Otitis in newborns and infants
With otitis media, most parents are familiar firsthand. Eight out of ten newborns and infants before the year at least once had inflammation of the organs of hearing. Why the youngest children are more often exposed to this disease and how to help the child, we will tell in this article.
What it is
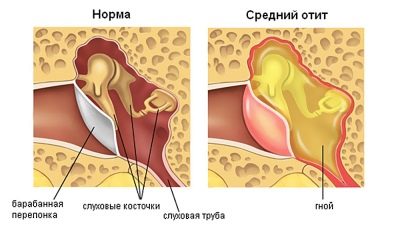
The inflammatory process occurring in one of the departments of the human ear, called "otitis". Accordingly, with inflammation of the outer ear, they say otitis externa, middle ear - about average, internal - about internal otitis or labyrinth.
In infants of the first year of life, otitis media is more common.
In babies, this disease is usually acute. It is possible to speak about chronic otitis when the episodes of inflammation recur 5 times a year.
Inflammation can be either catarrhal (normal inflammation), or purulent or exudative (inflammation with accumulation and separation of pus).
The main causes that cause inflammation of the hearing organs are pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic bacteria (cocci, pyocyanic stick, moraxella, etc.). Many of them calmly reside in the nasopharynx, without causing disease.
With any infection, colds, under the influence of other external factors, bacteria mechanically penetrate into the auditory tube and the middle ear. There for microbes there are excellent conditions for reproduction - warm, humid. So begins the inflammation.
The otitis media can get into the organs of hearing when sneezing, mis-blowing, sniffing, coughing. On the bloodstream, microbes penetrate the ear much less.
Sometimes viruses cause illness, for example, during illness. measles. In any case, it is not accepted to consider otitis as an independent illness. In 99% of cases, it is only a complication of previous upper respiratory tract diseases, viral or bacterial infections.
The main danger of otitis lies in the possibility of losing hearing. This can happen with purulent inflammation, when the structure of the hearing organs is disturbed, with labyrinthitis.
Purulent otitis in severe form can also cause inflammation of the meninges if the purulent masses burst inward, not outward. Most of the acute inflammation without pus does not lead to hearing loss.
Age features
The first six months after the birth of the child from viral infections protects the innate immunity - the antibodies that the crumb mum transmitted during pregnancy. Therefore, severe viral diseases at this age are more rare than the rule.
After six months, the baby becomes vulnerable to hundreds of various viruses, for which the immunity of the child is not ready. Immune protection when confronted with microbes and viruses is “trained”, it produces its own antibodies, and this takes time. That is why so often even mild forms of diseases in infants of early age are complicated, including otitis.
As for children up to six months, they have otitis media - also not uncommon. But the reason lies not even in a state of immunity, but in the physiological age-related features of the structure of the organs of hearing.
In babies, the auditory tube is short and wide.
It is located almost horizontally.That is why it can easily penetrate breast milk, water, nasal mucus, together with bacteria, which existed peacefully in the nose, and in the ear quickly activated and began to multiply.
The nasal mucus in babies is produced more actively, besides, babies often cry and excess tears flow down the nasal duct into the nasal cavity. When "sniffing" they can easily be in the auditory tube.
You should not worry, because as the child grows, his auditory tube grows too. It lengthens, becomes narrower, its location in space changes to a more vertical. The risks of falling into the tube of the contents of the nose, mouth is sharply reduced. That is why in children after 5-6 years the number of otitis rapidly decreases.
The reasons
Thus, the most common causes of ear inflammation are:
- hypothermia;
- mechanical injury (for example, when cleaning the child’s ears with cotton swabs);
- bacterial infection;
- viral infection and its complications;
- getting into the cavity of the middle ear fluids (milk, tears, water, nasal mucus);
- allergic reaction.
Symptoms and signs
External otitis usually manifested by the formation of boils on the ear and behind the ear. The ear is red, swollen, very sore. Diagnosis of labor is not, because the source of the pain immediately noticeable. With external otitis, the temperature rises, the general condition of the child worsens.
Otitis media detect is somewhat more difficult. It is accompanied by a strong shooting pain in the ear, which is aggravated by the movement of the head. The temperature does not always rise. The child has a noise in the ear, stuffiness. If not only the auditory tube is inflamed, but also the eardrum, then the temperature rises, other symptoms, including pain, also become stronger.
Purulent otitis always accompanied by almost unbearable pain and high fever. The child will feel relieved only after the outflow of pus begins. Purulent masses put pressure on the eardrum and eventually break through it. After the pus comes out, the pain subsides, the temperature decreases, recovery begins. The breakthrough of the eardrum is gradually scarring, it is being restored. Perforation of the membrane does not affect hearing.
