Features of treatment of otitis media in children at home
Inflammation of the ears in childhood is a frequent phenomenon, because anatomical features of the structure of children's hearing organs contribute to otitis. According to statistics, up to 90% of children have had otitis at least once before the age of 7, and therefore it is important for parents to know what the features of treatment of this disease are at home.
About pathology
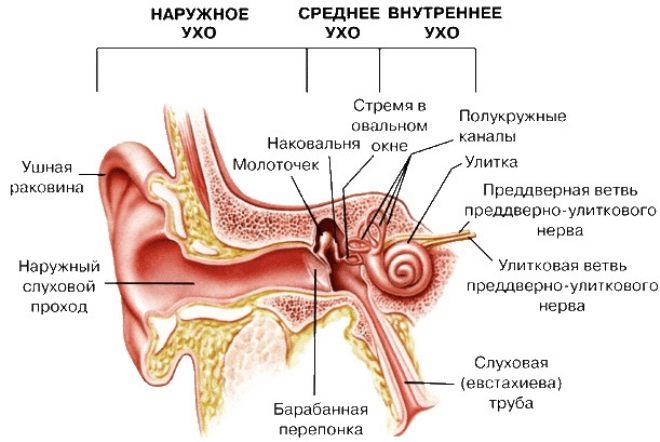
The organs of hearing are arranged quite difficult. They have three main sections: the outer ear - the auricle, the middle - the eardrum, the cavity and the auditory ossicles, the inner - the labyrinth and the auditory nerves that go directly to the brain. Inflamed can any of the departments. And in this case they talk about otitis, indicating in which department the inflammation happened: medium, external or internal otitis.
The frequency of pediatric otitis decreases after approximately 8-9 years. By this time, the hearing organs of children develop and become identical to adults.
The reasons
Inflammation in the organs of hearing in children develops for a variety of reasons. This may be a trauma or hypothermia, but most often otitis occurs due to the fact that pathogenic microbes, viruses, fungi, and liquid get into the ear sections. In this case, most otitis does not develop as an independent disease, but as a complication.
Why is this happening, to understand is simple: in case of illness, the child actively sniffs, sneezes, and the contents of the nasal passages can easily get into the auditory tube. The environment there is very favorable for the development of the inflammatory process.
The auditory tube in children has its own characteristics, with which the frequent incidence of otitis is associated: it is located almost horizontally, it is short and wide, and therefore it is easier to throw any fluid into it. When a child becomes a teenager, the auditory tube is lengthened, narrowed and almost vertical, and therefore adults are less likely to suffer from inflammation of the hearing organs.
With the flu, acute respiratory viral infections, adenoids, the mucous membranes of the nose swell, the nose is difficult to breathe, and therefore the ventilation of the auditory tube is disturbed. Viral otitis as a complication of chickenpox or measles is also a fairly common phenomenon. Children with diseases of ENT organs suffer from otitis more often, and this is a proven fact.
More often than others, parents of prematurely born children, who often suffer from colds, as well as toddlers who are subject to pressure drops (flying on diving airplanes, swimming) encounter otitis children.
The outer ear can inflame by itself, without comorbidities, but the average and inner otitis usually develops against the background of other diseases, and this should not be forgotten when planning a child’s treatment at home.
What are the symptoms and signs?
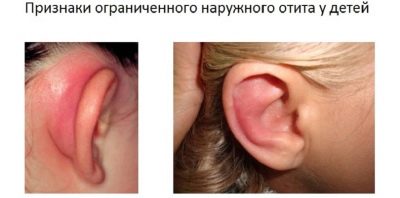
Otitis of the outer ear is very easy to recognize: an inflammatory process occurs outside, in the area of the auricle, sometimes boils appear on it. The pathological process is able to spread to the ear region. The disease can leak without temperature, as well as at temperatures up to 38 degrees and even higher - it is quite individual.
With moderate otitis media in children, there is severe pain in the ear, which becomes stronger when trying to move his head, chew, speak. Catarrhal otitis media (non-purulent) is both unilateral and bilateral. Exudative purulent otitis media is also able to affect both one and both ears.
But most often the kids develop exactly one-sided form.
In addition to pain, a rise in temperature can begin, lethargy, noise in the ears and a decrease in the perception of sound information are observed. With purulent form, the strongest pains precede the integrity of the eardrum under the pressure of pus, after which the contents flow out and the condition improves.
