Gastroduodenitis in children: from symptoms to treatment
Gastroduodenitis in children is not uncommon, and lately doctors are sounding the alarm - the number of babies with such a diagnosis is growing rapidly. That is why parents are recommended to be more attentive to the health of their sons and daughters and to consult a doctor in time if signs of gastroduodenitis appear.
About the disease
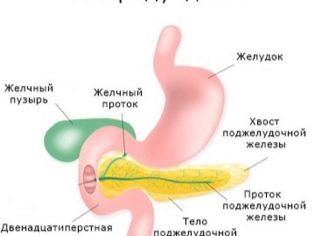
Gastroduodenitis is the inflammatory process of the digestive tract that flows in the membranes of the duodenum and the part of the stomach that is adjacent to the spine. Simultaneous inflammation of the antrum of the stomach and duodenum occurs, as a rule, not by itself, but as a consequence of improper treatment of gastritis or duodenitis.
The disease has quite characteristic signs - the child is sick, he has heartburn, his appetite is reduced, there is pain in the stomach, especially after eating, the stool is often broken. Gradually, inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the digestive organs lead to a change in their structure, which affects the functioning of the organs of the digestive system.
Doctors say that in almost 70% of cases children are diagnosed with chronic gastroduodenitis. And experts from the World Health Organization recently published evidence that signs of gastroduodenitis are found in about every third child of school age on the planet.
Children living in developed countries and accustomed to consume a lot of carbohydrates, sugar, salt, fast food as food, inactive children and adolescents are especially susceptible to illness.
In ICD-10, the disease is assigned a K-29 number followed by a variation number after the dot.
Causes of the disease
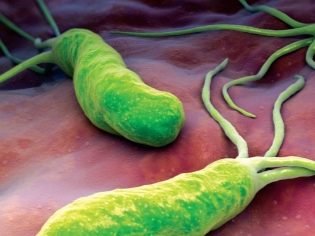
Scientists have found that in about seven out of ten children, the painful process in the stomach and duodenum is caused by bacteria Helicobacter pylori, which are familiar to many of the commercials. The role of these microorganisms in the state of health of the stomach has been identified relatively recently, and the phenomenon has been called Helicobacteriosis.
But there are a lot of carriers of Helicobacterium, and not everyone has a disease of the digestive tract. It was revealed that children with gastroduodenitis who are not just carriers of Helicobacter pylori, but also infected with some other pathogens such as enteroviruses and herpes viruses, are ill. A simultaneous inflammatory process in the stomach and in the duodenal sections sometimes occurs with existing gastritis, which is either treated incorrectly or not treated at all.
Experts have found that children who have a certain genetic predisposition to this disease are more susceptible to gastroduodenitis.
Also, the disease often starts for the first time after suffering a viral or bacterial disease that has weakened the protective and compensatory functions of the child’s body.
The following categories of babies are most susceptible to illness:
- born of pathological pregnancy and as a result of complicated childbirth;
- tots that were early transferred to artificial feeding;
- children prone to extensive and serious allergic forms, for example, atopic dermatitis, angioedema.
The state of health of other digestive organs affects the likelihood of the disease by gastroduodenitis - amid inflammation of the pancreas, intestinal dysbiosis, enterocolitis, gastroduodenitis develops much more often. Also, the disease occurs in children with kidney problems, with diabetes, as well as in children with long and persistent foci of infection in the body, for example, with untreated teeth, chronic tonsillitis. According to some reports, the course of the disease is exacerbated with parasitic infections, worms. Also, the disease often develops on the background of high acidity of gastric juice.
Doctors believe gastroduodenitis is a disease dictated by the very lifestyle of modern children - the ailment most often develops in children who eat unbalanced, irregularly, violate the regimen, eat a large number of products that can irritate the mucous membranes of the digestive organs.
The probability of illness increases if the child is accustomed to snacking on a dry sandwich with sandwiches and pies from the school cafeteria, if he swallows "on the run", badly chews food, constantly in a hurry.
Sometimes the disease develops as a response of the body to long-term use of antibacterial drugs, hormonal drugs.
After analyzing hundreds of thousands of case histories, gastroenterologists came to the conclusion that the likelihood of gastroduodenitis in schoolchildren increases, because during this period, children experience more pronounced psychological problems, stress, emotional stress associated with their studies and interpersonal relationships with their peers. Sometimes no associated diseases are found in the child, not even the long-suffering Helicobacter pylori. And then they talk about a psychosomatic or psychogenic disorder.