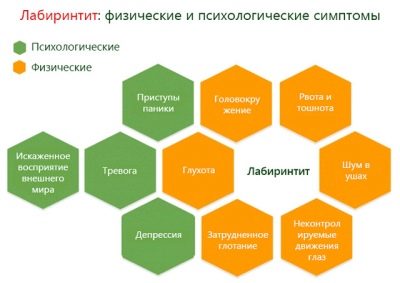
Internal otitis - the most difficult and difficult among all the inflammations of the auditory analyzer. It is rarely completed without consequences for hearing and the organs of equilibrium located in it, but it cannot but rejoice at the fact that such otitis occurs in children extremely rarely.
The symptoms of labyrinthitis, as it is also called, are as follows: sweating, lethargy, refusal of food due to dizziness and nausea, too pale or, on the contrary, reddened skin, increased or slow pulse.
After some time, parents may pay attention to hearing loss. The baby stops responding to voices to which it had previously responded with a smile or by turning the head, does not turn on the noise of the rattle, does not flinch if the door suddenly slam.
Then there are severe pains in the ear, which become more intense when the head position and body position change. Attempts to turn the child on its side will be accompanied by a loud and piercing roar.
How to recognize otitis media in infants?
With the diagnosis of otitis in children older than two years, problems usually do not arise, because such babies are already able to tell their mother what and where they have pain. Everything is much more difficult with infants, they do not speak, they do not indicate the source of pain.
By the nature of crying, many mothers are able to determine that the child is in pain. Such crying is sharp, sheer, the child literally goes into a scream. The cry is almost permanent.
A hungry baby greedily takes the breast or a bottle of the mixture, but after a few seconds he stops sucking and starts screaming loudly again. This is due to the fact that sucking and swallowing movements only increase the pain in the ear.
The child's behavior changes dramatically, he becomes moody, lethargic, sleep is disturbed, he can refuse to eat after he realizes that sucking is painful. When such signs are detected, the mother must measure the temperature of the child and examine the ears for secretions from them.
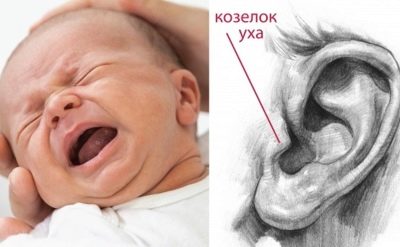
To confirm the suspicion of using the method of pressure on the tragus. The tragus is a cartilage located in the center at the entrance to the auditory foramen. He stands, it is difficult not to notice. Mom presses the hryashchik-trestle with the index finger of her hand. If there is an inflammatory process in the ear, then such an effect increases the pain, the child begins to cry.
It is best to conduct a diagnostic test when the baby is at rest. If he roars without a test, it will be difficult to distinguish the change in the nature of the pain and crying.
First, in this way, the left ear is checked, then the right ear. Then they press simultaneously on both the trestle. This will make it possible not only to establish if there is otitis at all, but from which side it develops, or it is bilateral. Children usually have unilateral inflammation, but anything can happen.
It is somewhat easier to understand a child who is already 9-10 months old. Such a baby will rub the sore ear, pull it. If the movement is repeated often and combined with temperature, a positive reaction when pressing on the trestle, then we can safely say that the child has otitis.
It will be easier to recognize otitis media if you know that in young children ear inflammation usually manifests itself in the evening or at night. It all starts with a sharp pain. Therefore, if the baby woke up and suddenly shouted, this is also a reason to check if he has signs of otitis.
If a baby has purulent or blood-like discharge from the ear, there can be no doubt - inflammation does occur, and only a doctor can determine its exact location and extent.
At the first sign of otitis in a child under one year old, a doctor must be called. Self-medication and experiments with folk remedies at this age and with such a disease are absolutely unacceptable.
Diagnostics
The doctor examines the ears visually with the use of an otoscope. Establishes the presence or absence of pus, as well as the degree of inflammation. A visual inspection allows you to conclude whether the eardrum is intact.
If purulent exudate is found, take a sample for bacteriological analysis to determine the type of microbe that caused the inflammation. This is required in order to select antibiotic drugs for the treatment of otitis media.
If bacteria and viruses are not detected, blood tests do not show antibodies to viral ailments, and baccavi does not show the presence of microbes, the doctor may suggest allergic otitis. In this case, treatment is prescribed completely different.
If you suspect that there is internal otitis, it is imperative to conduct a study of auditory function using tone audiometry for babies.
First aid
If a child from 2 years old can call a doctor at home, and the older child can be taken to the clinic, then for children of the first year of life, delay is unacceptable, because purulent otitis from the punitive they can develop in just 5-7 hours.
Parents best to call an ambulance, especially if the crumbs have a fever.
Waiting for the doctor does not cost anything to bury in the ears, since there is no certainty that the eardrum is intact.
Drops can only be dripped with a holistic membrane, and this integrity can only be assessed when viewed with an otoscope with a light bulb - a special tool. Therefore, first aid should consist in the fact that the child should be picked up, and putting the patient’s eye down should the calf be able to calm down for a while.
It is also not worth doing warming compresses in the context of emergency care, because at home there is no way to find out if pus is formed inside the inflamed cavity.
When purulent otitis warming only exacerbates the already strong inflammation. Compress is a good way of treatment, but only after the doctor examines the child.
