What are the selections after ovulation?
The period after ovulation is very important, especially for women who want to become mothers and are planning a pregnancy. And it is precisely the second phase of the female cycle that becomes informative for them - the very first possible signs of the desired pregnancy are being searched for in this particular period. The nature of vaginal discharge is an indicator that can tell a lot. About what selection accompany the second half of the female cycle, will be discussed in this material.
The physiology of change - what happens to a woman?
Nature has provided a certain cyclical nature for the female body. Fertility woman is not always, but only during ovulation, when a mature oocyte gets the opportunity to leave the follicle on the ovary, in which it matured during the first phase of the menstrual cycle, since all follicle maturation processes, its perforation and oocyte release are associated with certain hormonal changes and are regulated hormones.
Naturally, changes in hormonal levels are accompanied by a change in the nature of vaginal discharge, which consists of cervical secretions and vaginal secretions. They are very sensitive to the fluctuations of hormones in the blood of women.
During the period of ovulation, nature made sure that the nature of the discharge prompted the fair sex that a favorable time for conception was occurring. Before the oocyte leaves the follicle, secretions become more abundant under the influence of an increased level of estrogen; a woman may experience a feeling of moisture in the perineum. Discharges are usually mucous, transparent or unclear, light, viscous, and viscous, resembling in their structure chicken raw egg white.
Estrogens liquefy cervical mucus in order to ensure the openness of the cervical canal, it is through him that spermatozoa will go to the reproductive tract further to the egg cell. The vaginal environment, usually quite acidic, becomes more neutral, less aggressive during the ovulation period, increasing the chances of male germ cells for survival, thus increasing the likelihood of conception.
The egg cell lives for about a day. And already a day after ovulation, the nature of the discharge begins to change the hormone progesterone, the concentration of which increases, regardless of whether the pregnancy occurs or not. Progesterone makes the secretion creamy, scanty, thickens them, sometimes under the action of this hormone secretions become yellowish - this is a variant of the norm. There comes the so-called "dry period".
If the pregnancy during ovulation occurs, the progesterone level will remain high until the very birth, if conception did not occur, then the corpus luteum, which forms on the ovary at the site of the perforated follicle, dies a few days before the onset of menstruation, the level of estrogen increases, the secretion again become more abundant, sometimes watery, and then menstrual bleeding begins.
The nature of the discharge at the onset of pregnancy
By themselves, the discharge after ovulation, which was marked by fertilization, is not a way to diagnose pregnancy in the early stages, but for an attentive woman who knows well the peculiarities of her own menstrual cycle, they can become an auxiliary “hint”.
The mucus inherent in the ovulation window, after a couple of days, is replaced by a scanty discharge, light, odorless. Suppose a yellowish color, its presence is associated with a growing level of progesterone. The discharge may be watery only the first couple of days after sexual intercourse in ovulation, and such a feature is associated with the process of sperm liquefaction, to which seminal fluid is exposed.
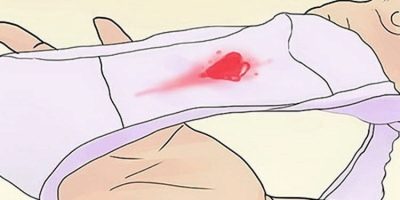
During the week the embryo makes a fascinating journey from the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it is to implant, and this process takes place all differently, but in most cases 5-7 days after ovulation. Thus, a week after ovulation (approximately), signs of implantation bleeding may appear - smearing pink or brownish discharge, and sometimes just bloody fibrous inclusions in light discharge.
Such bleeding does not threaten the woman, the child, its appearance is due to the fact that the chorionic villi disrupt the integrity of the endometrial blood vessels when the fetus attaches to the wall of the uterus.
Such discharge during the implantation period is not for everyone and not always. For many women, this bleeding does not occur at all, and this is also completely normal.
Important! Implant discharge stops 1-2 days after the start. They do not require any treatment.
Such secretions may be accompanied by additional symptoms, for example, a slight short-term increase in body temperature, feeling of a fever, headache, unreasonable increased fatigue, fatigue. Some women claim that for a few days at 7-8 days after ovulation, they feel a characteristic metallic taste in their mouth, as if there was an iron coin.
There was such a bleeding or not, but last week before the expected day of the beginning of the next menstrual period (which, most likely, will not be), there is a change in vaginal secretion. The amount of progesterone increases, the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) gradually increases, the discharge becomes thick, there are few of them.
A few days before menstruation, thrush manifests itself in many pregnant women, this is how a woman’s immune defenses respond to violent actions from progesterone — this hormone begins to depress immunity so that the body does not discard the fetus.
If a woman has previously had thrush, then candida fungi begin to multiply rapidly as soon as the immune system weakens. Therefore, curd (cheesy) whitish discharge with itching and a weak yeast odor may well be regarded as an early sign of pregnancy before a delay, but at the same time it is definitely not worth leaving them without attention and treatment.