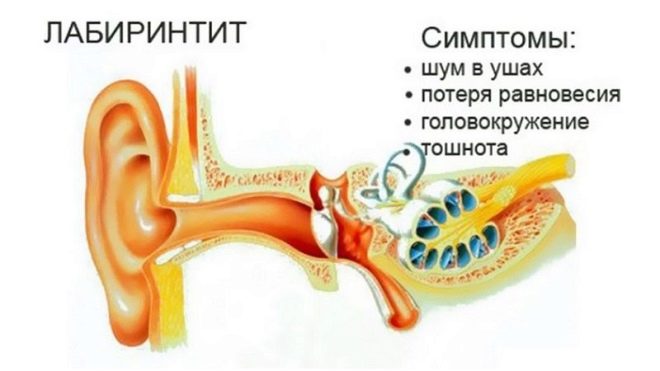
Internal otitis most often develops as a complication of a severe medium, and the process in the labyrinth is purulent, serous and necrotic. When it is observed deterioration of the child, vomiting, loss of balance, a strong decrease in auditory function.
It is this otitis that most often leads to the development of persistent hearing loss in the future.
After external and average otitis, the hearing will return; after internal purulent, it is usually impossible to restore it completely.
In infants, it is more difficult to recognize the beginning inflammation in the ears than in boys and girls, who, because of their age, are already able to articulate the presence of pain in a certain part of the body. A baby of ear pain cries shrilly, screams, it is almost impossible to calm him down.
Regardless of whether viral, microbial, or other otitis has developed, the body temperature of the toddler rises. When you try to suckle or eat from the bottle, the pain in the ear becomes stronger, and the child stops eating without being satisfied, which leads to a new fit of crying. Disturbed sleep, appetite. The child looks painful, can constantly pull at his ear. When pressing on the "trestle" - the cartilaginous protrusion in front of the entrance to the ear - the pain increases.
First aid
If a child has an ear, parents should clearly understand that age in this matter is a very important factor. If a baby is small, a newborn baby, then from acute catarrhal to purulent otitis media is within reach. Sometimes just a few hours is enough for one form to flow into another. If the baby is already 2-3 years old, then the disease will not develop at such a rapid rate.
That is why young children need to call an ambulance, and a child after 2 years must show a doctor as soon as possible.
Considering that the ear pain most often starts at night, when the clinic is closed, It is important to know the rules of first aid for otitis.
First of all, parents should not drip anything into their ears. Ear drops are an important part of therapy, but only when the membrane maintains integrity. If it is damaged, the medicine will only harm the child, hitting the labyrinth. Therefore, you should not even try to examine the membrane and assess how well it is, this is the task of the doctor with an otoscope (special device). If pus, blood, serous fluid flows from the ear, it is not necessary to drip all the more - it is a sign of a violation of the integrity of the membrane.
Popular dry compresses before the doctor can not impose. It is possible to warm only when the form is catarrhal. If suppuration is present, warming will intensify the pus formation process. Do not give children sleeping pills, painkillers.
To properly provide first aid before the examination by a doctor should:
- put the child with a sore ear down or take it on the arms, if it’s a nursing baby, pressing the sore ear to the arm or chest, this will help the baby to calm down a bit;
- nasal drops with a vasoconstrictor effect can be instilled into both nasal passages, for example, “Nazivin” (such drops will help in narrowing the vessels and the auditory tube, which will slightly reduce the swelling);
- on the temperature you can give medicine with antipyretic effect, it is desirable that this would be "Paracetamol".
These measures will help to wait for medical care.
When is home treatment acceptable?
It is possible to treat otitis at home in almost all cases. The exceptions are exudative otitis media in infants and suppurative internal inflammations.In this case, it is better to go on the proposal of physicians in the hospital, because there the state of the child will be monitored around the clock.
The question of whether a small patient can be released is treated at home, is decided by the ENT doctor, who necessarily examines the affected ear by means of an otoscope. If something flows from the ear, then a sample of the outflowing fluid is taken for bacteriological analysis (bacterial otitis is contagious!).
It all depends on how severe the inflammatory disease is, what diseases accompany it. In some cases, the child It is recommended to make a computed tomographic study of the temporal bones, and if the hearing is severely damaged, then an audiometric examination by a hearingologist.
Severe otitis media needs to be monitored by a neurologist.
