Catarrhal otitis in a child
Inflammations in the ears cause babies to experience a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. One of the variants of the disease is medium - catarrhal otitis. What parents should know about this pathology is described in this article.
What it is?
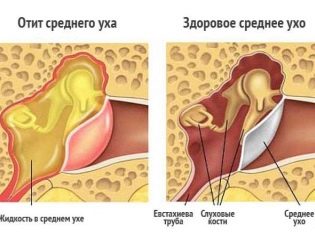
Inflammation middle ear causes the child to develop symptoms of otitis, which can occur in a variety of clinical options. Quite often, babies have catarrhal otitis media. In most cases, this type of disease is replaced by another - purulent, proceeding much harder.
To conduct a differential diagnosis between these pathological conditions can only pediatric ENT.
The most common cause leading to the development of inflammation in the middle ear is various bacterial infections.
The development of catarrhal otitis can also lead penetration of viruses and fungal flora into the Eustachian tube. These types of diseases are much less common.
You can have catarrhal otitis at any age. Unfavorable symptoms of the disease occur in infants and children of school age.
The Eustachian tube is the main structural element that is present in the cavity of the middle ear. Infection through it and the development of catarrhal otitis is possible from the nasal passages.
Normally, there are anatomical messages between the nasal cavity and the ears. Having a small size, pathogenic viruses and bacteria easily reach the Eustachian tube, contributing to the development of severe inflammation in it.
The pathological process can be one- or two-sided. Children suffering from immunodeficiency states or having severe chronic diseases often have damage to both ears at once. Right otitis, according to statistics, occurs in children more often. Typically, the catarrhal variant of this disease is usually easier than purulent.
The inflammatory process, which triggers the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the disease in a sick baby, also leads to the development of marked edema of the mucous membranes lining the middle ear cavity. This pathological condition contributes to the plethora of blood vessels, as well as pronounced lymphocytic infiltration.
With catarrhal otitis in the damaged ear a large amount of pathological secretion is formed - mucus. It can be quite dense in consistency.
Usually the first symptoms of the disease appear 3-5 days after the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the ear cavity.
Prolonged accumulation of inflammatory exudate may cause the secondary bacterial flora to join inflammation. This pathological condition quite often leads to the development of purulent otitis.
Pediatricians note that the development of the chronic form leads to pronounced decrease in immunity. Usually this condition occurs in children with chronic diseases of internal organs.
Children suffering from diabetes or various cardiovascular pathologies have a higher risk of chronic acute catarrhal otitis in the future.
Symptoms
The very first clinical signs of this disease can be expressed slightly. The classic symptom of the disease is the appearance of congestion in the affected ear. Usually this symptom leads to a violation of the perception of various sounds. Pronounced hearing loss in catarrhal otitis, as a rule, does not occur.
The inflammatory process contributes to the development of the child intoxication symptoms. Body temperature in catarrhal otitis usually reaches 37.5-39 degrees. On the background of such an increase, the baby may feel a fever or severe chills.
The health of the crumbs significantly worsens the appearance of severe headache and fatigue, which develops in a sick child during the acute period of the disease.
Severe intoxication syndrome leads to a strong thirst in the baby. The lips of the child become very dry, they may even crack. The tongue is usually coated with white bloom.
When a bacterial infection spreads from the ear cavity to the nasal paranasal sinuses, this results in marked congestion during breathing. Some babies may also have a runny nose.
Severe pain in the area of the affected ear can also extend to the neck, the mandible, and in some cases even take up half of the face.
A rather frequent symptom of middle ear inflammation is autophony. This is a pathological condition when the baby hears his voice during the pronunciation of words or sounds.
With the development of the inflammatory process, this symptom in a child disappears completely. This already indicates that the ear cavity is completely filled with pathological exudate, and the pressure inside the Eustachian tube has greatly increased. This leads to the fact that the baby begins to feel a strong feeling of "bursting" inside the damaged ear.
The mood and behavior of the sick baby noticeably change. The child becomes more capricious, refuses from the usual favorite foods, feels very sleepy even in the daytime.
Severe pain in the ear can also disrupt sleep at night. The child becomes more restless and may wake up several times during the night.
A characteristic symptom that occurs with this type of disease is the appearance of pain when pressing on the ear tragus. This clinical sign increases with the development of this pathology.
This symptom allows parents to identify and suspect the disease on their own, even for the smallest children, who still can not complain about the deterioration of their health.
Diagnostics
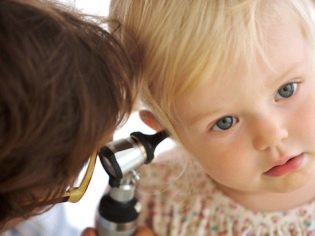
When the first symptoms or changes in the child's behavior occur, parents must consult a pediatric otolaryngologist for advice. Establish the correct diagnosis and conduct a full-fledged differential diagnosis is possible only through special examinations.