The only thing that parents can do is give a baby a fever reducing agent if the temperature exceeds 38.0 degrees. It is better to prefer drugs based on paracetamol.
For the smallest patients, there is antipyretic in the form of rectal suppositories and syrups. It is also allowed to drop vasoconstrictive drops “Nazol” or “Nazivin” into the baby’s nose to relieve puffiness in the auditory tube. This will slightly reduce the pain at the time.
Treatment
Otitis in infants is treated at home. The only exceptions are internal otitis (labyrinthitis) and severe suppurative otitis media, with which there is a real risk of inflammation of the meninges. Such children are hospitalized and treated under the supervision of pediatricians and ENT doctors.
After examination and analysis, the doctor makes detailed recommendations. For purulent otitis, ear drops with antibiotics are always prescribed. With an allergic form of the ear disease - drops with corticosteroids.
If the cause of the inflammation is viruses, the doctor may advise osmotically active drops with anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Purulent otitis media and catarrhal otitis media with severe leakage may require the use of antibiotics orally - babies are most often recommended “Amoxiclav», «Amosin". The ear drops, like “Otinum"And"Otipaks».
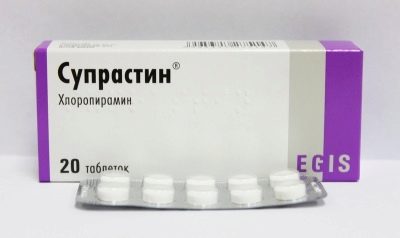
In case of allergic otitis, also in case of severe inflammation with general sensitization, antihistamines can be recommended, for example, “suprastin”.
If otitis media is accompanied by nasal congestion and rhinitis, then vasoconstrictor nasal drops are prescribed for a course of no more than 3-5 days, since their longer taking can lead to persistent drug dependence.
Ear drops are usually instilled 3-4 times a day, 2-4 drops in each ear canal. Nose drops - in the morning and in the evening. The dosage and frequency of antibiotics is determined by the doctor based on the weight of the child.
In addition, vitamins and iron preparations can be prescribed, since on the background of otitis often a decrease in hemoglobin occurs.
In case of catarrhal otitis without a purulent complication, the child may be allowed to do warming compresses. For this, parents will need:
- cotton wool;
- bandage;
- gauze;
- compress paper;
- heated vegetable oil.
In gauze make a vertical slot for the auricle. The size of a piece of gauze is 10x10 cm. It is moistened with warm sunflower oil and applied to the diseased ear by passing the auricle through the slot. Then put a layer of paper for compresses, its size is 12x12 cm. Then apply dry gauze measuring 14x14 cm and gently fix the compress with a bandage so that it does not let air through.
Compress is applied for 4-6 hours. Do not do the procedure at night. Vodka and alcohol for such treatment can not be used. Compress can be set only when the temperature of the child is at normal values.
With a competent and thorough approach, the treatment of otitis media in infants and newborns will not take more than five to six days. In this case, acute pain usually manages to "win" in a day or two.
In severe cases, the doctor may suggest a puncture of the eardrum. This is done if the pus cannot come out. To avoid its breakthrough inside, make a small incision on the membrane. This is not dangerous. After the discharge of the purulent contents, the incision will be healed, the integrity of the membrane will be fully restored.
After the course of treatment, you should definitely visit a baby otolaryngologist with a baby, who will examine the baby’s ears and find out if the auditory function has suffered.
External otitis is treated with antibiotic ointments, turunda with antimicrobial drugs, warming compresses.When an abscess or boil is formed, its surgical dissection may be indicated.
What you can not do:
- You can not warm the ears, if the child has a purulent form of otitis.
- Do not bury the baby in the nose and ears of breast milk, which is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria.
- Do not stop taking antibiotics at the first sign of improvement. The course (it is usually 5-7 days) should definitely be completed.
- Do not bury the child in the ears homemade home drops.
- Do not use alcohol products for the treatment of an infant.
- You can not put warming compresses at elevated body temperature.
About when to treat otitis antibiotics will tell Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.
Prevention
The risk of injury to the ears can be reduced if you use not cotton buds for hygienic cleaning, but self-made turkey gauze.
If you quickly and correctly respond to nasal congestion, to the snot in a child, correctly treat rhinitis, then this significantly reduces the likelihood of developing such complications as otitis.
To prevent nasal mucus from thickening, including after entering the auditory tube, the child must breathe with sufficiently moisturized cool air. The best parameters for children up to a year are air temperature from 18 to 21 degrees, humidity - 50-70%.
When picking up a child for a walk, it should be remembered that it is not necessary to muffle him, but it is also impossible to allow drafts and wind to blow his head and ears. Caps should be chosen so that they cover the ears even in summer. At the same time it is not necessary to choose a warm hat, if it is already warm outside. If there is a strong wind outside, it is better to postpone walking with the baby.
After feeding, the child must be held in an upright position so that the burping does not fall into the auditory tube.