With the onset of pregnancy, menstrual bleeding does not occur within a fixed term. Before this, the amount of cervical mucus does not increase.
Characteristics of some types of vaginal secretions
Allocations after ovulation can tell a lot to specialists about the state of health of a woman, about the sufficiency of hormonal support for her cycle. Here are several selections with descriptions.
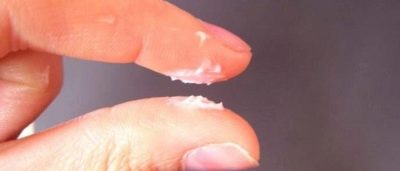
Whites
This is the norm. After the release of the oocyte, such creamy (creamy) secretions suggest that the woman has successfully entered the second phase of her cycle and progesterone “rules the ball” in her body. A doctor should be consulted only if the discharge of white color is abundant, sticky, with clots, that is, heterogeneous in structure. Pathological leucorrhoea can have a lot of causes from genital infections to inflammation of the reproductive organs.
If ovulation did not occur under the influence of various factors, the follicle did not rupture, then follicular cyst formation is possible, and then strong white secretions become pathological.
White moderate discharge can be both during pregnancy in the first days and outside of pregnancy. You need to focus on your feelings - if the discharge does not cause inconvenience, then there is nothing to worry about.
Brown and pink
A large range of unusual secretions - pink, brown, red, dark beige - options for bleeding, just the blood in them is present in different quantities and with different periods of "limitation". Also, an unusual secretion with signs of the presence of red blood cell blood cells with it can be observed in tumors in the reproductive organs of the female system.
Watery
Liquid discharge, resembling water in its consistency, is usually normal in the second phase of the female cycle. If they are abundant and cause inconvenience, discomfort, you should consult a doctor. Especially pay attention to the smell and impurities. If there are “flakes” in them, they are frothy and have an unpleasant smell, this may indicate such a pathological condition as vaginal dysbacteriosis. Also, this nature of vaginal secretion often accompanies the initial stages of inflammatory processes of the reproductive organs.
Yellow
As already mentioned, such secretions may well speak about the reproductive health of a woman, about the onset of the second phase of her female cycle, which takes place under the action of progesterone. If yellow discharge is accompanied by a rise in temperature, itching in the perineum, it is possible that the woman has cervical erosion, an inflammatory process in the appendages.
It is important to recognize the pain and in time to consult a doctor.
Green gray
Highlighting such a color is a sign of infection, norm options exist. Usually, the appearance of this type of secretion is accompanied by an additional itch, an unpleasant odor resembling the smell of rotten fish, and pain may occur in the lower abdomen.
They are thick or liquid, it does not matter much, as well as the amount - you should hurry to the doctor to start treatment in time.
What does the lack of secretion?
Such a concept as the absence of secretions, there is only among women, in medicine it is believed that the lack of secretion is impossible in principle.
If there is little excreta so much that the daily lining during the day remains clean, this is not considered a deviation from the norm, since the second half of the female cycle is a “dry” period associated with a decrease in the amount of secretion.
Recommendations
To navigate in your own menstrual cycle and know its features on different days is very important. This will help not only to effectively protect themselves, but also to become pregnant, if you want, faster. In addition, a change in well-being on certain days, which is not similar to the norm, can speak about the development of pathologies even at the initial stages, when treatment does not present much difficulty.
Women who are concerned about their reproductive health, It is recommended to keep a table and schedule of basal temperature, to note the features of cervical mucus on different days of the cycle. If there are unusual discharge, for example, from the chest after ovulation, you should consult a doctor, there may be serious hormonal disruptions. Data on temperature and excretion are entered into the female calendar, which, if something happens, will be able to help the doctor to quickly find the cause of the woman’s health problems.
A woman during the ovulation period is not recommended to use tampons, since they impede the free flow of vaginal secretions, which is very active during this period. Stagnation of secretion with an inserted tampon can lead to inflammatory processes in the genital tract, to ascending inflammatory processes.
The use of sanitary pads is permissible if secretion is very abundant.
To make the second phase of the cycle more favorable, remember that use of painkillers during ovulation is not recommended if you are planning to conceive. It is also desirable for a woman in the second phase of the cycle to refrain from consuming large amounts of drinks with a high content of caffeine. These include strong black tea and coffee. If conception is planned, it is better to refrain from eating dark chocolate.
A woman should not abuse syringing, especially to use for it solutions with high acidity, for example, lemon water. Such methods reduce the chances of conception by increasing the acidity of the vagina, but dry it and gradually cause dystrophic changes in the mucous membranes of the genital tract and cervix.
For the normal functioning of the female body in the second phase of the cycle, stressful situations should be avoided, since chronic emotional and psychological stress leads to changes in the hormonal background and subsequent changes in the secretion of the cervix and vagina.
For secretions after ovulation, see the following video.