Types and classification
Gastroduodenitis in a child can be endogenous (caused by internal causes) and exogenous (caused by external causes). Also distinguish acute inflammatory process and chronic. As already mentioned, chronic lesions are detected much more often.
Sometimes a child’s disease has a latent, latent course, sometimes the ailment is monotonous, and sometimes recurrent gastroduodenitis is diagnosed.
In direct connection with the destructive modifications that caused inflammation in the membranes of the stomach and duodenum, the surface form is erosive, hemorrhagic, atrophic and mixed.
Signs of pathology
In its clinical picture, gastroduodenitis is very similar to ordinary gastritis. The child complains of weakness, increased fatigue, he may have disturbed sleep at night, and in the daytime he often suffers from headaches. Even insignificant physical activity leads to the fact that the child quickly gets tired, tired. Often doctors find signs of vegetovascular dystonia (VVD) in such children.
After eating, the child complains of abdominal pain, a feeling of heaviness in the area of the stomach and a little lower. When an exacerbation of the disease occurs, the pains become stronger, they give to the hypochondrium and near the navel. Increased pain usually occurs 60-120 minutes after eating, at times when the child is hungry, as well as at night.
Burping is increasing. It becomes “bitter”, the child complains of heartburn, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. Drooling increases, appetite is disturbed, constipation is replaced by diarrhea and vice versa.
In some cases, the child drowsiness increases, moderate tachycardia, excessive sweating, bloating in a couple of hours after meals are observed.
The chronic form of the disease is most often exacerbated in certain seasons - in spring and autumn. In the absence of adequate treatment and correction of the child’s condition, complications such as the development of gastric and duodenal ulcers, cholecystitis, and inflammation of the pancreas are not excluded.
What to do?
If the parents have noticed signs of possible gastroduodenitis in the child, they must show him to the pediatrician, and then in the direction from the pediatrician doctor visit the pediatric gastroenterologist. The specialist will first of all evaluate the external signs - children with gastroduodenitis often have pale skin, bruises under the eyes, skin with minimal elasticity, as well as brittle and fragile nails and hair. The uvula is usually covered with a yellowish tinge.
Complete blood count shows a moderate lack of hemoglobin. Be sure to assign a study on parasites - analysis of feces on the eggs of the worm, Giardia.
Coprogram and fibrogastroduodenoscopy is performed. To assess how affected the membranes of the digestive tract organs are, a biopsy can be performed. The child measures the acidity level of the gastric juice, and also makes tests for the detection of Helicobacter pylori. Both x-rays of the stomach and ultrasound of the abdominal organs can be recommended.
Treatment
The effectiveness of treatment depends largely on how parents are ready for long-term adherence to the recommendations of the doctor, the main of which is a therapeutic diet. A child should eat at least 6 times a day in small portions. At his table should be present dishes, steamed, baked or boiled. All fat or fried, chips, carbonated drinks, canned foods, pizza and fast food, as well as factory sweets under the strictest ban.
Much attention should be paid to the emotional and psychological state of the child. Recommended to him visiting a child psychologist, elimination of all stress factors. In periods of exacerbations of chronic disease, doctors recommend comply with bed rest.
Of the drugs that a doctor can prescribe, should be called antacids, if the acidity is high, anti-secretion drugs - "Omeprazole." Additionally, adsorbents can be prescribed, but not all physicians support their use. For example, the well-known pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky considers the use of sorbents in this case unjustified.
If the disease is chronic, during the period of remission, the child visits the physiotherapy room, where he can be treated with electrophoresis, laser treatment, UHF, hydrotherapy. Also, phytotherapy, drinking mineral waters recommended by a gastroenterologist, taking vitamins are recommended without aggravation. The child should at least once a year visit a specialized sanatorium or a spa treatment in an organization specializing in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Folk remedies in children’s gastroduodenitis are not strongly recommended to treat, in order not to bring the situation to severe complications. Clinical recommendations include elements of phytotherapy, but only with the knowledge of the attending physician in the general scheme of treatment during remission. In the acute period, such funds are prohibited.
It will take a long time to treat a child - for several years, children with such a diagnosis are registered with a gastroenterologist, and they are examined every year. Forecasts are ambiguous - on the one hand, gastroduodenitis “responds well” to the prescribed treatment, and on the other hand, periods of exacerbations occur quite often; any stress, any “flaws” in dieting, and workload at school can trigger them.
Child with gastroduodenitis It is necessary to treat teeth and diseases of the throat and oral cavity in time to eliminate the foci of inflammation outside the gastrointestinal tract.
More information about the disease tells the specialist in the video below.