which area of the brain is damaged, how much blood has accumulated, what are the changes in brain tissue and membranes due to the pressure of the blood mass and leaching, but in general, the forecasts are still unfavorable.
Depending on the exact location of the hemorrhage, there are several types of pathology:
- epidural - accumulation of blood is observed between the skull and the gray brain matter, brain tissue is not affected;
- subdural - accumulation of blood is present between the pia mater and the dura mater;
- subarachnoid - bleeding is localized between the shell and the gray matter;
- interventriculare - blood accumulates in the space between the ventricles of the brain and in them;
- parenchymal (intracerebral) - blood accumulates in the medulla, it permeates it.
It should be noted that all these types are considered dangerous, but it is customary to call parenchymal and epidural hemorrhages most severe.
They are quite difficult to establish, and therefore at the time of diagnosis, pathology can already have the scale of a global catastrophe.
There are three degrees of pathology, as recommended by WHO. Russian doctors use the four-stage classification.
- 1 degree corresponds to a hemorrhage affecting only the walls of the ventricles of the brain, not their cavity.
- 2 degrees corresponds to the pathology with the penetration of blood into the ventricles of the brain.
- With 3 degrees the blood extends beyond the ventricles and fills the lateral ventricles
- With 4 degrees there is a massive hemorrhage with damage to the ventricles, lateral ventricles and the medulla.
The size of the hemorrhage also matter.
If the lesion area is no more than a centimeter, they speak of a mild form of pathology, with an increase in the area of hemorrhage up to one and a half centimeters they put a medium-severe form, if the area of lesion exceeds one and a half centimeters, we will talk about pathology in a severe form.
The reasons
Cerebral hemorrhage can develop for a variety of reasons related to the development of the child in the womb, or with the actions of physicians and certain complications in the process of delivery.
Quite often, cerebral haemorrhage occurs in very premature babies who were born before the 32nd week of pregnancy. Their brain is immature, weak, it is not able to withstand the change of pressure during childbirth, the integrity of the vessels is already broken due to the premature birth of the baby.
Neurosurgeons note that the percentage of the possibility of bleeding in the brain of a premature baby weighing more than one and a half kilograms is about 50%. In babies, whose weight at birth is less than a kilogram, stroke of varying severity is observed in 100% of cases.
Other reasons include the following.
- Acute hypoxia during childbirth. Sharp oxygen starvation can develop during abrupt rapid births, as well as during prolonged labor with a long stay of the baby in the dry period (after the release of amniotic fluid). The non-traumatic nature of hemorrhage in this case somewhat increases the chances of a more favorable outcome for life.
- Actions obstetrician. Imposition of forceps, improper extraction of the fetal head can lead to a fracture of the cranial bones, and then a traumatic hemorrhage develops.
- Prolonged pregnancy. If childbirth occurs after 42 weeks, the likelihood of the baby getting a cranial injury during childbirth increases, because the bones of the skull at this time begin to lose the elasticity necessary for the unimpeded passage through the birth canal. Birth injury to the skull can be the main cause of subsequent cerebral outpouring of blood.
- Unfavorable pregnancy. Acute haemorrhage in the brain during gestation usually results in abortion, fetal death. After birth, pathology may develop due to certain malformations of the vessels, heart, and brain. It can also be caused by intrauterine infection of the fetus with dangerous viruses and bacteria.
If a woman is at risk (the woman is older than 40, the pregnancy was accompanied by preeclampsia, severe toxemia, bearing a large fetus with a narrow pelvis, etc.), the woman is usually offered to reduce the risk of hemorrhage in the baby through surgical delivery.
After cesarean, cerebral disorders, circulatory disorders in infants develop infrequently.
Symptoms and signs
A child who has a slight hemorrhage at birth will not know about it immediately. It may be more sluggish at birth, it may scream later, but in a few hours the symptoms will appear and doctors will be able to diagnose the pathology.
They manifest the symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage, acutely, suddenly. The condition of the baby is deteriorating. What specific signs there will be is difficult to say; it all depends on the size and location of the hematoma inside the skull.
Most often there are convulsions, vomiting begins, the child loses consciousness. Strabismus may suddenly appear (pupils begin to "look" in the direction of the affected hemisphere). Many babies have trouble breathing, it becomes intermittent, and then it may stop.
Usually, the hospital manages to provide first aid and to provide the child with an artificial respiration apparatus.
A persistent cry may indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage, low pressure and squint - about epidural bleeding.
Experienced neonatologists have many signs by which they can distinguish not only pathology, but also suggest its size and localization. However, without accurate diagnosis, the conclusion is not made.
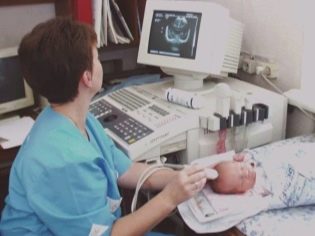
To confirm hemorrhage, babies are carried out on an emergency basis by neurosonography and computed tomography of the brain.
Treatment
Treat the child begin immediately, as soon as the diagnosis is confirmed. If necessary, provide resuscitation care.Therapy is primarily aimed at normalizing blood circulation in the brain, at reducing intracranial pressure. If the hematoma is large and the child’s condition is severe, an emergency neurosurgical operation can be performed.
If the child’s life can be saved, parents are warned about a long recovery period without any guarantees, because the consequences of cerebral hemorrhage can be very diverse.
In the process of recovery, which can last several months, several years, and sometimes a whole life, the child will be shown a dispensary observation by a neurologist, whose recommendations to parents will have to strictly follow.
Forecasts and consequences
The infant brain is unique in its own way.
He has a high ability to adapt and compensate. And that is why, in the case of lungs hemorrhages in the brain, if they are properly treated, in most cases it is possible to cope. But even with them, the process of rehabilitation of the child will take a long time.
If the degree of hemorrhage was higher than the second, and the course is severe, then the probability of disability of the child in the future is high. The degree of damage to brain function will depend on how destructive the hematoma is for it. Common lesions in such cases are cerebral palsy, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, dementia.
In the case of severe hemorrhage parenchymal species, the survival rate of children is extremely small. Almost one hundred percent death is recorded in case of hemorrhage with a sickle rupture or cerebellum tasting.
Reviews
According to the reviews of moms, the main thing is not to lose composure when the pediatrician in the maternity hospital reports hemorrhage in the baby’s brain. Hemorrhages occur more often than we used to think, and not every child has to become disabled because of this.
Moms willingly share their stories and emphasize that long-term treatment and the recovery period have done their job - in most cases children grow up quite normal, attend kindergartens, go to school for five, do not complain about anything.
Severe forms of hemorrhage in a child - a reason for going to a psychologist. Believe me, every maternity hospital has a psychologist to work with pregnant women and women in labor. He will help to believe in the best, tune in to the wave of the baby.
Experienced neonatologists claim that children whose moms cry and are nervous are worse off than children, whose moms internally gather and aim for the best. Children feel supported even when unconscious in intensive care.
You can learn about hemorrhages in the brain in newborns and the current global practice of treatment and care in the following video.