Basic principles of therapy
Otitis is treated conservatively. The exception is the situation of purulent otitis, in which the membrane is very strong and does not want to perforate. In this case, a simple procedure is carried out in the conditions of the manipulation cabinet - puncture of the membrane, followed by washing the middle ear cavity with medicinal solutions. Next, the child is prescribed home treatment.
The basic principle is to reduce pain, reduce inflammation. This helps drop with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. If bacteria are to blame for the disease, then they are treated with an antibiotic, more often - topically, in drops. But sometimes it can be assigned and systemic antimicrobial drug in pills or in suspension.
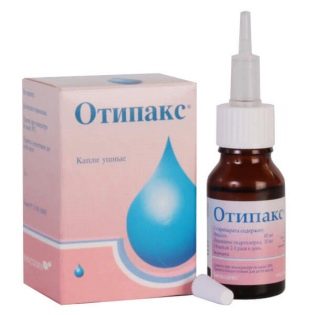
Drops, as we remember, are permissible only for a whole membrane. Most often, children are prescribed such agents as “Otofa”, “Tsipromed”, “Otinum”, “Otipaks”, furatsilinovy alcohol, for pain relief - “Lidocaine” in the ear. Before you bury them, you need to warm the bottle in your hand so that the temperature of the liquid in it is approximately equal to the body temperature. So the procedure will be more pleasant and effective. Drops from 2 to 4 times a day, depending on the degree of the disease.
It is important to adhere to the principle of pairing: if you treat the right ear, you must bury the medicine in the left ear.
Among the systemic antibiotics for purulent microbial otitis recommend most often "Amoxiclav", "Flemoksin", "Flemoklav". After the start of taking such drugs, usually within a few days, a noticeable improvement occurs.
Here the main thing that is required of parents is not to quit treatment, having been delighted with the improvement. This can lead to the fact that some pathogens will survive and will be resistant to antibiotics.
Then it will be very difficult to cure the second wave of otitis caused by "hardened" microbes.
If only the outer ear has become inflamed, warming dry cotton-gauze compresses are applied (in the absence of pus), a cotton wool moistened with anti-inflammatory drops, for example “Norfloxacin”, is introduced into the sink. If inflammation does not go away within 3-4 days, surgical opening of abscesses and treatment with ointments with antibacterial composition are indicated.
When treating otitis media, it is important not to forget to perform all the recommended instillations in time. It is advisable not to bathe the child at the time of treatment, do not go for a walk when the temperature rises. After the pain has passed, you need to get a referral to a physical room for physiotherapy to improve the ventilation of the auditory tube, electrophoresis.
If otitis is internal, the child is given antibiotics intramuscularly, it is often shown to introduce the corticosteroid hormone "Prednisolone" to save the hearing, and then drugs that help strengthen the blood circulation of the labyrinth: Neyromidine or Vestibo.
It is very important to monitor the state of hearing of the child. If the loss progresses, it is necessary to urgently resolve the issue of wearing hearing aids, to diagnose the real degree of hearing loss.
Compresses with otitis do only if the otitis is not purulent.For children, their options are needed only gauze and cotton wool - alcohol solutions for compresses in children do not apply.
Doctors do not recommend using folk remedies for treating inflammation of the ears in children.
Anyway, they do not give permission for this, especially if children have fever, pain is intense, there is pus. If the permission is still obtained, then you can with great care apply aloe juice, diluted in half with saline, for instillation in the ears, a compress in the ear with warm vegetable oil, children after three years - compresses with camphor oil.
Relapse prevention
In order not to get sick again after recovery, it is recommended to pay special attention to the prevention of recurrent otitis. To do this, it is important to vaccinate "Prevenar" against pneumococcal infection, sometimes, when the causative agent of ear inflammation is pneumococcus, it helps reduce the likelihood of inflammation and serious consequences.
When a child has a cold head, it is important to teach not to sniff the nose in order to avoid nasal mucus with bacteria and viruses entering the auditory tube. You can not clean the child's ears with cotton buds, since this significantly increases the risk of injury to the eardrum.
An infant should not be laid immediately after eating or drinking. This will help not only to reduce colic, but also to prevent otitis media caused by getting into the tube of a piece that the child will burp after eating.
Opinion Dr. Komarovsky, like many other pediatricians, on this subject is: in order to preserve the health of the ears, it is important to timely and correctly treat all ENT diseases (from the common cold to the adenoids). While swimming or bathing a child should not swallow water especially when it comes to river or sea water.