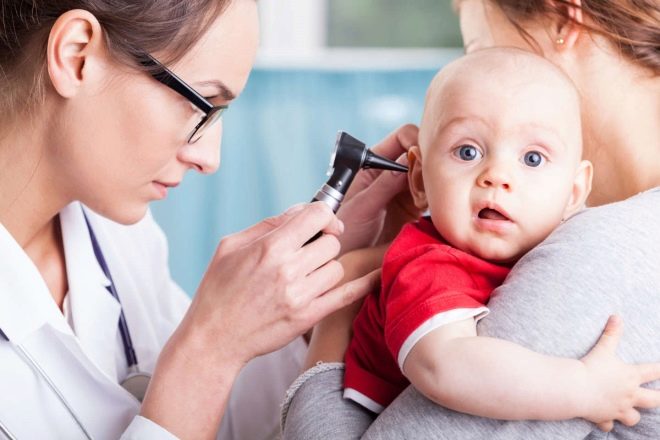
During the initial clinical examination and examination of the children's otolaryngologist examines the ear cavity. For this purpose, special medical tools are used.
Laboratory tests are conducted to establish the cause of the disease, as well as determine the severity of the disease.
Complete blood count can reveal moderate leukocytosis. In this pathological condition, the number of leukocytes increases in the peripheral blood. Inflammatory changes are also accompanied by accelerated ESR.
During the clinical examination, the doctor may pick up biological material for conducting baccosev. With this test, you can also quite accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. To obtain the results usually takes from 3 to 10 days.
This test allows not only to identify a specific type of microorganisms, but also to choose a specific therapy that will lead to the recovery of the baby.
Treatment
Therapy of the youngest patients is carried out in the hospital. It is necessary for the prevention of the development of secondary complications of the disease, as well as for rapid recovery.
The time of hospitalization may be different and depends on the initial severity of the disease.
The most severe cases of the disease are treated in intensive care units.
The main goal is to eliminate inflammation in the cavity of the inflamed ear, and also to prevent the transition from the acute to the chronic form of the disease. Usually, a complex of drugs and physiotherapy is prescribed to eliminate the adverse symptoms of catarrhal otitis.
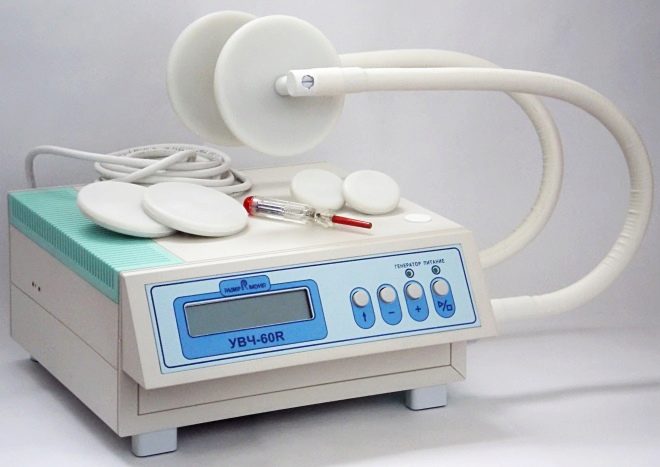
To restore hearing and reduce high blood pressure in the Eustachian tube successfully used UHF-therapy, ultrasound and phonophoresis. To achieve a positive effect usually requires a whole course of physiotherapy, consisting of 8-12 procedures.
If the cause of the disease has become a bacterial infection, various types of antibacterial drugs are used. Currently, doctors prefer products with a wide range of actions.
Clavulanic acid-protected penicillins are the most commonly used drugs used to treat bacterial forms of otitis.
Many types of chronic otitis occur on the background of reduced work of the immune system. To normalize immunity, doctors prescribe multivitamin complexes and interferon preparations for babies. These funds are also used at the exchange rate.
Prolonged use of immunomodulatory drugs must be discussed with a child immunologist.
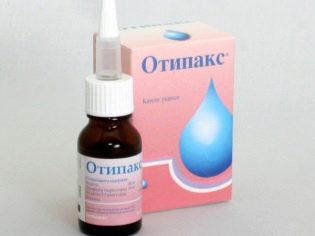
To eliminate pain in the affected ear, ear drops are used. Usually they are appointed for 7-14 days. You can use these drugs 3-4 times a day.
«Otipaks» helps to eliminate severe inflammation in the cavity of the affected ear, and also reduces the possibility of secondary bacterial infection and spread of the process.
Ear drops should be used only after a preliminary examination by a pediatric ENT doctor. Many of the drugs are contraindicated in the presence of an ear perforation in the ear cavity. To identify this pathological deviation can only otolaryngologist using a special medical instrument.
To reduce high body temperature, antipyretic agents are used. In children, the most optimal use of drugs containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. These drugs should be used only when the body temperature rises above 38 degrees.
Children should not take products containing acetylsalicylic acid. These drugs can lead to the development of multiple unwanted complications.
Over the course of catarrhal otitis necessarily carried out careful monitoring. The most dangerous are considered 3-5 days from the moment of onset of the disease. As a rule, at this time the process may turn into a purulent form.
To identify the complications of the disease requires a mandatory general blood test. The increase in white blood cells against the background of the treatment is an unfavorable sign that requires mandatory consultation with your doctor.
To prevent the transition from acute catarrhal otitis to chronic mandatory strengthening of immunity. To do this, doctors recommend that babies observe the correct mode of the day, eat high-quality protein foods, and regularly walk in the fresh air. Any strong stresses and excessively active physical exertion can only lead to a decrease in immunity.
About what is otitis and how to treat it, see the next video.